| [1] Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, et al. Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet. 2006;367(9524): 1747-1757.[2] Monteiro P, Antunes A, Goncalves LM, et al. Long-term clinical impact of coronary-collateral vessels after acute infarction. Rev Port Cardiol. 2003;22(9):1051-1061.[3] Perez-Castellano N, Garcia EJ, Abeytua M, et al. Influence of collateralcirculation on in-hospital death from anterior acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31(3): 512-518.[4] Kodama K, Kusuoka H, Sakai A, et al. Collateral channels that develop after an acute myocardial infarction prevent subsequent left ventricular dilation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996; 27(5): 1133-1139.[5] Fukuda K, Yuasa S. Stem cells as a source of regenerative cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2006;98(8):1002-1013.[6] Blau HM, Brazelton TB, Weimann JM. The evolving concept of a stem cell: entity or function? Cell. 2001;105(7):829-841.[7] Orlic D, Hill JM, Arai AE. Stem cells for myocardial regeneration. Circ Res. 2002;91(12):1092-1102.[8] 唐洁,陈涛,米杰,等.经冠状动脉移植自体骨髓单个核细胞修复犬梗死心肌[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(13): 3765-3770.[9] Ryu JH, Kim IK, Cho SW, et al. Implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells using injectable fibrin matrixenhances neovascularization in infarcted myocardium. Biomaterials. 2005;26(3):319-326.[10] Carnieto A Jr, Dourado PM, da Luz PL, et al. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition protects against myocardial damage in experimental acute ischemia. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2009;64(3):245-252.[11] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[12] Bianco P, Robey PG. Marrow stromal cells. J Clin Invest. 2000; 105(12):1663-1668.[13] Woodburg D, Schwarz EJ ,Prockp DJ, et al. Adult rat human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[14] Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ, el al. Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human bone-marrow-derived angioplasty prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis, reduces remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med. 2001;7(4):430-436.[15] Perin EC, Dohmann HF, Borojevic R, et al. Transendocardial autologous bone marrow cell transplantation for severe, chronic ischemic heart failure. Circulation. 2003;107(18): 2294-2302.[16] Li RK, M ickle DA, W eisel RD, et al. Optimal time for cardio-myocyte transplantati0n to maximize myocardial function after left ventricular injury. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001; 72(6):1957-1963.[17] Assmus B, Schachinger V, Teupe C, et al. Transplantation of progenitor cells and regeneration enhancement in acute myocardial Infarction(ToPcARE-AMI). Circulation. 2002;106: 3009-3017.[18] Khan M, Kutala VK, Vikram DS, et al. Skeletal myoblasts transplanted in the ischemic myocardium enhance in situ oxygenation and recovery of contractile function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293(4):H2129-2139.[19] Guo C, Haider HKh, Wang C, et al. Myoblast transplantation for cardiac repair: from automyoblast to allomyoblast transplantation. Ann Surg. 2008;86(6):1841-1848.[20] Baikova JP, Fatkhudinov TKh, Bolshakova GB, et al. Pathways of bone marrow mononuclear cell differentiation after transplantation into postinfarction heart. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2011;152(1):128-132.[21] 黎志宏,张湘生.体外培养骨髓单个核细胞分泌促血管生长因子的实验研究[J].中国医师杂志,2006;8(4):456-457.[22] Ware JA, Simons M. Angiogenesis in ischemic heart disease. Nature Med. 1997;3(2):158-164.[23] Isner JM, WalshK, Symes J, et al. Arterial gene transfer for therapeutic angiogenesis in patients with peripheral artery disease. Hum Gene Ther. 1996;7(8):959-988.[24] Isner JM, Vale PR, Symes JF, et al. Assessment of risks associated with cardiovascular gene therapy in human subjects. Circ Res. 2001;89(5):389-400.[25] Takahashi T, Kalka C, Masuda H, et al. Ischemia- and cytokine-induced mobilization of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells for neovascularization. Nat Med. 1999;5(4):434-438.[26] Kawamoto A, Gwon HC, Iwaguro H, et al. Therapeutic potential of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells for myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 2001;103(5):634-637.[27] Tomita S, Mickle DA, Weisel RD, et al. Improved heart function with myogenesis and angiogenesis after autologous porcine bone marrow stromal cell transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;123(6):1132-1140.[28] Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302):964-967.[29] Matsumoto R, Omura T, Yoshiyama M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-expressing mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25(6): 1168-1173.[30] Ducharme A, Frantz S, Aikawa M, et al. Targeted deletion of matrix metalloproteinase-9 attenuated left ventricular enlargement and collagen accumulation after experimental myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 2000;106(1):55-62.[31] Mukherjee R, Brinsa TA, Dowdy KB, et al. Myocardial infarct expansion and matrix metalloproteinase inhibition. Circulation. 2003;107(4):618-625.[32] King MK, Coker ML, Goldberg A, et al. Selective matrix metalloproteinase inhibition with developing heart failure: effects on left ventricular function and structure. Circ Res. 2003;92(2):177-185.[33] Deb A, Wang S, Skelding KA, et al. Bone marrow-derived cardiomyocytes are present in adult human heart: A study of gender-mismatched bone marrow transplantation patients. Circulation. 2003;107(9):1247-1249. |
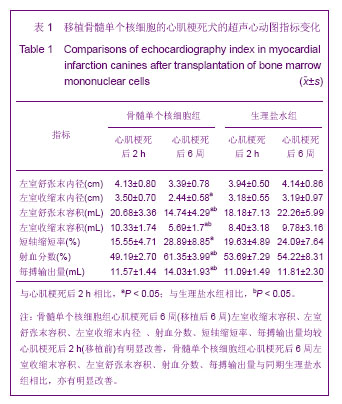
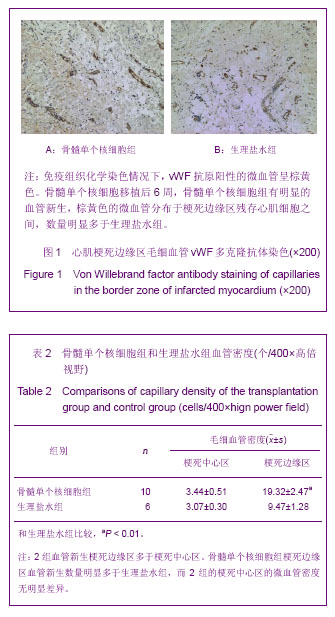

.jpg)