中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (32): 5757-5764.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.32.003
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
诱导剂共培养:谁更适宜骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞的分化?
陈增生1,褚 强2,刘艳凤3,宋 璇4,李 萍5
- 青岛市立医院,1检验科,2超声科,4输血科,山东省青岛市 266071;3青岛市四方区医院检验科,山东省青岛市 266033;5青岛大学医学院附属医院输血科,山东省青岛市 266000
-
收稿日期:2013-05-11修回日期:2013-06-22出版日期:2013-08-06发布日期:2013-08-06 -
通讯作者:李萍,硕士,主管技师,青岛大学医学院附属医院输血科,山东省青岛市 266000 -
作者简介:陈增生★,男,1981年生,山东省招远市人,汉族,2011年青岛大学医学院毕业,硕士,技师,主要从事干细胞方面的研究。
Induction ways of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into nerve cells
Chen Zeng-sheng1, Chu Qiang2, Liu Yan-feng3, Song Xuan4, Li Ping5
- 1 Department of Laboratory, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
2 Department of Ultrasound, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
3 Department of Laboratory, Sifang District Hospital, Qingdao 266033, Shandong Province, China
4 Department of Blood Transfusion, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
5 Department of Blood Transfusion, Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2013-05-11Revised:2013-06-22Online:2013-08-06Published:2013-08-06 -
Contact:Li Ping, Master, Technician-in-charge, Department of Blood Transfusion, Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China lpxkck@126.com -
About author:Chen Zeng-sheng★, Master, Technician, Department of Laboratory, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China Redapple_02@126.com
摘要:
背景:目前骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化的方法较多,采用不同诱导方法对骨髓充质干细胞分化成神经细胞的比例是不同的。 目的:比较化学诱导法和共培养法诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为神经细胞的差异。 方法:大鼠全骨髓血细胞分离纯化法培养骨髓间充质干细胞,分为化学诱导组和共培养组,分别采用加入化学诱导剂β-巯基乙醇和Transwell小室共培养方法诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化。 结果与结论:诱导培养1周后从化学诱导和共培养组的骨髓间充质干细胞出现突起,且呈辐射生长,2周后均可见神经元特异性烯醇化酶阳性细胞。共培养组中第四五天可见星级神经细胞状结构,并形成更多的突起,神经元特异性烯醇化酶染色阳性率为(70.82±2.46)%。而在第六七天化学诱导组中神经细胞形态样细胞形成,并有连接,神经元特异性烯醇化酶染色阳性率为(52.37±1.83)%。提示细胞微环境在骨髓间充质干细胞分化成神经细胞发挥主导作用,且化学诱导法诱导效率低于共培养法。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈增生,褚 强,刘艳凤,宋 璇,李 萍. 诱导剂共培养:谁更适宜骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞的分化?[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(32): 5757-5764.
Chen Zeng-sheng, Chu Qiang, Liu Yan-feng, Song Xuan, Li Ping. Induction ways of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into nerve cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(32): 5757-5764.
Morphology of cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Lots of erythrocytes covered the entire bottom of culture flask with whole bone marrow culture after inoculation. A large number of blood cells were removed after low glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium was changed at the first time, scattered adherent cells could be seen in the bottom of the bottle, with fusiform or polygonal appearance, and uneven part was a whirlpool-like growth. The formation of multiple fibroblast-like cell clusters could be seen after 6 or 8 days, few round cells could be seen around the cell clusters. Fibroblast-like growth was pooled into a piece after 12 or 16 days. Adherent cells were long spindle-shaped after passage for 2-3 days. Primary cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells had a multiple differentiation potential and maintained a higher purity over 90% after repeated passages[22-23, 25-26] (Figure 1).

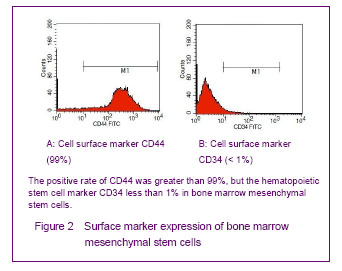
Surface marker expression of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Flow cytometry results showed that bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells strongly expressed hyaluronan receptor CD44, with the positive rate of over 99%, but did not express the hematopoietic stem cell marker CD34 (< 1%) (Figure 2).
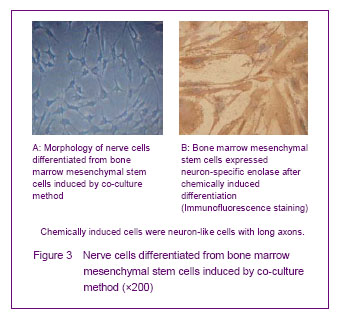
Co-culture and chemical induction methods for inducing differentiation into nerve cells
Nerve cells inoculated in the 6-well plates of Transwell co-culture system, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were found to have pyknosis smaller than flat cells. Formerly, most of the cell bodies had rounded protrusion formation, and cells gradually became long stellate for 3 days. The stellate cells gradually increased, and could cross each other to form a connection with a neuron-like morphology (Figure 3) for 4 or 5 days. Neural-like cells accounted for 62.4% of the total cells. Immunofluorescence results showed Neuron-specific enolase positive rate was (60.47± 1.89)%, suggesting the performance characteristics of neurons (Figure 3). Most of the cells were still flat and wide long spindle-shaped similar as morphology characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and did not form a neuron-like morphology in the control group after cultured for 8 days. Neuron-specific enolase was also negative in the control group.
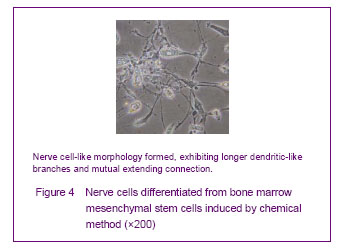
Chemically induced culture results
Cells showed adherent growth after 1-3 days in the chemically induced group, and no obvious morphological changes were observed. The cell body significantly shrank and a circle or a triangle extended at 4 days. Some cells formed longer dendritic-like branches, and mutual extending connection; some cells were similar to neurons, and the long axons appeared to render the nerve cell-like morphology (Figure 4) at 5-6 days. Nerve cells accounted for 50.4% of the total cells, and the positive rate for neuron-specific enolase was (40.91± 1.63)%.
| [1] Lin L, Fu X, Zhang X, et al. Rat adipose-derived stromal cells expressing BMP4 induce ectopic bone formation in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27(12): 1608-1615.[2] Tao H, Rao R, Ma DD. Cytokine-induced stable neuronal differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a serum/feeder cell-free condition. Dev Growth Differ. 2005;47(6):423-433.[3] Tang Y, Yasuhara T, Hara K, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived stem cells: a promising therapy for stroke. Cell Transplant. 2007;16(2):159-169.[4] Bang OY, Lee JS, Lee PH, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005; 57(6):874-882.[5] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[6] Sanchez-Ramos J, Song S, Cardozo-Pelaez F, et al. Adult bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neural cells in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2000;164(2):247-256.[7] Kopen GC, Prockop DJ, Phinney DG. Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(19): 10711-10716.[8] Buzańska L, Machaj EK, Zab?ocka B, et al. Human cord blood-derived cells attain neuronal and glial features in vitro. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 10):2131-2138.[9] Lei Z, Yongda L, Jun M, et al. Culture and neural differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31(9):916-923. [10] Jin K, Mao XO, Batteur S, et al. Induction of neuronal markers in bone marrow cells: differential effects of growth factors and patterns of intracellular expression. Exp Neurol. 2003;184(1):78-89.[11] Choong PF, Mok PL, Cheong SK, et al. Generating neuron-like cells from BM-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(2):170-183.[12] Li Y, Chopp M, Chen J, et al. Intrastriatal transplantation of bone marrow nonhematopoietic cells improves functional recovery after stroke in adult mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20(9):1311-1319.[13] Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intracerebral transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurol Sci. 2001;189(1-2): 49-57.[14] Chopp M, Zhang XH, Li Y, et al. Spinal cord injury in rat: treatment with bone marrow stromal cell transplantation. Neuroreport. 2000;11(13):3001-3005.[15] Mahmood A, Lu D, Yi L, et al. Intracranial bone marrow transplantation after traumatic brain injury improving functional outcome in adult rats. J Neurosurg. 2001;94(4):589-595.[16] Schwarz EJ, Alexander GM, Prockop DJ, et al. Multipotential marrow stromal cells transduced to produce L-DOPA: engraftment in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Hum Gene Ther. 1999;10(15):2539-2549.[17] Mezey E, Chandross KJ, Harta G, et al. Turning blood into brain: cells bearing neuronal antigens generated in vivo from bone marrow. Science. 2000;290(5497):1779-1782.[18] Brazelton TR, Rossi FM, Keshet GI, et al. From marrow to brain: expression of neuronal phenotypes in adult mice. Science. 2000;290(5497):1775-1779.[19] Park KW, Eglitis MA, Mouradian MM. Protection of nigral neurons by GDNF-engineered marrow cell transplantation. Neurosci Res. 2001;40(4):315-323.[20] Ogawa S. Biochemical and immunological laboratory findings in Kawasaki disease. Nihon Rinsho. 2008;66(2):315-320.[21] Azizi SA, Stokes D, Augelli BJ, et al. Engraftment and migration of human bone marrow stromal cells implanted in the brains of albino rats--similarities to astrocyte grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(7):3908-3913.[22] Yang NL, Yang F, Xu LL. Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neurons induced by neural cells by co-culture method. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;11(29):5611-5614.[23] Kuo CK, Tuan RS. Tissue engineering with mesenchymal stem cells. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2003;22(5):51-56.[24] Jia XJ, Sun XJ, Xu LL. Differentiation of hnman bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes under a cerltain inicroenvironment. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(34):6635-6638.[25] Shin M, Yoshimoto H, Vacanti JP. In vivo bone tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells on a novel electrospun nanofibrous scaffold. Tissue Eng. 2004;10 (1-2):33-41.[26] Lu P, Blesch A, Tuszynski MH. Induction of bone marrow stromal cells to neurons: differentiation, transdifferentiation, or artifact? J Neurosci Res. 2004;77(2):174-191.[27] Xu LL, Yang NL. Differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts in vitro. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12 (38): 7483-7486.[28] Wu B, Wu YC, Zheng QX, et al. The proliferation, adhesion and induced differentiation into neurocytes of bone marrow stromal cells on IKVAV peptide nanofiber gel. Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2007;9(8):740-744.[29] Chu K, Kim M, Park KI, et al. Human neural stem cells improve sensorimotor deficits in the adult rat brain with experimental focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2004;1016(2): 145-153.[30] Andrews EM, Tsai SY, Johnson SC, et al. Human adult bone marrow-derived somatic cell therapy results in functional recovery and axonal plasticity following stroke in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2008;211(2):588-592. [31] Castro RF, Jackson KA, Goodell MA, et al. Failure of bone marrow cells to transdifferentiate into neural cells in vivo. Science. 2002;297(5585):1299.[32] Terada N, Hamazaki T, Oka M, et al. Bone marrow cells adopt the phenotype of other cells by spontaneous cell fusion. Nature. 2002;416(6880):542-545. [33] Park KS, Lee YS, Kang KS. In vitro neuronal and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood. J Vet Sci. 2006;7(4):343-348.[34] Battula VL, Bareiss PM, Treml S, et al. Human placenta and bone marrow derived MSC cultured in serum-free, b-FGF-containing medium express cell surface frizzled-9 and SSEA-4 and give rise to multilineage differentiation. Differentiation. 2007;75(4):279-291. [35] Kögler G, Sensken S, Airey JA, et al. A new human somatic stem cell from placental cord blood with intrinsic pluripotent differentiation potential. J Exp Med. 2004;200(2):123-135.[36] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [3] | 王正东, 黄 娜, 陈婧娴, 郑作兵, 胡鑫宇, 李 梅, 苏 晓, 苏学森, 颜 南. 丁酸钠抑制氟中毒可诱导小胶质细胞活化及炎症因子表达增多[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [4] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [5] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [6] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [7] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [8] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [9] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [10] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [11] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [12] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [14] | 史洋洋, 秦英飞, 吴福玲, 何 潇, 张雪静. 胎盘间充质干细胞预处理预防小鼠毛细支气管炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [15] | 梁学奇, 郭黎姣, 陈贺捷, 武 杰, 孙雅琪, 邢稚坤, 邹海亮, 陈雪玲, 吴向未. 泡状棘球绦虫原头蚴抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向成纤维细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
Design
Main reagents for induced differentiation are as follows:
.jpg)
Results were expressed as mean±SD and analyzed by t-test. A value of P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
1不同诱导方法对骨髓充质干细胞分化成神经细胞的比例是不同的,实验之目的即希望比较化学诱导法和共培养法诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为神经细胞效率的差异。 2大鼠全骨髓血细胞分离纯化法培养骨髓间充质干细胞,化学诱导剂β-巯基乙醇诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化神经细胞的效率低于Transwell小室共培养的效果。
骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞分化的发现历程: 早在2000年,Ramos等便成功对骨髓间充质干细胞进行体外诱导,使其分化为神经细胞,并成功表达了神经元特异性核心抗原和Tau蛋白等神经元标志蛋白。同时,Zhao等将骨髓间充质干细胞注入脑梗死9周的大鼠大脑后发现了骨髓间充质干细胞可在体内分化为神经细胞,并有胶质细胞、少突胶质细胞和神经元的生成。Mezey等也将成人骨髓细胞移植到小鼠大脑中,发现其分化成了可以表达特异性神经抗原的细胞,并通过这一发现提出了用骨髓源细胞作为神经细胞来源来治疗神经退行性疾病或者中枢神经系统损伤的疾病。随后,Brazerlton等和Mezey等又研究证实骨髓间充质干细胞不仅可以在脑内分化为神经细胞,同时体外培养的骨髓间充质干细胞也可经骨髓移植、脑部直接注射等途径顺利通过血脑屏障进入脑内,这又为临床应用骨髓间充质干细胞治疗神经退行性疾病和修复由创伤或梗死引起的组织损伤提供了实验依据。自此人们认为骨髓间充质干细胞作为细胞供体对临床治疗神经退行性疾病有着潜在的应用价值;但骨髓间充质干细胞的分化机制及影响因素等问题尚不清楚,如经骨髓间充质干细胞分化后的细胞是否能表现出成熟的神经细胞所特有的功能,是否能真正地应用于临床治疗神经系统性疾病。Aleksandrova等认为成熟神经细胞所特有的功能主要表现为可以分泌神经递质和表达神经受体。Chai等发现骨髓间充质干细胞在体外条件下可分化成具有神经元形态特征的神经细胞,并可以释放一定的神经递质。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||