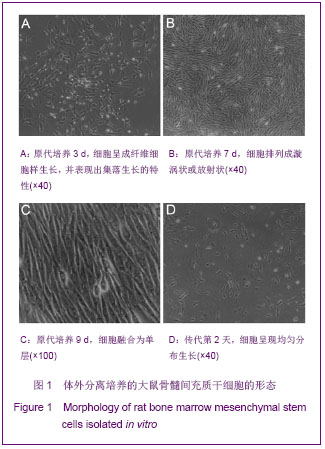
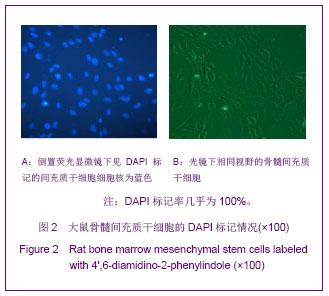
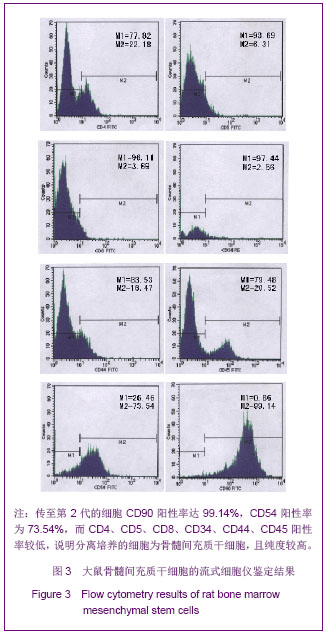
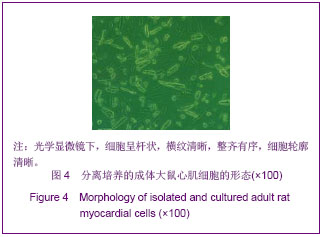
| [1]Taha MF, Valojerdi MR, Mowla SJ. Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) on cardiomyocyte differentiation from mouse embryonic stem cell. Int J Cardiol. 2007;120(1):92-101.[2]Menasche P. Skeletal muscle satellite cell transplantation. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;58(2):351-357.[3]Chen M, Xie HQ, Deng L, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes bone marrow-derived cells differentiation to cardiomyocyte phenotypes in vitro. Cell Prolif. 2008; 41(2): 336-347.[4]Larionov PM, Chernyavskii AM, Kuznetsova IV, et al. Cardiomyocyte regeneration in pericicatricial zone of the myocardium after laser tunneling and implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2009;148(4): 692-696.[5]Shim WS, Jiang S, Wong P, et al. Ex vivo differentiation of human adult bone marrow stem cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;324(2):481-488.[6]Williams AR, Hatzistergos KE, Addicott B, et al. Enhanced effect of human cardiac stem cells and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to reduce infarct size and restore cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2013; 127(2):213-223.[7]Xu YL, Gao YH, Liu Z, et al. Myocardium-targeted transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells by diagnostic ultrasound-mediated microbubble destruction improves cardiac function in myocardial infarction of New Zealand rabbits. Int J Cardiol. 2010;138(2):182-195.[8]Quevedo HC, Hatzistergos KE, Oskouei BN, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells restore cardiac function in chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy via trilineage differentiating capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(33):14022-14027.[9]Yamahara K, Nagaya N. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of heart disease. Regen Med. 2007;2(2):107-109.[10]Orlic D. Adult bone marrow stem cells regenerate myocardium in ischemic heart disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;996:152-157.[11]Boyle AJ, Whitbourn R, Schlicht S, et al. Intra-coronary high-dose CD34+ stem cells in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease: a 12-month follow-up. Int J Cardiol. 2006;109 (1): 21-27.[12]Brenner C, Franz WM. The use of stem cells for the repair of cardiac tissue in ischemic heart disease. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2011;8(2):209-225.[13]Fuh E, Brinton TJ. Bone marrow stem cells for the treatment of ischemic heart disease: a clinical trial review. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2009;2(2):202-218.[14]Strauer BE, Brehm M, Schannwell CM. The therapeutic potential of stem cells in heart disease. Cell Prolif. 2008;41 Suppl 1:126-145.[15]Behrends JC. Evolution of the Ion Channel Concept: The Historical Perspective. Chem Rev. In press. [16]Zaydman MA, Silva JR, Cui J. Ion Channel Associated Diseases: Overview of Molecular Mechanisms. Chem Rev. In press.[17]Zhang W, Hirschler-Laszkiewicz I, Tong Q, et al. TRPM2 is an ion channel that modulates hematopoietic cell death through activation of caspases and PARP cleavage. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;290(4):C1146-1159.[18]Crozatier B. Central role of PKCs in vascular smooth muscle cell ion channel regulation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006;41(6): 952-955.[19]Drummond HA, Jernigan NL, Grifoni SC. Sensing tension: epithelial sodium channel/acid-sensing ion channel proteins in cardiovascular homeostasis. Hypertension. 2008;51(5): 1265-1271.[20]DeCaen PG, Yarov-Yarovoy V, Sharp EM, et al. Sequential formation of ion pairs during activation of a sodium channel voltage sensor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(52): 22498-22503.[21]Xie Y, Dengler K, Zacharias E, et al. Effects of the sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin (TTX) on cellular ion homeostasis in rat brain subjected to complete ischemia. Brain Res. 1994;652(2):216-224. [22]Amaya F, Decosterd I, Samad TA, et al. Diversity of expression of the sensory neuron-specific TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium ion channels SNS and SNS2. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2000;15(4):331-342.[23]Wu WK, Li GR, Wong TM, et al. Involvement of voltage-gated K+ and Na+ channels in gastric epithelial cell migration. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008;308(1-2):219-226.[24]Wu WK, Li GR, Wong HP, et al. Involvement of Kv1.1 and Nav1.5 in proliferation of gastric epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207(2):437-444.[25]Gao R, Shen Y, Cai J, et al. Expression of voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit in human ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 2010;23(5):1293-1299.[26]Mauro T, Guitard M, Behne M, et al. The ENaC channel is required for normal epidermal differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118(4):589-594.[27]Papadatos GA, Wallerstein PM, Head CE, et al. Slowed conduction and ventricular tachycardia after targeted disruption of the cardiac sodium channel gene Scn5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(9):6210-6215.[28]Conti CR. Ion channel therapy of ischemic heart disease: from calcium channel blockers to late sodium current inhibition. Clin Cardiol. 2011;34(2):66-67.[29]Li GR, Deng XL. Functional ion channels in stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2011;3(3):19-24.[30]Mareschi K, Rustichelli D, Comunanza V, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from amniotic fluid originate neural precursors with functional voltage-gated sodium channels. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(5):534-547.[31]Li GR, Deng XL, Sun H, et al. Ion channels in mesenchymal stem cells from rat bone marrow. Stem Cells. 2006;24(6): 1519-1528.[32]Park KS, Jung KH, Kim SH, et al. Functional expression of ion channels in mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord vein. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8):2044-2052.[33]Melnikova IN, Gardner PD. The signal transduction pathway underlying ion channel gene regulation by SP1-C-Jun interactions. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(22):19040-19045.[34]Akbarali HI. Signal-transduction pathways that regulate smooth muscle function. II. Receptor-ion channel coupling mechanisms in gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;288(4):G598-602.[35]Moore P. Cell biology: ion channels and stem cells. Nature. 2005;438(7068):699-704.[36]Pillozzi S, Becchetti A. Ion channels in hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:217910.[37]Deng XL, Sun HY, Lau CP, et al. Properties of ion channels in rabbit mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;348(1):301-309.[38]Tao R, Lau CP, Tse HF, et al. Functional ion channels in mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;293(5):C1561-1567.[39]Park KS, Choi MR, Jung KH, et al. Diversity of ion channels in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008;12(6):337-342.[40]Maltsev VA, Wobus AM, Rohwedel J, et al. Cardiomyocytes differentiated in vitro from embryonic stem cells developmentally express cardiac-specific genes and ionic currents. Circ Res. 1994;75(2):233-244. |
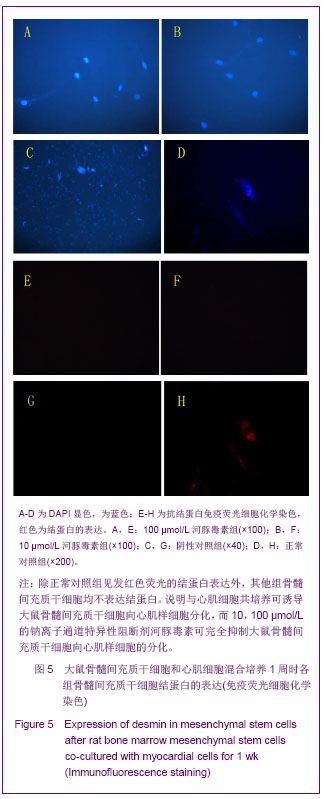
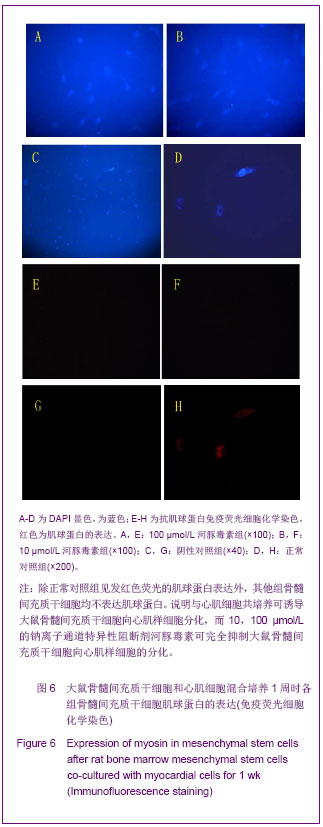
.jpg)