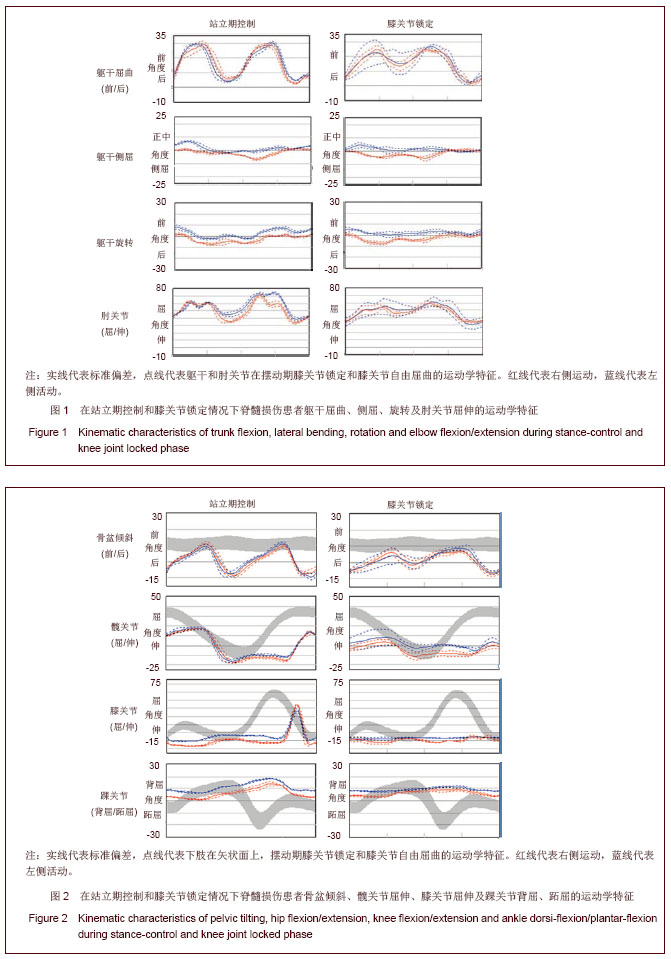
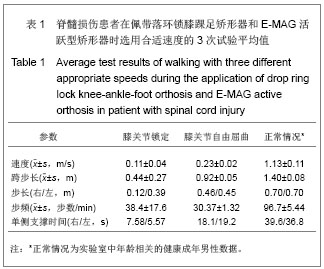
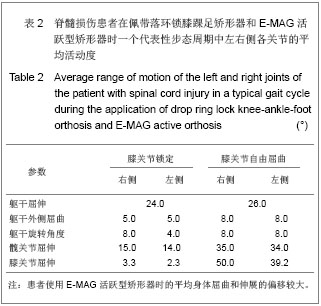
| [1]International Campaign for Cures of Spinal Cord Injury Paralysis: 2012.[2]Thuret S, Moon LD, Gage FH. Therapeutic interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(8):628-643.[3]Anderson KD. Targeting recovery: priorities of the spinal cord-injured population.J Neurotrauma. 2004;21(10): 1371-1383.[4]Nash MS. Exercise as a health-promoting activity following spinal cord injury. J NeurolPhysTher. 2005;29(2):87-103, 106.[5]Widerstrom-Noga EG, Turk DC. Types and effectiveness of treatments used by people with chronic pain associated with spinal cord injuries: influence of pain and psychosocial characteristics.Spinal Cord. 2003;41(11):600-609. [6]Waxman SG, Hains BC. Fire and phantoms after spinal cord injury: Na+ channels and central pain. Trends Neurosci. 2006; 29(4):207-215.[7]Eaton MJ. Cell and molecular approaches to the attenuation of pain after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23(3-4): 549-559.[8]Kirshblum S. Treatment alternatives for spinal cord injury related spasticity. J Spinal Cord Med. 1999;22(3):199-217.[9]Mohammad TK. What Are the Next Steps in Designing an Orthosis for Paraplegic Subjects? Int J Prev Med. 2012;3(3): 145-159.[10]Kim CM, Eng JJ, Whittaker MW. Level walking and ambulatory capacity in persons withincomplete spinal cord injury: relationship with muscle strength. Spinal Cord. 2004; 42(3):156-162.[11]Zheng JZ, Tian SY. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press.1991. 郑建仲,田时雨.神经病诊断学(第二版)[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,1991.[12]Betz RR, Chafetz RS, Vogel LC, et al.Description of sensory preservation in children and adolescents with incomplete spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2011; 34(3):297-300.[13]Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, et al. Worldwidestroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population- basedstudies: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8(4):355-369.[14]Langhorne P, Duncan P. Does the organization of postacute stroke carereally matter? Stroke. 2001;32(1):268-274.[15]Maguire C. How to improve walking, balance and socialparticipation following stroke: a comparison ofthe long term effects of two walking aids-anesand an orthosis TheraTogs-on the recovery ofgait following acute stroke. A study protocol for amulti-centre, single blind, randomised controltrial. BMC Neurol. 2012;12:18.[16]Yu W, Ravelo A, Wagner TH, et al. The relationshipsamong age, chronic conditions, and healthcare costs. Am J Manag Care. 2004;10(12):909-916.[17]Woo C, Guihan M, Frick C, et al. What’s happening now! Telehealthmanagement of spinal cord injury/disorders. J Spin Cord Med. 2011:34(3): 322-331.[18]Farris RJ, Quintero HA, Goldfarb M. Preliminary Evaluation of a Powered Lower Limb Orthosis to AidWalking in Paraplegic Individuals. IEEE Trans Neural SystRehabil Eng. 2011;19(6): 652-659. [19]MunceSE, Guilcehr SJ, Couris CM, et al. Physician utilizationamong adults with traumatic spinal cord injury in Ontario: a population-based study. Spinal Cord. 2009; 2009;47(6):470-476. [20]Anupam G, Arun BT. Functional outcome following rehabilitation in chronic severe traumatic brain injury patients: A prospective study. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2012;15(2): 120-124.[21]Yang JF, Norton J, Nevett-Duchcherer J. Volitional Muscle Strength in the Legs Predicts Changes in Walking Speed Following Locomotor Training in People With Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Phys Ther. 2011; 91(6): 931-943.[22]Wirz M, Bastiaenen C, Bie R, et al. Effectiveness of automated locomotor training inpatients with acute incomplete spinal cord injury:A randomized controlled multicenter trial. BMC Neurol. 2011;11:60.[23]Morris C, Bowers R, Ross K, et al.Orthotic management of cerebral palsy: recommendations from a consensus conference. Neuro Rehabilitation. 2011;28(1):37-46. [24]Morris C. Orthotic Management of Children with Cerebral Palsy. JPO J Prosth Orth. 2002;14(4): 150-158.[25]Tardieu C, Lespargot A, Tabary C, et al. For how long must the soleus muscle be stretched each day to prevent contracture? Dev Med Child Neurol. 1988;30(1):3-10.[26]Charlton P, Ferguson D, Peacock C, et al. Preliminary clinical experience of a contracture correction device. Prosthet Orthot Int. 1999;23:163-168. [27]Meadows CB. The influence of polypropylene ankle-foot orthoses on the gait of cerebral palsied children. [PhD thesis]. Strathclyde, UK: University of Strathclyde, 1984. [28]Gage JR. Gait Analysis in Cerebral Palsy. London: MacKeith Press, 1991.[29]Condie DN, Meadows CB. Conclusions and recommendations. In: Condie DN, Meadows CB, eds. Report of a Consensus Conference on the Lower Limb Orthotic Management of Cerebral Palsy. Copenhagen: International Society of Prosthetics & Orthotics, 1995:15-19.[30]Morris C. Orthotic Management of Children with Cerebral Palsy. Neuro Rehabilitation. 2011;28(1):37-46.[31]Kunkel CF, Scremin AM,Eisenberg B, et al. Effect of “standing” on spasticity, contracture and osteoporosis in paralyzed man. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74:73.[32]Ogilvie C, Bowker P, Rowly DI. The physiological benefits of paraplegic orthotically aided walking. Paraplegia. 1993; 31: 111.[33]Middleton JW, Yeo JD, Blanch L, et al. Clinical evaluation of a new orthosis, the “walkabout”, for restoration of functional standing and short distance mobility in spinal paralysed individuals. Spinal Cord. 1997;35:574-579.[34]Jacobs PL, Johnson B, Mahoney ET. Physiologic responses to electricity assisted and frame supported standing in persons with paraplegia. Spinal Cord Med. 2003; 26(4): 384-389.[35]Rasmussen AA, Smith KA, Damiano DL, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Combination of Bilateral Stance-Control Knee-Ankle-Foot Orthoses and a Reciprocating Gait Orthosis in an Adult With a Spinal Cord Injury. J Prosthet Orthot. 2007;19:42-47.[36]Scivoletto G, Petrelli A, Lucente LD, et al. One year follow up of spinal cord injury patients using a reciprocating gait orthosis:preliminary report. Spinal Cord. 2000;38(9):555-558.[37]Middleton JW, Sinclair PJ, Smith RM, et al. Postural controlduring stance in paraplegia: effects of medially linked versusunlinked knee-ankle-foot orthoses. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80(12):1558-1565.[38]E-MAG 活跃型 E-MAG控制系统,2-646d237-33页控制系统,2012,奥托博克假肢矫形公司.[39]Harvey L, Davis G, Smith M, et al. Energy expenditure during gait using the walkabout and isocentric reciprocal gait orthosis in persons with paraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998;79(8): 945-949.[40]Harvey LA. A comparison of the walkabout and the isocentric reciprocal gait orthosis in T9-12 paraplegics. Spinal Cord. 1997;35(9):580-584.[41]Winchester PK, Carollo JJ, Parekh RN, et al. A comparison of paraplegic gait performance using two types of reciprocating gait orthosis. Prosthet Orthot Int. 1993;17(2):101-106.[42]Kaoru A. Comparison of static balance, walking velocity, and energy consumption with knee-ankle-foot orthosis, walkabout orthosis, and reciprocating gait orthosis in thoracic-level paraplegic patients. JPO. 2006;18(3):87-91.[43]Katz DE, Haideri N, Song K, et al. Comparative study ofconventional hip-knee-ankle-foot orthoses versus reciprocatinggaitorthoses for children with high-level paraparesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997;17:377-386.[44]SPINAL CORD INJURY, Facts and Figures at a Glance. published by National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center, Birmingham, Alabama. 2005.[45]Spinal Cord Injury Facts & Statistics,© 2002-12 Spinal Cord Injury Information Pages.2012. |