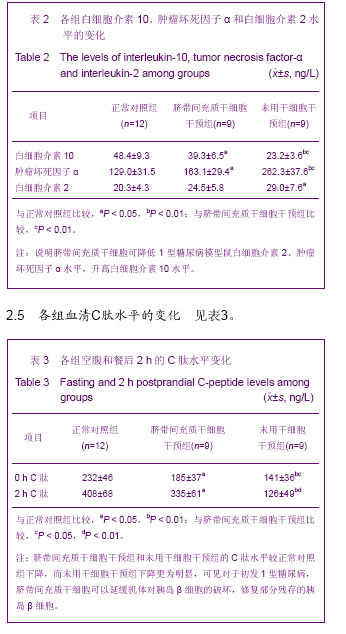
| [1] Parving HH, Tarnow L, Nielsen FS,et al. Cyclosporine nephrotoxicity in type 1 diabetic patients. A 7-year follow-up study.Diabetes Care. 1999;22(3):478-483.[2] Jones D.Retuning the immune system: the future of type 1 diabetes therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(8):600-601.[3] Voltarelli JC, Couri CE, Stracieri AB,et al. Autologous nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2007; 297(14):1568-1576.[4] Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol. 2002;30(1): 42-48.[5] Li H, Guo ZK, Li XS,et al. Functional and phenotypic alteration of intrasplenic lymphocytes affected by mesenchymal stem cells in a murine allosplenocyte transfusion model.Cell Transplant. 2007;16(1):85-95.[6] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E,et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions.Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372.[7] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105 (4): 1815-1822.[8] Wen Y, Ouyang J, Yang R,et al. Reversal of new-onset type 1 diabetes in mice by syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;374(2):282-287.[9] Ye Z, Wang Y, Xie HY,et al. Immunosuppressive effects of rat mesenchymal stem cells: involvement of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2008;7(6): 608-614.[10] Dor Y, Brown J, Martinez OI,et al. Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem-cell differentiation. Nature. 2004;429(6987):41-46.[11] Hasegawa Y, Ogihara T, Yamada T,et al. Bone marrow (BM) transplantation promotes beta-cell regeneration after acute injury through BM cell mobilization. Endocrinology. 2007; 148(5): 2006-2015.[12] Gao X, Song L, Shen K,et al.Transplantation of bone marrow derived cells promotes pancreatic islet repair in diabetic mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;371(1):132-137.[13] Gabr MM, Sobh MM, Zakaria MM,et al.Transplantation of insulin-producing clusters derived from adult bone marrow stem cells to treat diabetes in rats. Exp Clin Transplant. 2008;6(3):236-243.[14] Urbán VS, Kiss J, Kovács J,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells cooperate with bone marrow cells in therapy of diabetes.Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):244-253.[15] Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS,et al. Local delivery of marrow-derived stromal cells augments collateral perfusion through paracrine mechanisms.Circulation. 2004;109(12): 1543-1549.[16] Lammert E, Cleaver O, Melton D. Induction of pancreatic differentiation by signals from blood vessels.Science. 2001; 294(5542):564-567.[17] Bosco D, Armanet M, Morel P,et al. Unique arrangement of alpha- and beta-cells in human islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 2010;59(5):1202-1210.[18] Nikolova G, Jabs N, Konstantinova I,et al.The vascular basement membrane: a niche for insulin gene expression and Beta cell proliferation. Dev Cell. 2006;10(3):397-405.[19] Chung CH, Hao E, Piran R,et al. Pancreatic β-cell neogenesis by direct conversion from mature α-cells.Stem Cells. 2010; 28(9):1630-1638.[20] Thorel F, Népote V, Avril I,et al. Conversion of adult pancreatic alpha-cells to beta-cells after extreme beta-cell loss. Nature. 2010;464(7292):1149-1154.[21] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105 (4):1815-1822.[22] Weiss ML, Troyer DL.Stem cells in the umbilical cord.Stem Cell Rev. 2006;2(2):155-162. |
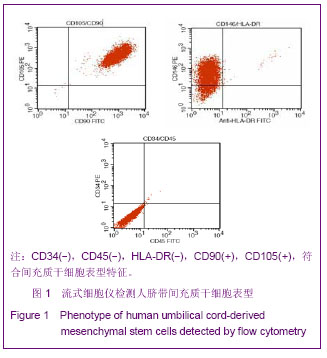
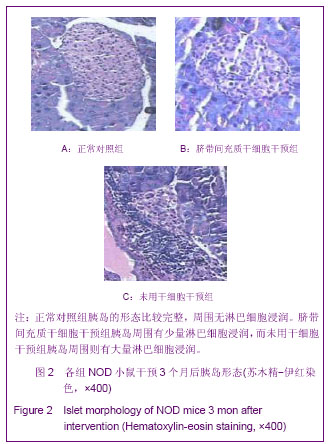
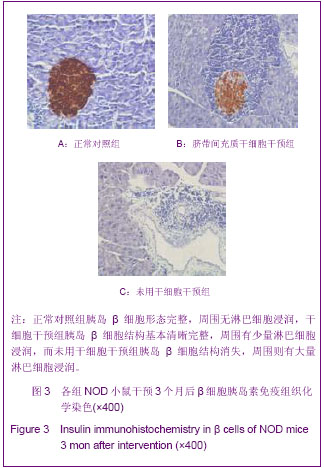
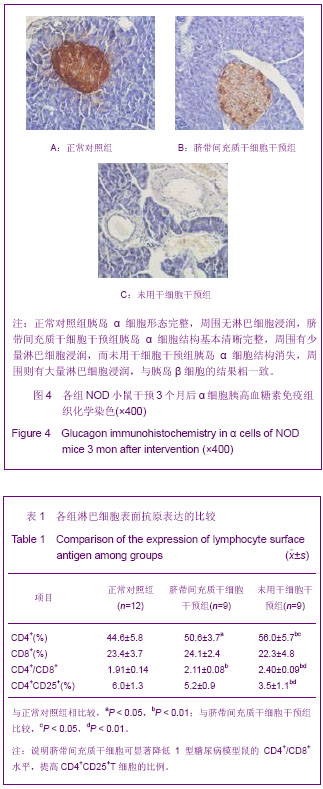

.jpg)