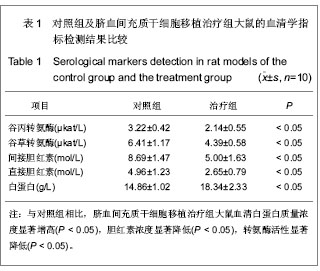
| [1] Takami T, Terai S, Sakaida I. Advanced therapies using autologous bone marrow cells for chronic liver disease.Discov Med. 2012;14(74):7-12.[2] Russo FP, Parola M. Stem cells in liver failure.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26(1):35-45. [3] Takami T, Terai S, Sakaida I. Stem cell therapy in chronic liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012;28(3):203-208. [4] Bassiouny AR, Zaky AZ, Abdulmalek SA, et al. Modulation of AP-endonuclease1 levels associated with hepatic cirrhosis in rat model treated with human umbilical cord blood mononuclear stem cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011;4(7): 692-707.[5] Hwang S, Hong HN, Kim HS, et al. Hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis. Cell Biol Int. 2012; 36(3):279-288.[6] Gao B, Bataller R. Alcoholic liver disease: pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(5): 1572-1585.[7] Zhang Z, Lin H, Shi M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve liver function and ascites in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27(2):112-120.[8] Wang HJ, Ren L, Wang GS, et al. Xiandai Shengwu Yixue Jinzhan. 2012;12(1):46-48.王海久,任利,汪庚申,等.骨髓间充质干细胞(BMSCs)移植于大鼠肝硬化模型的动物实验研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2012, 12(1): 46-48.[9] Hwang S, Hong HN, Kim HS, et al. Hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of thioacetamide-induced liver cirrhosis. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(3): 279-88.[10] Wang D, Zhang H, Liang J, et al. Effect of allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in a polyI:C-induced primary biliary cirrhosis mouse model. Clin Exp Med. 2011;11(1):25-32.[11] Zhong YS, Lin N, Deng MH, et al. Deficient proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infections and cirrhosis of the liver. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55(2):438-445.[12] Dai LJ, Li HY, Guan LX, et al. The therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on hepatic cirrhosis. Stem Cell Res. 2009;2(1):16-25.[13] Tan GS, Xiang XH, Wang Y, et al. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2009;17(11): 1074-1078.谭国胜,向贤宏,王于,等.脂肪间质干细胞移植对大鼠肝硬化模型的治疗作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2009,17(11): 1074-1078.[14] El-Ansary M, Abdel-Aziz I, Mogawer S, et al. Phase II trial: undifferentiated versus differentiated autologous mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in Egyptian patients with HCV induced liver cirrhosis. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(3): 972-981.[15] Liu Y, Shi ZL, Zhao ZZ, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(10):1837-1840.刘英,施占立,赵宗泽,等.人脐带源间充质干细胞移植改善四氯化碳诱导肝硬化大鼠的肝纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(10):1837-1840.[16] Zhang D, Jiang M, Miao D. Transplanted human amniotic membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver cirrhosis in mouse. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16789.[17] Jung KH, Uhm YK, Lim YJ, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve glucose homeostasis in rats with liver cirrhosis. Int J Oncol. 2011; 39(1):137-143.[18] Forbes SJ, Newsome PN. New horizons for stem cell therapy in liver disease.J Hepatol. 2012;56(2):496-499. [19] Jung KH, Uhm YK, Lim YJ, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve glucose homeostasis in rats with liver cirrhosis.Int J Oncol. 2011;39(1): 137-143. [20] Nikeghbalian S, Pournasr B, Aghdami N, et al. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow-derived mononuclear and CD133(+) cells in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.Arch Iran Med. 2011;14(1):12-17.[21] Chen Z, Qi LZ, Zeng R, et al. Stem cells and hepatic cirrhosis. Panminerva Med. 2010;52(2):149-165. |
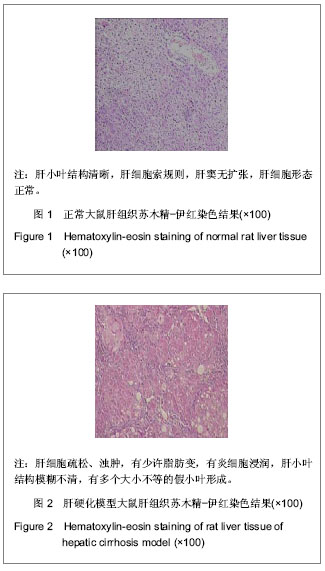
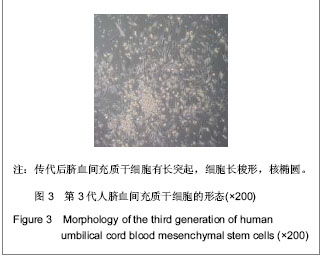
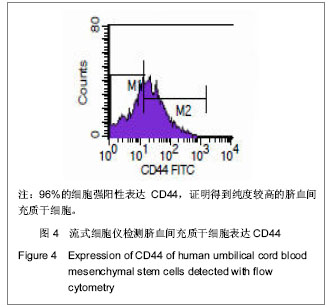
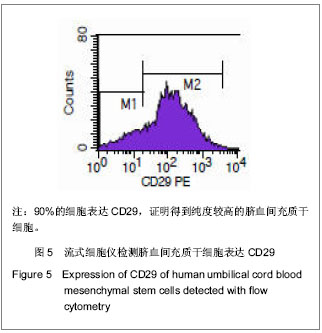

.jpg)