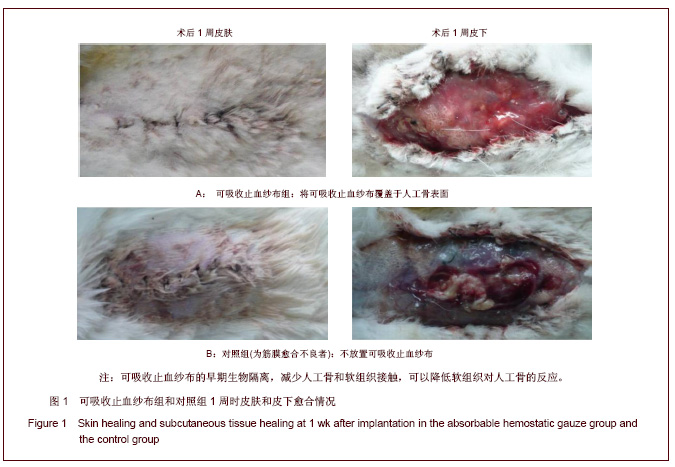
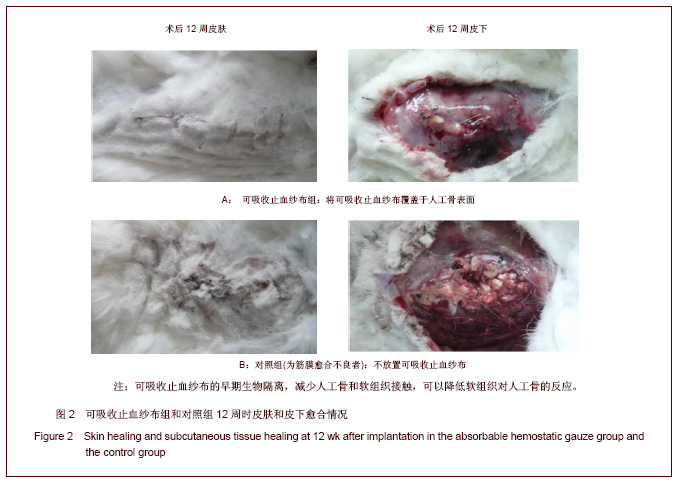
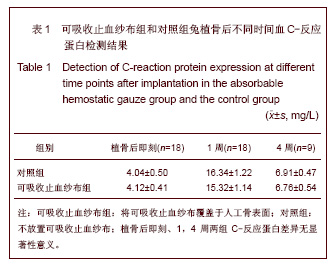
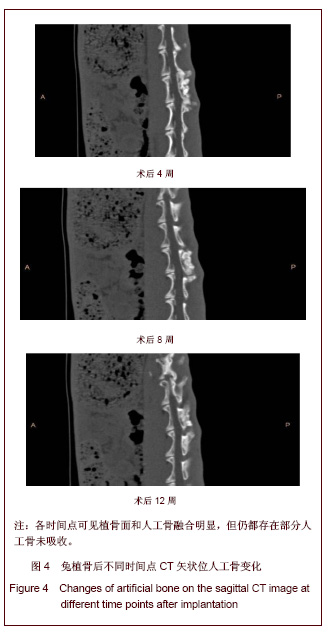
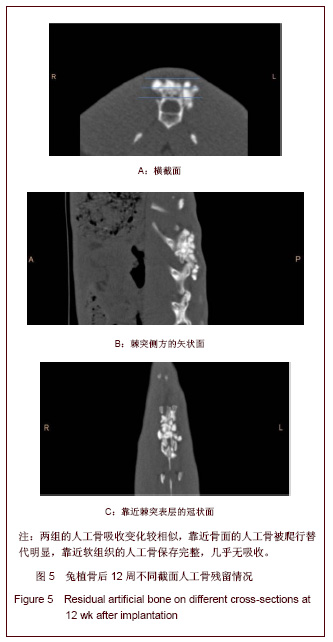
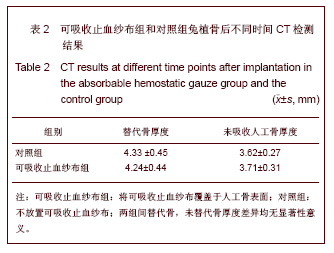
| [1] Song YJ,Zhu XD,Li M.Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2005; 13(22):1742-1744. 宋元进,朱晓东,李明.生物植骨材料在脊柱融合术中的应用[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(22):1742-1744.[2] Motomiya M,Ito M,Takahata M,et al. Effect of Hydroxyapatite porous characteristics on healing outcomes in rabbit posterolateral spinal fusion model . Eur Spine J.2007;16(12): 2215-2224. [3] Ma X,Hu YY,Xiong Z,et al.Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi. 2005;22(11):1387-1389. 马兴,胡蕴玉,熊卓,等. 新型仿生活性人工骨诱导兔腰椎横突间脊柱融合研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(11):1387-1389.[4] Xu WB,Jia LS,Lu JX.Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2005; 13(22):1736-1738. 许卫兵,贾连顺,卢建熙.兔骨髓基质干细胞体外培养复合β-TCP进行胸椎后侧融合实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005, 13(22): 1736-1738.[5] Chen L,Gu Y,Chen XQ,et al.Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2010; 30(7): 677-683. 陈亮,顾勇,陈晓庆,等.丝素蛋白增强型磷酸钙复合rhBMP-2用于绵羊腰椎椎体间融合的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(7): 677-683.[6] Crawford CH 3rd, Carreon LY, McGinnis MD, et al. Perioperative complications of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on an absorbable collagen sponge versus iliac crest bone graft for posterior cervical arthrodesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(13):1390-1394.[7] Dai LY, Jiang LS.Single-level instrumented posterolateral fusion of lumbar spine with beta-tricalcium phosphate versus autograft: a prospective, randomized study with 3-year follow-up.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(12):1299-1304. [8] Li G,Yuan TZ,Zhao M,et al.Zhongguo Wuzhexue Zazhi. 2010; 10(27):6762. 李刚,袁太珍,赵敏,等. β-TCP人工骨伤椎植骨成形联合后外侧融合治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折13例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2010, 10(27):6762.[9] Gu YJ,Fu QH,Shao XH,et al.Kouqiang Yixue. 2005;25(2):105. 顾亚军,傅其宏,邵现红,等. 可吸收止血纱布在腭裂术中的应用 [J].口腔医学,2005,25(2):105.[10] Guo Y,Tian GL.Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi. 2003;18(11): 664-666. 郭阳,田光磊. S-100吸收性止血绫于兔皮肤、皮瓣移植术中的应用观察 [J].中国康复医学杂志,2003,18(11):664-666.[11] Zhang Y.Zhongguo Xiandai Yiyao. 2012;14(1):18-19. 张勇.乳腺癌手术中应用可吸收止血纱布140例临床研究 [J].中国现代医药,2012,14(1):18-19.[12] Liu HC.Zhongguo Dangdai Yiyao. 2011,18(21):187-190. 刘华春.椎板切除术应用泰绫预防硬膜外瘢痕粘连[J]中国当代医药,2011,18(21):187-190.[13] Xiao H,Yang YN,Tang LF,et al.Zhongguo Shenghua Yaowu Zazhi. 1997;18( 4):200-202. 肖杭,杨永年,唐玲芳,等.吸收性明胶海绵和止血绫在家兔肌肉、血管与脑组织中吸收性观察[J].中国生化药物杂志,1997, 18(4): 200-202.[14] Dai WD,Lin H,Fang TL,et al.Zhongguo Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Xuebao. 2009;28(1):108-116. 戴文达,林红,方涛林,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞结合多孔β-TCP构建生物相容性人工骨[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2009, 28(1):108-116.[15] Minamide A, Yoshida M, Kawakami M.The use of cultured bone marrow cells in type Ⅰ collagen gel and porous hydroxyapatite for posterolateral lumbar spine fusion . Spine. 2005;30(10):1134-8.[16] Ma X,Hu YY,Wu XM,et al.Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2008;27(2):84-86. 马兴,胡蕴玉,吴小明,等. 结构型PLGA/TCP/Col/ADSCs-OB仿生活性人工骨的体外构建及其在兔腰椎横突间脊柱融合的实验研究[J].生物医学工程研究,2008, 27(2):84-86.[17] Minamide A,Tamaki T,Kawakami D.Experimental Spinal fusion using sintered bovine bone coated with type I collagen and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 . Spine. 1999;24(18): 1863-1870. [18] Wang J,Qiu Y,Xia CL,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007,11(28):5536-5539. 王健,邱勇,夏春林,等. 富集自体骨髓间质干细胞复合羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙植骨材料在脊柱融合中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(28):5536-5539.[19] Zhang P,Gang YK,Li H.Linchuang Guke Zazhi. 2006;9(1):1-4. 张蒲,干耀恺,李华.富集骨髓干细胞结合β磷酸三钙在脊柱融合的临床应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2006, 9(1):1-4.[20] Glassman SD, Carreon LY, Djurasovic M,et al. RhBMP-2 versus iliac crest bone graft for lumbar spine fusion: a randomized, controlled trial in patients over sixty years of age. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(26):2843-2849. |