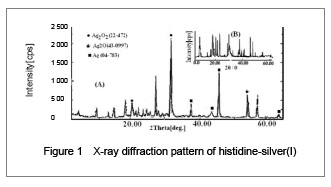
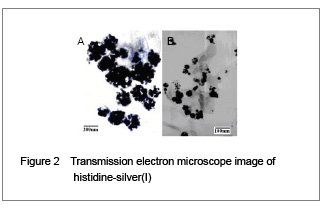
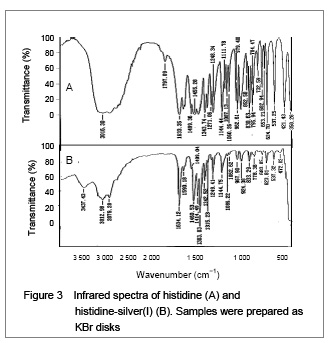
His-silver(I) nanoparticles synthesized from micro emulsions were determined to have a mean particle size of 34.6 nm by X-ray diffraction, and 39.2 nm from transmission electron microscope images. Fourier transform infrared provided further insight into the interaction of histidine with silver(I). The asymmetrical (OCO) stretching band of the carboxylate anion (COO−) at 1 590.18 cm
−1[14-15] became a shoulder. The COO− symmetrical stretching band at 1 460.53 cm
−1 and 1 383.83 cm
−1 increased in intensity. These changes are typical complexation of the carboxylate anion with a metal cation
[16-17]. In this case, most of the carboxylate anion must have become bound, complexed or chelated to the silver(I) because the asymmetrical stretching band at 1 590.18 cm
−1 moved to a higher frequency
[18]. This band may be overlaid by other higher frequency bands, resulting in deepening of the peak valley between 1 634 and 1 590 cm
−1. Furthermore, shifting of the symmetrical (OCO) stretching band at 1 455 cm
−1 to a higher frequency also suggests the complexation of silver(I)
[19], and this band may also be concealed by other higher frequency bands that increase the intensity of the band. Three bands between 600-700 cm
−1 were assigned to the in-plane bending (δ) or wagging (w) of (OCO)
[18]. Reports have suggested that Ag
+ may bind to the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group from the amidogen (HNCO) in this system
[16]. However, the carboxylate anion competes against the amidogen for binding, complexation or chelatation of silver(I). Oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen, which means that the carboxylate anion with two oxygen atoms may more easily bind, complex or chelate with Ag
+ than the amidogen one oxygen and one nitrogen. The mechanism of binding involves formaldehyde reduction of soluble silver(I) to elemental silver. Previous studies have shown that the coordination of imidazole with silver(I) produces an imidazole ring band at about 1 820 cm
−1, but its source is still unknown
[16, 19]. However, in our experiments, it shows that a band is observed at 1 797.09 cm
−1 in the histidine spectra (Figure 3A), but no band is observed in the histidine-silver(I) spectra (Figure 3B). In summary, the infrared spectra suggested that silver(I) could coordinate with the oxygen atom of the α-carboxy group, and nitrogen atoms of the α-amino-group and the imidazole ring. These coordination possibilities are all consistent with the structure of histidine-silver(I) shown in Figure 4, and the results could also confirm previous studies
[10].