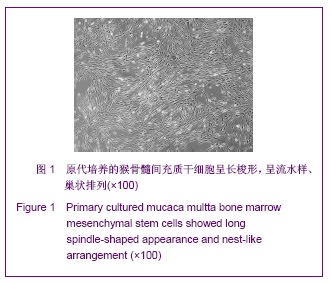
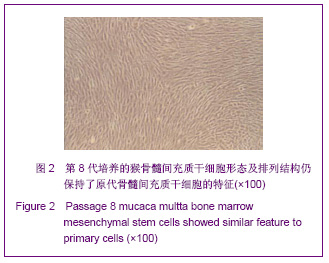
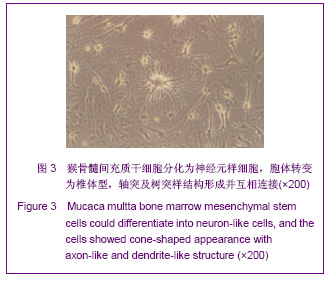
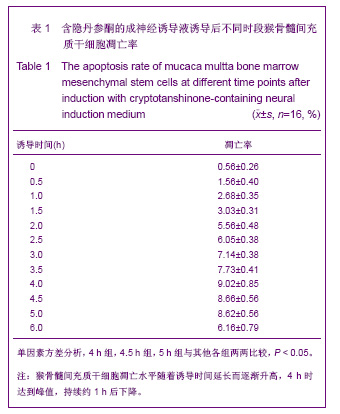
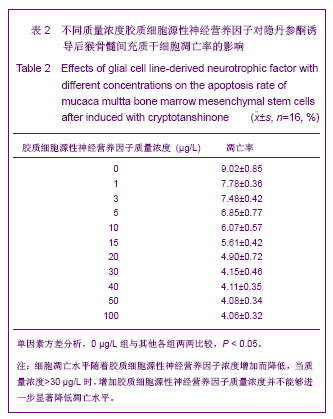
| [1] Park BW, Kang EJ, Byun JH,et al. In vitro and in vivo osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from skin, bone marrow and dental follicle tissues. Differentiation. 2012;83(5):249-259.[2] Ghaedi M, Soleimani M, Shabani I,et al. Hepatic differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells on a novel nanofiber scaffold. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012;17(1):89-106.[3] Bojin FM, Gruia AT, Cristea MI, et al. Adipocytes differentiated in vitro from rat mesenchymal stem cells lack essential free fatty acids compared to adult adipocytes. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21(4):507-512.[4] Liu XG,Deng YB,Cai H. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2010;14(10): 1813-1816. 刘晓刚,邓宇斌,蔡辉.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子与猴骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及向神经元前体细胞分化:不同质量浓度对诱导剂隐丹参酮作用有差异吗[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(10):1813-1816.[5] Wang Y, He W, Bian H,et al. Small molecule induction of neural-like cells from bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(5):1527-1536.[6] Wang XS, Li HF, Zhao Y, et al. Radix Astragali-induced differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(7):497-502.[7] Ma K, Fox L, Shi G,et al. Generation of neural stem cell-like cells from bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Neurol Res. 2011;33(10):1083-1093.[8] Yin YQ, Chen B, Ke JL, et al. Xuefuzhuyu injection induces neuronal differentiation of rat bone morrow mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(3):177-182.[9] Deng YB, Yuan QT, Liu XG,et al. Functional recovery after rhesus monkey spinal cord injury by transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal-stem cell-derived neurons. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005;118(18):1533-1541.[10] Deng YB, Liu XG, Liu ZG,et al. Implantation of BM mesenchymal stem cells into injured spinal cord elicits de novo neurogenesis and functional recovery: evidence from a study in rhesus monkeys. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(3):210-214. [11] Savitt J, Singh D, Zhang C,et al. The in vivo response of stem and other undifferentiated spermatogonia to the reversible inhibition of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in the adult. Stem Cells. 2012;30(4):732-740.[12] Cass WA, Peters LE, Fletcher AM,et al. Evoked dopamine overflow is augmented in the striatum of calcitriol treated rats. Neurochem Int. 2012;60(2):186-191.[13] Baudry C, Reichardt F, Marchix J,et al. Diet-induced obesity has neuroprotective effects in murine gastric enteric nervous system: involvement of leptin and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor. J Physiol. 2012;590(Pt 3):533-544.[14] Airavaara M, Pletnikova O, Doyle ME,et al. Identification of novel GDNF isoforms and cis-antisense GDNFOS gene and their regulation in human middle temporal gyrus of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(52):45093-45102.[15] Yi T, Lee DS, Jeon MS,et al. Gene expression profile reveals that STAT2 is involved in the immunosuppressive function of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Gene. 2012;497(2):131-139.[16] Park HW, Cho JS, Park CK, et al. Directed induction of functional motor neuron-like cells from genetically engineered human mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(4): e35244.[17] Hao L, Wang J, Zou Z,et al. Transplantation of BMSCs expressing hPDGF-A/hBD2 promotes wound healing in rats with combined radiation-wound injury. Gene Ther. 2009;16(1): 34-42.[18] Gauglitz GG, Jeschke MG. Combined gene and stem cell therapy for cutaneous wound healing. Mol Pharm. 2011; 8(5):1471-1479.[19] Dong SW, Ying DJ, Duan XJ,et al. Bone regeneration using an acellular extracellular matrix and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells expressing Cbfa1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2009;73(10):2226-2233. [20] Liu H, Honmou O, Harada K,et al. Neuroprotection by PlGF gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells after cerebral ischaemia. Brain. 2006;129(Pt 10):2734-2745.[21] Horita Y, Honmou O, Harada K,et al. Intravenous administration of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells protects against injury in a cerebral ischemia model in the adult rat. J Neurosci Res. 2006;84(7):1495-1504.[22] Toyama K, Honmou O, Harada K,et al. Therapeutic benefits of angiogenetic gene-modified human mesenchymal stem cells after cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1): 47-55.[23] Jin GZ, Cho SJ, Choi EG,et al. Rat mesenchymal stem cells increase tyrosine hydroxylase expression and dopamine content in ventral mesencephalic cells in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(11):1433-1438.[24] Peng Y, Zhang QM, You H, et al. Growth-associated protein 43 and neural cell adhesion molecule expression follow-ing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2010;5(13):975-980.[25] Wang D, Zhang JJ. Electrophysiological functional recovery in a rat model of spinal cord hemisection injury following bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation under hypothermia. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(10): 749-755.[26] Glavaski-Joksimovic A, Virag T, Chang QA,et al. Reversal of dopaminergic degeneration in a parkinsonian rat following micrografting of human bone marrow-derived neural progenitors. Cell Transplant. 2009;18(7):801-814.[27] Naruse K, Sato J, Funakubo M,et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells improves mechanical hyperalgesia, cold allodynia and nerve function in diabetic neuropathy. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27458.[28] Ma K, Fox L, Shi G,et al. Generation of neural stem cell-like cells from bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Neurol Res. 2011;33(10):1083-1093.[29] Kopen GC, Prockop DJ, Phinney DG. Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(19):10711-10716.[30] Zhang H,Sun TW. Guoji Gukexue Zazhi. 2011;32(2):104-107. 张杭, 孙天威. 骨髓间充质干细胞分化为神经细胞研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2011,32(2):104-107.[31] Sun D, Bullock MR, McGinn MJ,et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor-enhanced neurogenesis contributes to cognitive recovery in rats following traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):56-65. [32] Pei JJ,Wu R,Zhao HB,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(10): 1808-1812. 裴晶晶,吴润,赵红斌,等.Ca2+信号介导红景天苷促进小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞的定向分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(10): 1808-1812.[33] Ni WF, Yin LH, Lu J,et al. In vitro neural differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells induced by cocultured olfactory ensheathing cells. Neurosci Lett. 2010;475(2):99-103.[34] Deng J, Petersen BE, Steindler DA,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells spontaneously express neural proteins in culture and are neurogenic after transplantation. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4): 1054-1064.[35] Kim SU, de Vellis J.Stem cell-based cell therapy in neurological diseases: a review. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87(10): 2183-2200.[36] Wang CL,Su JB,E LL,et al. Jiepou Xuebao. 2001;32(2): 132-135. 王常利,苏剑斌,鄂玲玲,等. GDNF及HSV-GDNF对坐骨神经损伤大鼠脊髓运动神经元Bcl-2表达的影响[J].解剖学报,2001, 32(2):132-135. |