设计:三维有限元生物力学分析。
时间及地点:实验于2008年5月至2010年10月在上海交通大学材料学院力学实验室完成。
材料:根据国人正常腰椎的测量数据选取1名健康成年男性志愿者,27岁,身高178 cm,体质量72 kg,先行X射线摄片,再行腰椎CT平扫。实验设备:Siemens公司16排螺旋CT机,计算机工作站,医学图像处理软件Materialise,CAD软件Catia,有限元分析软件为MSC公司的Patran和Marc软件,统计软件SPSS 10.0。
实验方法:采用Siemens 16层螺旋CT对已选定的研究对象进行螺旋扫描及断层图像处理。扫描时志愿者取仰卧位,尽量保持扫描断面与身体长轴垂直。扫描参数如下:层厚0.5 mm,球管电流与电压200 mA/120 kV。扫描范围自L3上方2 mm始至S1下方2 mm止。在CT工作站中,通过调整图像灰度,增加对比度等对图像观察细节进行调整,得到118幅清晰的骨窗断层图像和118幅清晰的软组织窗图像,以DICOM刻录为光盘保存。将DICOM格式的图像数据导入三维重建软件Materialise Mimics,通过筛选选取L4/5的图像72幅,去除周边软组织图像,界定目标图像的阈值,重建L4/5椎体的三维图像,提取出每层图像的轮廓曲线,并根据不同部位和形状的区别分割成不同的set,利用medcad模块拟和自由曲面,以iges格式导出。采用专业的CAD造型软件Catia作为实体建模平台,将Mimics生成的标准IGES格式的自由曲面数据导入,利用Catia的自由曲面建模功能把不同部位的自由曲面建成封闭实体,并利用布尔运算建立椎体的皮质骨和松质骨区域,同时在L4/5椎体之间建立椎间盘模型,包括髓核和纤维环,其中髓核的体积和位置参照文献[1],建立与椎体几何高度相似的三维模型。将L4/5椎体及椎间盘的三维实体模型导入patran前处理程序,因为椎体的几何模型非常不规则,故采用Tetmesh四面体网格自由划分技术对其进行网格划分,单元类型采用tet10单元,其中单元总数为114 953,节点个数为25 502,皮质骨部分包含81 120个单元,松质骨部分包含23 766个单元,椎间盘包含10 067个单元。根据韧带的解剖位置,利用划分椎体生成的节点,建立模拟韧带和关节囊的一维cable缆式单元。赋予各结构材料学参数:弹性模量、泊松比,韧带面积各参数参照文献[2-6],建立L4,5包含韧带和关节囊的非线性有限元模型,见图1。
有限元模型的单元划分:
Unit division of finite element models:

有限元模型的材料特性:
Characteristics of the materials of finite element models:


在典型的退变性腰椎滑脱退变过程中,主要表现为髓核的脱水和关节突关节的退变不稳,即髓核中液体成分减少转换成为颗粒状半固体状态;纤维环松弛;椎间盘高度的减低;继而小关节内关节软骨变薄或脱落,关节囊松弛,椎间异常活动增加,椎体向前滑移。作者将正常L4/5模型中模拟髓核的液体单元替换为固体单元,髓核的弹性模量改为正常髓核弹性模量的2倍,纤维环的弹性模量也改为正常的2倍,模拟纤维环和关节囊的松弛,椎间盘的高度由原来的4 mm降低为3 mm,模拟椎间盘高度减低;关节突关节的接触面积减为原来的50%,椎体相应向前滑移。模型的具体力学数据均引自文献[7]。建立的退变性腰椎滑脱的模型见图2。

退变性腰椎滑脱有限元模型的材质特性:
Material properties of the degenerative spondylolisthesis finite element model:

L4/5节段减压融合内固定有限元模型的单元划分:
Unit division of L4/5 segment decompression and fusion internal fixation finite element model:

L4/5节段减压融合内固定有限元模型的材料特性:
Material properties of L4/5 segment decompression and fusion internal fixation finite element model:

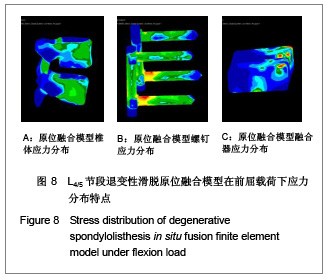
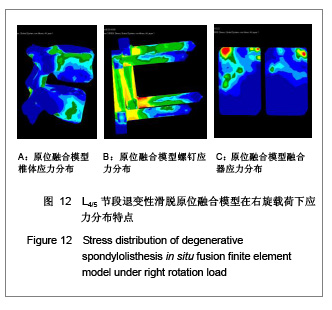
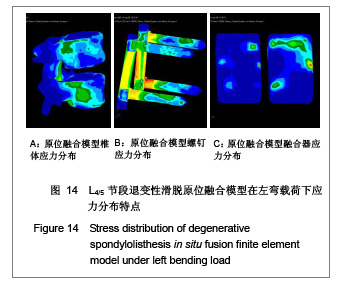
完全参照临床手术方法,在腰椎退变性滑脱模型的基础上,切除L4,5的后部结构,包括棘上韧带、棘间韧带、黄韧带、棘突及全椎板、L4两侧下关节突、L4,5椎间盘全部髓核及后1/3纤维环,加入椎间融合器和椎弓根螺钉,建立腰椎滑脱原位融合的三维有限元模型,见图3。

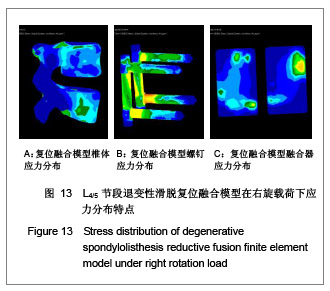
对正常腰椎三维有限元模型进行如上操作,建立腰椎滑脱复位融合的三维有限元模型,见图4。

忽略椎间融合器、椎弓根钉和椎体骨质之间的微动,且椎间融合器、椎弓根螺钉和椎体紧密接触,无滑动及压缩、变形。L5椎体下缘所有各节点各方向的位移为零,L4可以自由活动,并接受载荷。
假设条件:实验所涉及生物材料特性均假定为均质、连续和各向同性。受力时模型各截面不相互滑动,各单元有足够的稳定性,不计材料受力变形。
加载:将L5椎体下表面固定,在L4椎体上表面施加均匀分布的压应力,压应力大小根据人体体质量的2/3(约500 N)除以L4上表面的面积得到,模拟椎体在中立位的负载情况,另外,施加15 N•m的力偶矩,模拟椎体在前屈、后伸、左旋、右弯时的负载情况,力偶的施加方法,见图5。其中前屈、后伸的旋转轴是以轴向载荷作用下在矢状面产生最小位移的点确定的。
负荷加载方式:一对由集中力所产生的15 N•m纯力矩施加于模型的上表面,模拟前屈、后伸、左右侧弯和顺时针、逆时针轴向旋转,同样的纯力矩也施加于完整的模型上以作比较。实验中对模型施加轴向压缩载荷是基于Posne等的观点,他的研究结果表明,当进行力矩一运动研究时,加与不加轴向压缩载荷表现出的腰椎活动节段运动方式是非常相似的;同时,对模型施加前屈、后伸、侧弯和轴向旋转纯力矩被最广泛地用于评价脊柱的生物力学。

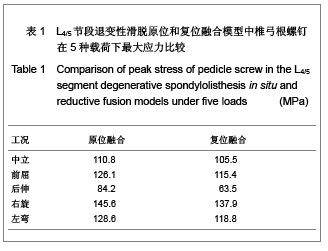
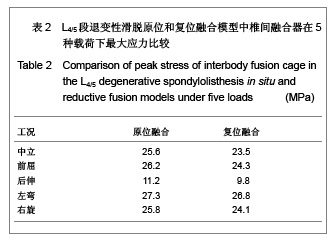
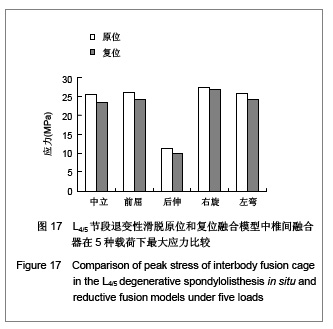
当求解器计算完毕,进入Patran后处理器。后处理器根据不同的需要把结果以不同的形式呈现出来。将L4,5椎体、椎弓根螺钉和椎体融合器作为研究对象,分别测定它们在退变性腰椎滑脱原位融合和复位融合时各种工况(中立位、前屈、后伸、左弯、右旋)下的Von mises 力,以应力云图方式显示不同工况下各部应力分布情况,并标示出最大应力部位。