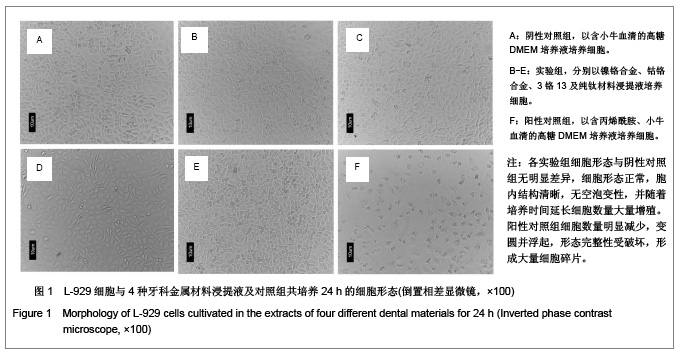
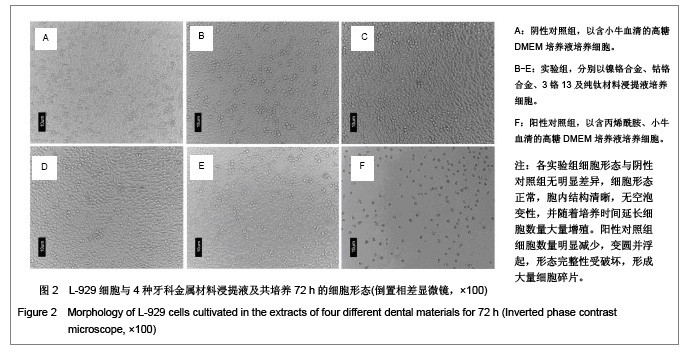
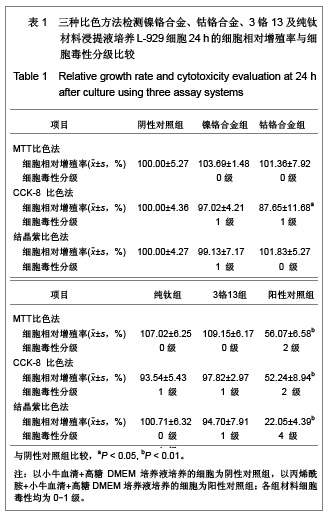
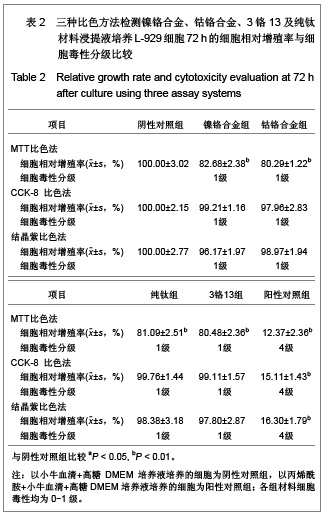
| [1] Gil FJ,Sánchez LA,Espías A,et al.In vitro corrosion behavior and metallic ion release of different prosthodontic alloys.Int Dent J.1999;49:361-367.[2] McGinley EL,Moran GP,Fleming GJ.Base-metal dental casting alloy biocompatibility assessment using a human-derived three-dimensional oral mucosal model.Acta Biomater.2012;8(1):432-438.[3] McGinley EL,Fleming GJ,Moran GP.Development of a discriminatory biocompatibility testing model for non-precious dental casting alloys.Dent Mater.2011;27(12):1295-1306. [4] Xu WX,Su JS.Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2012;30(3): 255-258. 许卫星,苏俭生.3种金属烤瓷冠修复后龈沟液中白细胞介素-8水平动态测定[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2012,30(3):255-258.[5] Galo R,Ribeiro RF,Rodrigues RC,et al.Effects of chemical composition on the corrosion of dental alloys.Braz Dent J. 2012;23(2):141-148.[6] Faria AC,Rosa AL,Rodrigues RC,et al.In vitro cytotoxicity of dental alloys and cpTi obtained by casting.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2008;85(2):504-508.[7] Faria AC,Rodrigues RC,Antunes RP,et al.Effect of temperature variation on the cytotoxicity of cast dental alloys and commercially pure titanium.J Appl Oral Sci.2009;17(5): 421-426.[8] Garhammer P,Schmalz G,Hiller KA,et al.Patients with local adverse effects from dental alloys: frequency, complaints, symptoms, allergy. Clin Oral Investig.2001;5(4):240-249.[9] Zhao XY. Zhonghua Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2009; 44(7): 401-403. 赵信义.浅谈烤瓷修复用镍合金的安全性及不良反应[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2009,44(7):401-403.[10] Venclíkova Z,Benada O,Bártova J,et al.Metallic pigmentation of human teeth and gingival:morphological and immunological aspects.Dent Mater J.2007;26(1): 96-104.[11] Kedici PS,Memiko?lu MM,Kansu G,et al.Case report: ionisation tendency of a base metal alloy in the oral environment.Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent.1995; 3(5): 231-234.[12] Kalkwarf KL.Allergic gingival reaction to esthetic crowns.Quintessence Int Dent Dig.1984;15(7):741-745.[13] Li RQ,Kan HX,Zheng ZF. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2009;13(25):4989-4992. 李榕卿,阚洪霞,郑宗富.镍铬合金烤瓷冠修复对牙周组织的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(25):4989-4992.[14] Li-Chun W,Ye S,Teng M.Comparison of clinical effects of au-pt based and ni-cr based porcelain crowns.Chin Med Sci J.2012;27(3):167-170.[15] Bai YX,Xie WL,Sun Y.Xiandai Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2009; 23(4):386-388. 白轶昕,谢伟丽,孙宇.两种非贵金属烤瓷冠的临床应用效果评价[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2009,23(4):386-388.[16] Zhang Y.Shiyong Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2010;26(2):244-247. 张英.3种全冠修复体对基牙龈沟液中酶水平的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2010,26(2):244-247.[17] ISO 10993-12:2002,Biological evaluation of medical devices- Part 12:Sample preparation and reference materials.[18] Hao HP.Beijing:Standards Press of China.2000:285-289, 334-347. 郝和平.医疗器械生物学评价标准实施指南[M].北京:中国标准出版,2000:285-289, 334-347.[19] Pu MH,Luo XJ.Kouqiang Yixue Yanjiu.2009;25(1):51-54. 浦美泓,罗晓晋.口腔修复非贵金属材料对L-929细胞毒性的研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2009,25(1):51-54. [20] Imirzalioglu P,Alaaddinoglu E,Yilmaz Z,et al.Influence of recasting different types of dental alloys on gingival fibroblast cytotoxicity.J Prosthet Dent.2012;107(1):24-33.[21] Wang X,Xia Y,Liu L,et al.Comparison of MTT assay, flow cytometry, and RT-PCR in the evaluation of cytotoxicity of five prosthodontic materials.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010;95(2):357-364. [22] Qiao GY,Shen QP,Su JS.Shanghai Kouqiang Yixue.2010; 19(1): 72-76. 乔广艳,沈庆平,苏俭生.3种临床常用烤瓷合金对小鼠成纤维细胞L929的毒性评价[J].上海口腔医学,2010,19(1):72-76.[23] Jin CS,Jiang J,Zhan DS. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2009;13(21):4181-4184. 金长山,江娟,战德松.细胞培养法评价自制镍铬烤瓷合金的细胞毒性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(21): 4181-4184.[24] Tu M,Liang W,Wu T,et al.Evaluation of cytotoxicity of resin bonding materials toward human oral epithelial cells using three assay systems.J Dent Sci.2009;4(4):178-186.[25] Mosmann T.Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation andcytotoxicity assays.J Immunol Methods.1983;65(1-2):55-63.[26] Lü XY,H.F.Kappert.Zhonghua Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.1995; 30(6): 377-379. 吕晓迎,H.F.Kappert.牙科材料细胞毒性评定的新方法(MTT试验)[J].中华口腔医学杂志,1995,30(6):377-379.[27] Xiong JW,Xiao H,Zhang ZX.Jiguang Shengwu Xubeao.2007; 16(5):559-562. 熊建文,肖化,张镇西.MTT法和CCK-8法检测细胞活性之测试条件比较[J].激光生物学报,2007,16(5):559-562.[28] Zhang D,Nan L,Ren L,et al.Kouqiang Yixue.2012;32(1):5-8. 张丹,南黎,任玲,等.CCK-8法和MTT法评价医用抗菌不锈钢细胞毒性的比较研究[J].口腔医学,2012,32(1):5-8. [29] Li N,Wan WT,Jin LH. Guizhou Daxue Xuebao.2009; 26(3): 18-20. 李宁,万文婷,金林红.CCK-8法和MTT法检测人前列腺癌PC3细胞活性的最佳条件比较研究[J].贵州大学学报:自然科学版,2009, 26(3):18-20.[30] Eckhardt A,Müller P,Hiller KA,et al.Influence of TEGDMA on the mammalian cell cycle in comparison with chemotherapeutic agents.Dent Mater.2010;26(3):232-241.[31] Thumwanit V,Kedjarune U.Cytotoxicity of polymerized commercial cyanoacrylate adhesive on cultured human oral fibroblasts.Aust Dent J.1999;44(4):248-252. |