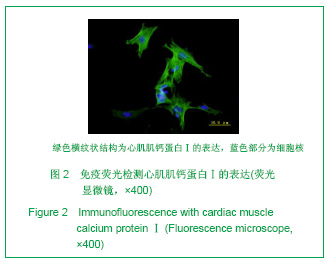
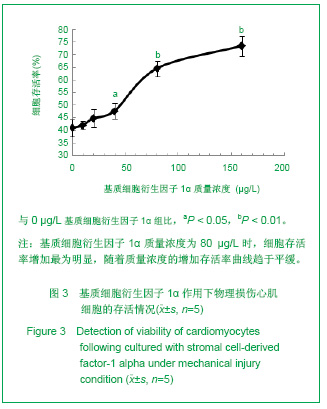
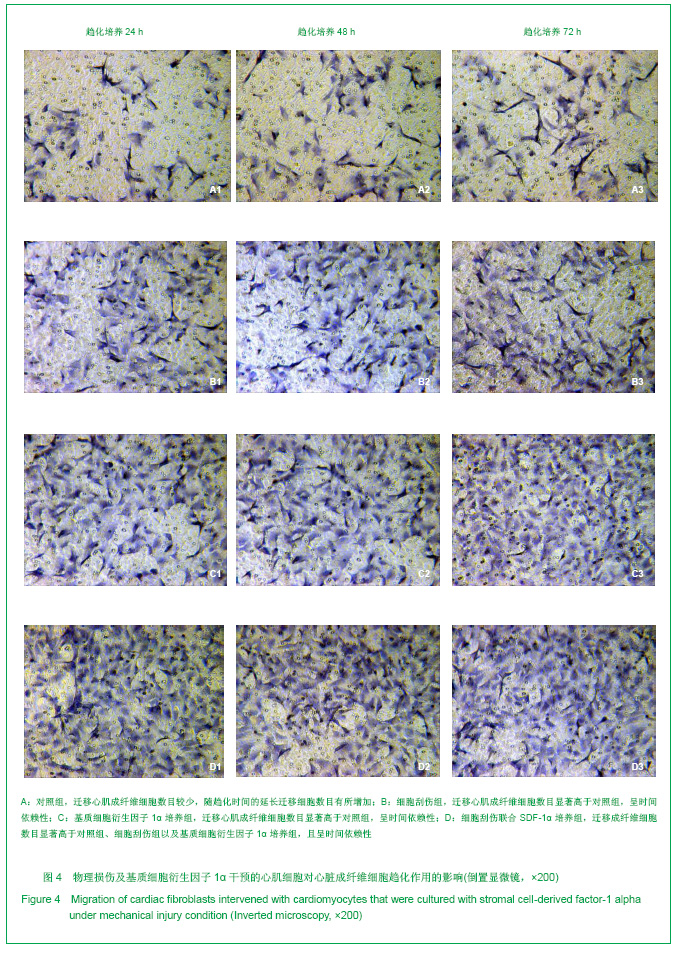
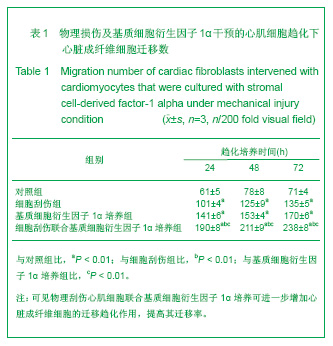
| [1] Thanopoulos BV, Rigby ML, Karanasios E, et al. Transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects in infants and children using the Amplatzer perimembranous ventricular septal defect occluder. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(7):984-989.[2] Chen Y, Xu ZY. Zhongguo Jieru Yingxiang yu Zhiliao Xue. 2010;7(5):579-582. 陈阳,徐仲英.经导管室间隔缺损封堵术后房室传导阻滞的危险因素[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2010,7(5):579-582.[3] Zhang G, Nakamura Y, Wang X, et al. Controlled release of stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha in situ increases c-kit+ cell homing to the infarcted heart. Tissue Eng, 2007;13(8):2063-2071.[4] Aiuti A, Webb IJ, Bleul C, et al. The chemokine SDF-1 is a chemoattractant for human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells and provides a new mechanism to explain the mobilization of CD34+ progenitors to peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1997;185(1):111-120.[5] Larocca TJ,Jeong D,Kohlbrenner E,et al.CXCR4 gene transfer prevents pressure overload induced heart failure.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;53(2):223-232.[6] Dong F, Harvey J, Finan A, et al. Myocardial CXCR4 expression is required for mesenchymal stem cell mediated repair following acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2012;126(3):314-324.[7] Majunke N, Bialkowski J, Wilson N, et al. Closure of atrial septal defect with the amplatzer septal occluder in adults. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103(4):550-554.[8] Bijulal S, Sivasankaran S, Ajitkumar VK. An unusual thrombotic complication during percutaneous closure of atrial septal defect. J Invasive Cardiol. 2009;21(2):83-85.[9] Xie QL, Wang Z, Zhang ML, et al. Linchuang Huicui. 2006; 21(20):1510. 解启莲,王震,张密林,等.室间隔缺损经导管诱导自然闭合1例[J]..临床荟萃,2006,21(20):1510.[10] De Falcol M, Cobellis G, De Luca A. Proliferation of cardiomyocytes: a question unresolved. Front Biosci(Elite Ed). 2009;1:528-536.[11] Goldsmith EC, Hoffman A, Morales MO, et al. Organization of fibroblasts in the heart. Dev Dyn. 2004;230(4):787-794.[12] Souders C, Bowers SLK, Baudino TA. Cardiac fibroblasts: the renaissance cell. Circ Res. 2009;105(12):1164-1176.[13] Porter KE, Turner NA. Cardiac fibroblasts: at the heart of myocardial remodeling. Pharmacol Ther. 2009;123(2): 255-278. [14] Liu Y, Ji C, Wu WK. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2012; 28(3):459-463. 刘颖,纪超,吴伟康.附子多糖保护缺氧/复氧乳鼠心肌细胞及其抗内质网应激的机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(3): 459-463.[15] Yu Y, Wang SR, Nie B, et al. ZhongGuo Zhongyao Zazhi. 2012;37(7):979-984. 于妍,王硕仁,聂波,等.黄芪注射液在逆转心肌细胞肥大过程中对心肌细胞线粒体结构和功能的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2012, 37(7): 979-984.[16] Dong Y, Zhang L, Shao SX, et al. Zhongguo Xibao Shengwuxue Xuebao. 2010;32(3):361-369. 董悦,张雷,邵素霞,等.缺血心脏成纤维细胞构建工程化心肌样组织的研究[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2010,32(3):361-369.[17] Liehn EA, Tuchscheerer N, Kanzler I, et al. Double-edged role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in experimental myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(23):2415-2423.[18] Tang JM, Wang JN, Song HX, et al. Adenovirus-mediated stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha gene transfer improves cardiac structure and function after experimental myocardial infarction through angiogenic and antifibrotic actions. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37(4):1957-1969.[19] Yin Q, Jin PF, Liu XB, et al. SDF-1a inhibits hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(1):9-16.[20] Shen L, Gao YX, Qian JY, et al. The role of SDF-1a/Rac pathway in the regulation of endothelial progenitor cell polarity, homing and expression of Rac1,Rac2 during endothelial repair. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;365(1-2):1-7.[21] Daisy P. Wang CC. Stromal-derived fctor-1 apha-loaded PLGA microspheres for stem cell recruitment. Pharm Res. 2011;28(10):2477-2489.[22] Yin YG, Huang L, Zhao XH, et al. Disan Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2007;29(6):475-478. 尹扬光,黄岚,赵晓辉,等.SDF-1对内皮祖细胞增殖迁移的影响及AMD3100对其的干预[J].第三军医大学学报,2007,29(6): 475-478.[23] Zhan SH, Deng M, Gu DM, et al. Shandong Yiyao. 2011; 51(32):13-15. 詹升华,邓敏,顾冬梅,等.CXCR4/SDF-1α信号对乳腺癌细胞的体外增殖和迁移的促进作用[J].山东医药,2011,51(32):13-15. |