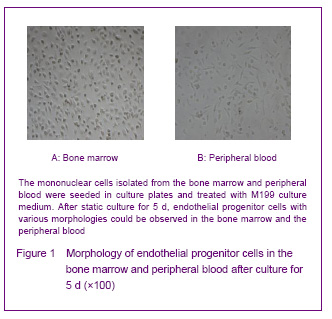
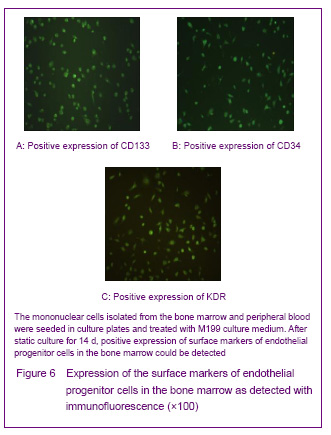
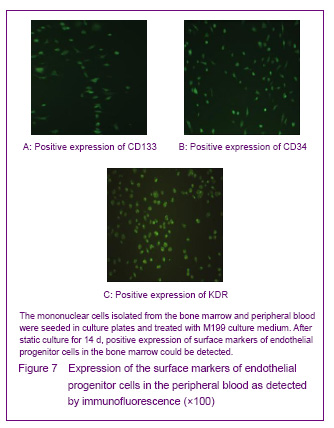
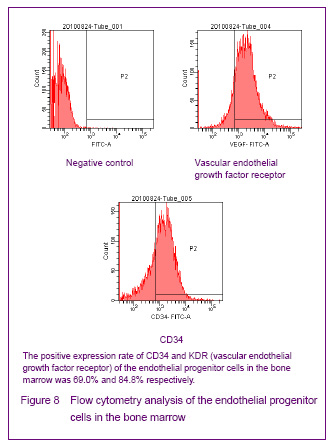
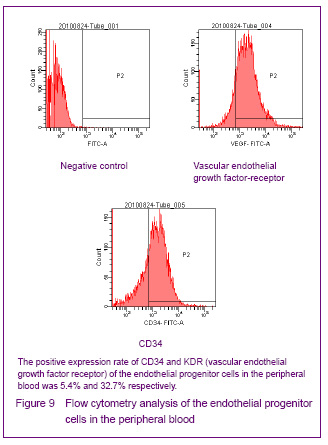
In 1997, Asahara et al [1] firstly proposed endothelial progenitor cells, the CD34+ mononuclear cells were isolated by magnetic sorting method from human peripheral blood, and the cells cultred in vitro were adherent and in spindle-shaped. The cells can be specifically homing in angiogenesis tissue, can express the endothelial progenitor cell-specific antigen, differentiate and proliferate into mature endothelial cells and form bureaucratic tone-like structure, the cells are the endothelial progenitor cells. Recent studies confirmed that both endothelial progenitor cells and hematopoietic stem cells are derived from a common blood-hemangioblastoma and settled in the bone marrow[2]. In addition, Asahara et al[3] established transgenic mouse bone marrow transplantation model found that these cells were not only exited in the peripheral blood, but also in the bone marrow, spleen and cord blood. Endothelial progenitor cells cultured for different times are in oval, long spindle or spindle-shaped, the morphology of tge cells mainly identified by cell surface markers, but unified endothelial progenitor cells specific surface markers have not found yet. Currently, the blood cell differentiation CD34, CD133, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, stem cell membrane receptor (cKit), stem cell antigen (Sca-1), von Willebrand factor are the major cell surface markers of endothelial progenitor cells[4]. CD133 is the hematopoietic stem cell marker earlier than CD34, and it has been regarded as a marker to distinguish immature of endothelial progenitor cells[5]. Now most of the studies using CD34+/vascular endothelial growth factor 2+ double-positive cell markers or CD34+/vascular endothelial growth factor 2+/CD133+ three positive markers to identify endothelial progenitor cells[6]. Therefore, we have chosen CD34, KDR and CD133 as the surface antibodies to identify endothelial progenitor cells.
Endothelial progenitor cells take part in angiogenesis after ischemic stroke. Endothelial progenitor cells gather at the injury and ischemia and hypoxia tissue, and plays an important role in endothelial repairing after vascular injury and establishment of collateral circulation vascular network, and has great application prospects in repairing damaged vascular endothelium, promoting nerve regeneration, promoting the establishment of collateral circulation and building microvascular tissue engineering networks.
Angiogenesis and angiogenesis are the two main forms of blood vessel growth. Various factors can give birth to new blood vessels through sprouting way under the existing vascular which called angiogenesis; angiogenesis is the formation of blood vessels in the avascular zone, that is endothelial progenitor cells raising and homing to the damaged or ischemic tissue area, and forming the new blood vessels or vascular network. Earlier, many scholars believe that angiogenesis only occurs in the embryonic period, and disappears after birth[7]. The discovery and the research of endothelial progenitor cells confirmed that angiogenesis plays an important role in postnatal vascular formation and vascular damage repairing. Zhang et al [8] transplanted the bone marrow cells marked with integrated LacZ gene to the mouse model of focal ischemia, and finding that a large number of marked bone marrow cells could be seen around the infarction and the cells were involved in angiogenesis. Besler et al [9] found that the bone marrow cells were large gathered around the infraction after injected into the cerebral ischemia rat, indicating that bone marrow-derived cells can migrate and “homing” to the damaged brain tissue. Endothelial progenitor cells can promote angiogenesis and promote the repairing of endothelial damage. Shirota et al[10] seeded the endothelial progenitor cells on the microvascular bracket, and found that a large number of endothelial progenitor cells proliferated in the vascular lumen and formed cobblestone and cobblestone-like cell layer which can improve microcirculation in the ischemic area and promote the nerve growth. Au et al [11] found that after endothelial progenitor cells transplantation, a large number of blood vessels or vascular network-like structures appeared, the perfusion could be seen in the cavity; Huang et al [12] transplanted the endothelial progenitor cells into the rabbits with carotid artery injury, and found that a large number of endothelial progenitor cells were gathered in the damaged blood vessels lumen or wall and on the surface of new blood vessels, the vascular re-endothelialization area was 91.6%, analysis results showed that endothelial progenitor cells can secrete the anti-thrombotic biologically active substances: nitric oxide, prostaglandins 1 and tissue-type plasminogen activator and other relevant factors, inhibit intimal hyperplasia, and endothelial progenitor cells transplantation can be considered as a treatment method to prevent thrombosis and restenosis after intervention.
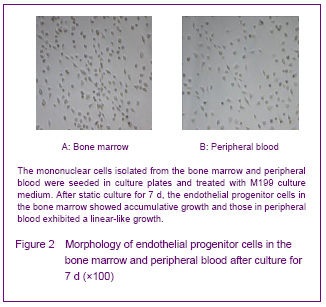
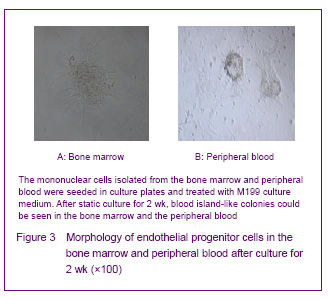
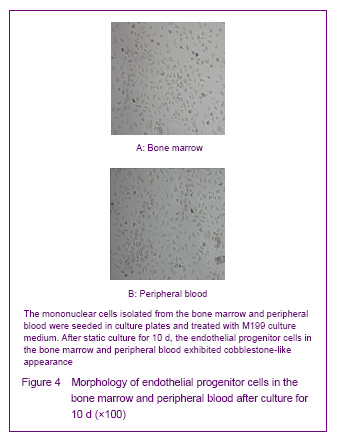
In 2004, Hur et al [13] proposed two types of endothelial progenitor cells from adult peripheral blood, according to the significant differences of their sources, morphology, surface markers and proliferation, the cells were named as early endothelial progenitor cells and late endothelial progenitor cells. Early endothelial progenitor cells were separated from the peripheral blood, elongated spindle-shaped and bipolar needle shape, colony aggregation growth, appeared after primary cultured for 4 to 7 days, and after cultured for 3 to 4 weeks, the cells were in oval cobblestone morphology, the proliferation ability was decreased gradually and apoptosis; the early endothelial progenitor cells has relationship with the macrophages and hematopoietic stem cells co-expressed surface markers of CD34, CD45 and CD133. Late endothelial progenitor cells were separated from the bone marrow, the endothelial progenitor cells appeared after mesecnhymal stem cells adherent cultured for 2 to 3 weeks, sand can sustained and steady proliferate for more than 12 weeks and in typical cobblestone-like morphology, and the cells can express the cell-specific antigens. Our experiments found that the endothelial progenitor cells both from the bone marrow or peripheral blood can expressed CD34, CD133 and KDR; the early and late endothelial progenitor cells were identified according to the strong cloned proliferation ability of stem cells, and the endothelial progenitor cells identified with this method is called late endothelial progenitor cells or endothelial outgrowth cells, and the endothelial outgrowth cells can also express the specific surface markers of CD34, CD133 and KDR. In our experiments, we found that the endothelial progenitor cells cultured from the bone marrow samples have strong proliferative activity, and in the early stage, the cells were in long spindle-shaped and bipolar needle shape, the cells were in colony-like aggregation growth; after cultured for 7 days, the cells were in typical cobblestone and paving stone-like shape; after 1-2 months later, a large number of long spindle-shaped cells mass were reunion and connected, and formed a large number of cell colonies, and then the cells were sub-cultured for many times successfully and finding that the proliferative activity is still strong and the cells were in blood vessel-like growth.
We isolated a large number of late endothelial progenitor cells from bone marrow which having the strong proliferation activity, morphology and surface markers in line with the reported features. During culturing process, the cells were found with the characteristics of blood vessel activity, and the cells were in lumen and bridging-like growth. The cells were subcultured for many times successfully and finding that the proliferative activity is still strong, large numbers of island-like colony growth appeared. Therefore, we believe that the late endothelial progenitor cells with strong proliferative activity can be obtained from the bone marrow, and a better seed source of vascular stem cells was founded. Some literatures reported that[14] the mononuclear cells isolated from the bone marrow were treated with EGM-2MV and M199 culture medium for different induction times and identified with different surface markers to identify the early and late endothelial progenitor cells, and the results found that bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells cultured in EGM-2MV medium can be differentiated into late endothelial progenitor cells, and the bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells cultured in M199 medium can be differentiated into long spindle-shaped early endothelial progenitor cells. The results indicated that the proliferative activity of the endothelial progenitor cells cultured in EGM-2MV medium was stronger than that cultured in the M199 medium, and the endothelial progenitor cells cultured in EGM-2MV medium have the angiogenesis capacity. Flow cytometry found that expression of cell surface markers CD133 and FLK-1 was lower than the previously reported. But in our experiment, we found a lot of late endothelial progenitor cells in M199 medium, surface markers CD34, CD133 and KDR of endothelial progenitor cells were positive, so the differences between early endothelial progenitor cells and late endothelial progenitor cells may come from the sources of specimen and the methods.
Isner et al[15] the used exogenous angiogenic growth factor to promote the establishment of micro-circulation ischemia, proposed a “therapeutic angiogenesis” concept. With the development of endothelial progenitor cells, the physiological significance of angiogenesis and the high proliferative potential and oriented homing characteristics of endothelial progenitor cells have been gradually elucidated, providing a new idea for the treatment of ischemic cerebrovascular disease with revascularization. According to the characteristics of vascular targeting positioning of endothelial progenitor cells, endothelial progenitor cells will be amplified in vivo and in vitro for transplantation therapy, or through the endothelial progenitor cells gene therapy to promote the endothelial progenitor cells highly express angiogenesis inducing factor, promote angiogenesis in ischemic cerebrovascular disease, improve the local ischemia blood flow and establish the collateral circulation. The effect of stem cells combined gene therapy with the endothelial progenitor cells as seed cells for the treatment of angiogenesis is more significant. We isolated endothelial progenitor cells from bone marrow and peripheral blood in this experiment, and a large number of late endothelial progenitor cells from bone marrow which having the strong proliferation activity, morphology and surface markers in line with the reported features were isolated, and found a better seed source of vascular stem cells, in order to provide technical and theoretical support for endothelial progenitor cells in experimental research and clinical studies of ischemic cerebrovascular disease.