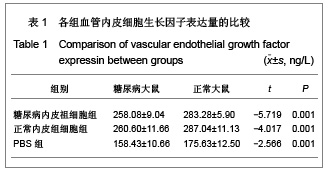
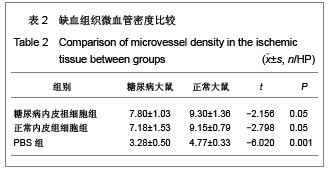
| [1] Werner N, Kosiol S,Schiegl T,et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and cardiovascular outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(10):999-1007.[2] Schmidtl C, Rossig L, Fichtlscherer S, et al. Reduced number of circulating endothelial progenitor ceils predicts future cardiovascular events: proof of concept for the clinical importance of endogenous vascular repair. Circulation. 2005; 111(22):2981-2987.[3] Ai J, Wang N, Du J, et al. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao. 2004; 20(11):1309-1312. 艾静,王宁,杜杰,等. Wistar大鼠2型糖尿病动物模型的建立[J].中国药理学通报,2004,20(11):1309-1312.[4] Akarte AS, Srinivasan BP, Gandhi S. Vildagliptin selectively ameliorates GLP-1, GLUT4, SREBP-1c mRNA levels and stimulates β-Cell proliferation resulting in improved glucose homeostasis in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2012 May 22.[5] Bogoslovsky T, Chaudhry A, Latour L, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells correlate with lesion volume and growth in acute stroke. Neurology. 2010;75(23):2059-2062.[6] Muthuraman A, Ramesh M, Sood S. Development of animal model for vasculatic neuropathy: Induction by ischemic-reperfusion in the rat femoral artery. J Neurosci Methods. 2010;186(2):215-221.[7] Li Calzi S, Neu MB, Shaw LC,et al. Endothelial progenitor dysfunction in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy: treatment concept to correct diabetes-associated deficits. EPMA J. 2010;1(1):88-100.[8] Isner JM, Asahara T. Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis as therapeutic strategies for postnatal neovascularization. Clin Invest. 1999;103(9):1231-1236.[9] Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor and the regulation of angiogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2000; 55:15-36.[10] Brea D, Rodríguez-González R,Sobrino T,et al. Proteomic analysis shows differential protein expression in endothelial progenitor cells between healthy subjects and ischemic stroke patients. Neurol Res. 2011;33(10):1057-1063.[11] Grisar JC, Haddad F, Gomari FA, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular disease and chronic inflammation: from biomarker to therapeutic agent. Biomark Med. 2011; 5(6):731-744. [12] Lee MO, Song SH, Jung S, et al. Effect of ionizing radiation induced damage of endothelial progenitor cells in vascular regeneration.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(2): 343-352.[13] Zeng L, Ding S, Yan Z, et al. Irradiation induces homing of donor endothelial progenitor cells in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Hematol. 2012;95(2):189-197. [14] Biscetti F, Straface G, De Cristofaro R, et al. High-mobility group box-1 protein promotes angiogenesis after peripheral ischemia in diabetic mice through a VEGF-dependent mechanism. Diabetes. 2010;59(6):1496-1505.[15] Gehling UM, Ergün S, Schumacher U, et al. In vitro differentiation of endothelial cells form AC133-positive progenitor cells. Blood. 2000;95(10):3106-3112.[16] Capobianco S, Chennamaneni V, Mittal M, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells as factors in neovascularization and endothelial repair. World J Cardiol. 2010;2(12):411-420. [17] Suzukj T, NishdaM, Frtami S, et al. Neoendothelializalion after peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in humans: a case report of a Tokaimura nuclear accident victim. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;58(2):487-492.[18] Jialal I, Fadini GP, Pollock K, et al.Circulating levels of endothelial progenitor cell mobilizing factors in the metabolic syndrome. Cardiol. 2010;106(11):1606-1608. [19] Napoli C, Hayashi T, Cacciatore F, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells as therapeutic agents in the microcirculation: an update. Atherosclerosis. 2011;215(1):9-22.[20] Jie KE, van der Putten K, Bergevoet MW, et al. Short- and long-term effects of erythropoietin treatment on endothelial progenitor cell levels in patients with cardiorenal syndrome. Heart. 2011;97(1):60-65. [21] Smadja DM, Duong-van-Huyen JP, Dal Cortivo L, et al. Early endothelial progenitor cells in bone marrow are a biomarker of cell therapy success in patients with critical limb ischemia. Cytotherapy. 2012;14(2):232-239. [22] Huang C, Zhang L, Wang Z, Pan H, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells are associated with plasma homocysteine in coronary artery disease.Acta Cardiol. 2011;66(6):773-777. [23] McClung JA, Nasser N, Saleem M, et al. Circulating endothelial cells are elevated in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus independently of HbA1c. Diabetologia. 2005;48(2): 345-350.[24] Loomans CJ, de Koning EJ, Staal FJ, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction: a novel concept in the pathogenesis of vascular complications of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53(1):195-199.[25] Kuki S, Imanishi T, Kobayashi K. Hyperglycemia accelerated endothelial progenitor cell senescence via the activation of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase. Circ J, 2006;70(8): 1076-1081.[26] Cubbon RM, Kahn MB, Wheatcroft SB. Effects of insulin resistance on endothelial progenitor cells and vascular repair. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009;117(5):173-190. |