中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (6): 1024-1028.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.06.013
• 脂肪干细胞 adipose-derived stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
Conophylline与尼克酰胺联合诱导脂肪源干细胞为功能性类胰岛细胞
杨 萍1,郑勤龙2,王劲峰1,黄家学1,3,4
- 1天津大学药物科学与技术学院,天津市 300072
2北欧生物科技(北京)有限公司,北京市 102206
3协和干细胞基因工程有限公司,天津市 300384
4中源协和干细胞生物工程股份公司,天津市 300050
Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into functional islet-like cells using Conophlline and Nicotinamide
Yang Ping1, Zheng Qin-long2, Wang Jin-feng1, Huang Jia-xue1, 3, 4
- 1 School of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Nordic Bioscience (Beijing) Ltd., Beijing 102206, China
3 Union Stem Cell & Gene Engineering Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300384, China
4 Zhongyuan Union Stem Cell Bioengineering Stock Company, Tianjin 30050, China
摘要:
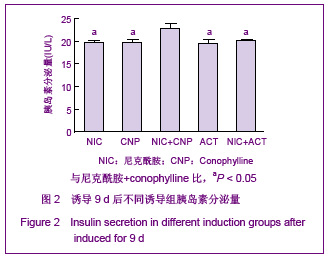
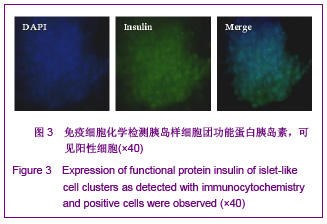
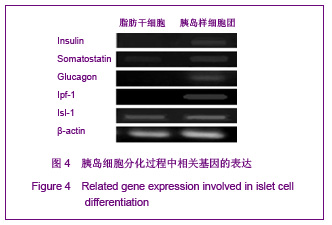
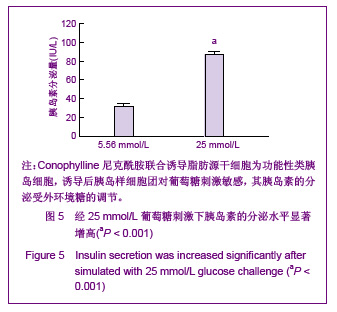
背景:1型糖尿病的胰岛移植治疗一直面临供体来源不足与免疫排斥两大关键问题,寻找一种自体来源的种子细胞通过组织工程方法制备类胰岛组织可以提供充足新型供体、降低异基因供体移植的不良反应。 目的:分析成人脂肪干细胞体外分化为对葡萄糖敏感、可分泌胰岛素的功能性胰岛样细胞团的能力,探索体外制备类胰岛组织的技术路线。 方法:首先分离纯化人体脂肪干细胞,采用新型植物诱导剂Conophylline与其他诱导因子的不同组合将脂肪干细胞诱导分化为胰岛样细胞团,观察不同组合的诱导分化效率,并利用特异性染色、RT-PCR,免疫细胞化学等方法对诱导分化后的细胞团在基因水平与蛋白水平上进行鉴定,最后用ELISA法检测细胞团在不同浓度葡萄糖刺激下胰岛素的分泌情况。 结果与结论:脂肪干细胞具有多能干细胞特性,可诱导分化为具有胰岛素分泌和葡萄糖浓度反应性类胰岛细胞团;Conophylline与尼克酰胺联合诱导可大幅度提高诱导分化效率。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)