中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (6): 974-979.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.06.005
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
庾佳佳1,汪新柱2,赵 琳1,孙 瑞1,闫雪萍3,张苍宇1,任广铁1,拓振合1
- 1兰州大学第二医院骨科,甘肃省兰州市 730030
2甘肃省中医院放射科,甘肃省兰州市 730050
3兰州大学口腔医学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000
Isolation, culture and osteogenic induction of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Yu Jia-jia1, Wang Xin-zhu2, Zhao Lin1, Sun Rui1,Yan Xue-ping2, Zhang Cang-yu1, Ren Guang-tie1, Tuo Zhen-he1
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China
2 Department of Radiology, Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
3 School of Stomatology, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
摘要:
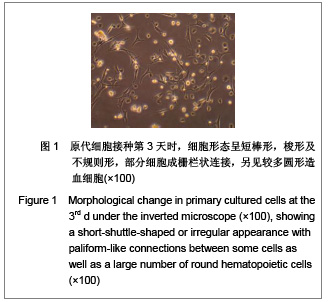
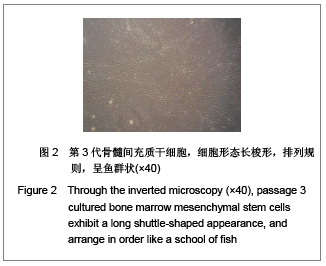
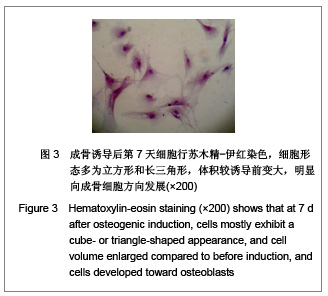
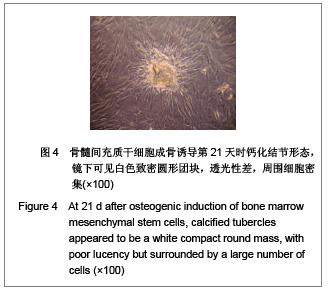
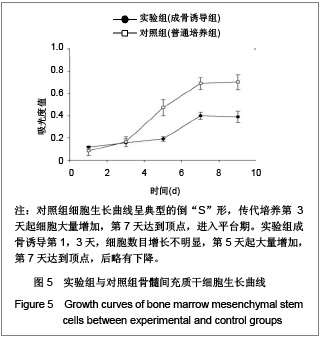
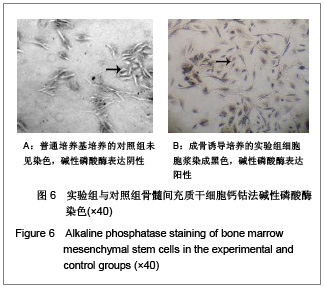
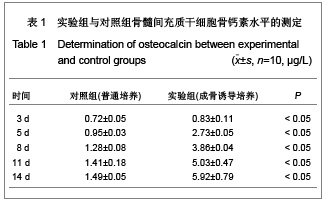
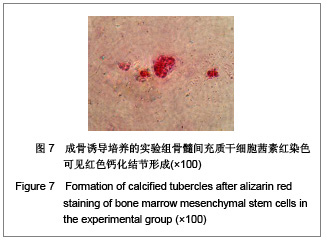
背景:骨髓间充质干细胞具有多向分化潜能,且可大量体外扩增培养,是重要的组织工程种子细胞。但尚无统一的体外培养及定向诱导方法。 目的:探讨体外定向诱导兔骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞的可行性。 方法:应用密度梯度离心法从兔四肢骨中分离纯化间充质干细胞,应用密度为1.073 g/mL的Percoll分离液,3 000 r/min×30 min离心,区别于相关报道的Ficoll分离液,2 000-2 500 r/min×(20-30) min离心以及全骨髓培养法体外扩增至第3代,分别在普通培养基(对照组)和成骨诱导培养基(实验组)中培养。 结果与结论:成功获得大量高纯度骨髓间充质干细胞。经成骨诱导后,实验组骨钙素含量明显高于对照组(P < 0.05)。实验组碱性磷酸酶和钙结节染色阳性,对照组均阴性。结果表明使用密度梯度离心法可成功建立兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养体系,骨髓间充质干细胞可定向诱导为成骨细胞。
中图分类号: