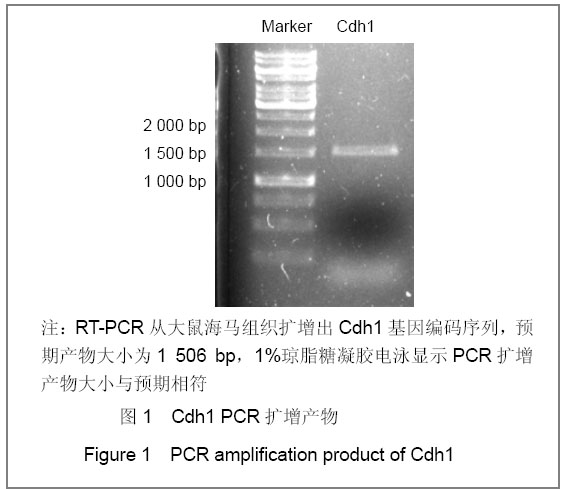
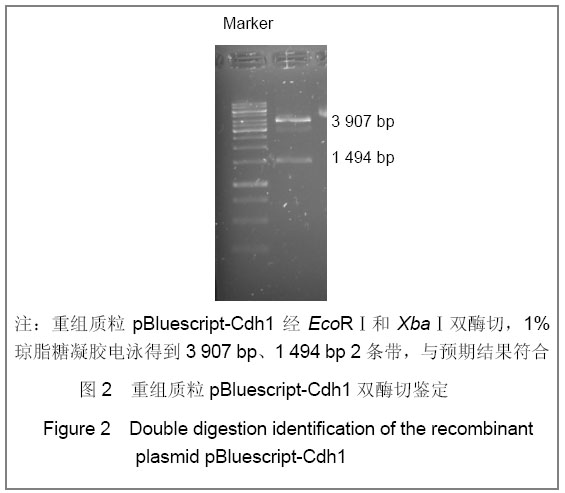
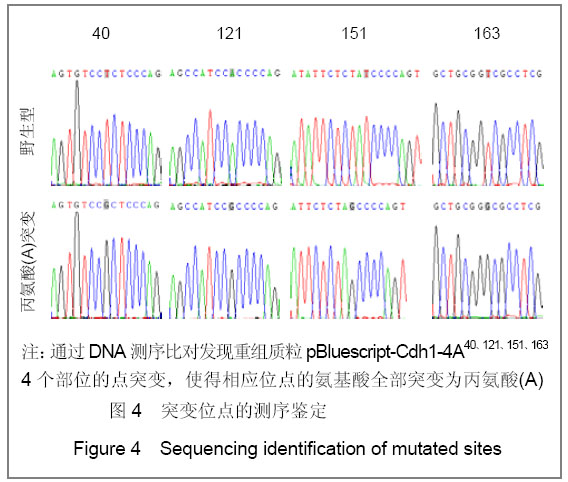
| [1] Konishi Y, Stegmuller J, Matsuda T, et al. Cdh1-APC controls axonal growth and patterning in the mammalian brain. Science. 2004; 303(5660):1026-1030.[2] van Roessel P, Elliott DA, Robinson IM, et al. Independent regulation of synaptic size and activity by the anaphase-promoting complex. Cell.2004; 119(5):707-718.[3] Juo P and Kaplan JM. The anaphase-promoting complex regulates the abundance of GLR-1 glutamate receptors in the ventral nerve cord of C. elegans. Curr Biol. 2004; 14(22): 2057-2062.[4] Almeida A, Bolanos JP, Moreno S. Cdh1/Hct1-APC is essential for the survival of postmitotic neurons. J Neurosci. 2005; 25(36):8115-8121.[5] Lasorella A, Stegmüller J, Guardavaccaro D, et al. Degradation of Id2 by the anaphase-promoting complex couples cell cycle exit and axonal growth. Nature. 2006; 442(7101):471-4.[6] Huynh MA, Stegmüller J, Litterman N,et al. Regulation of Cdh1-APC function in axon growth by Cdh1 phosphorylation. J Neurosci. 2009; 29(13):4322-7.[7] Yao WL,Zhang CH,Liu L,et al.Zhonghua Mazui Zazhi. 2008; 28(10):919-921.姚文龙,张传汉,柳璐,等.大鼠永生化神经前体细胞CDH1小干扰RNA真核载体的构建[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2008, 28(10):919-921.[8] Yao W, Qian W, Zhu C, et al.Cdh1-APC is involved in the differentiation of neural stem cells into neurons. Neuroreport. 2010; 21(1):39-44.[9] Qi YH,Qian W,Li P, et al. Disi Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2009; 30(15):1353-1356.祁月红,钱巍,李平,等.慢病毒介导RNA干扰Cdh1的表达对大鼠脊髓损伤的修复作用[J]. 第四军医大学学报,2009, 30(15): 1353-1356.[10] Yao WL,Zhang CH,Qian W,et al. Disi Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2009;30(13):1161-1165.姚文龙,张传汉,钱巍,等.APC-Cdh1在中枢神经系统中的表达分布特点[J].第四军医大学学报,2009, 30(13):1161-1165.[11] Harper JW, Burton JL, Solomon MJ. The anaphase-promoting complex: it's not just for mitosis any more. Genes Dev. 2002; 16(17): 2179-2206.[12] Gieffers C, Peters BH, Kramer ER, et al. Expression of the CDH1-associated form of the anaphase-promoting complex in postmitotic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999; 96: 11317-11322.[13] Puram SV, Bonni A. Novel functions for the anaphase-promoting complex in neurobiology. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011; 22(6):586-94.[14] Kim AH, Bonni A. Thinking within the D box: initial identification of Cdh1-APC substrates in the nervous system. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007; 34(3):281-7.[15] Liu L,Yao WL,Zhu C,et al.Disi Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2007;28(17):1544-1546.柳璐,姚文龙,祝畅,等.Cdh1小干扰RNA载体的构建及鉴定[J]. 第四军医大学学报,2007,28(17):1544-1546.[16] Peters JM. The anaphase-promoting complex: proteolysis in mitosis and beyond. Molecular Cell. 2002; 9(5):931-943. [17] Sullivan M and Morgan DO. Finishing mitosis, one step at a time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 8(11): 894-903.[18] Visintin R, Craig K, Hwang ES, et al. The phosphatase Cdc14 triggers mitotic exit by reversal of Cdk-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 1998; 2(6): 709-718.[19] Jaquenoud M, van Drogen F, Peter M. Cell cycle-dependent nuclear export of Cdh1p may contribute to the inactivation of APC/C(Cdh1). Embo J. 2002; 21(23): 6515-6526.[20] Allemandou F, Nussberger J, Brunner HR, et al. Rapid Site-Directed Mutagenesis Using Two-PCR-Generated DNA Fragments Reproducing the Plasmid Template. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2003; 2003(3):202-207. |