中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 296-300.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.02.020
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
人角质形成细胞Notch信号通路与转化生长因子β调控受体蛋白的作用
薛斯亮1,王晓珊2,李东川3,张 珏4, 5
- 1 四川大学华西医院皮肤科,四川省成都市 610041
2 四川省医学科学院四川省人民医院肿瘤科 四川省成都市 610041
3 成都市363医院妇产科,四川省成都市 610041
4 遵义医药高等专科学校,贵州省遵义市 563000
5 四川大学华西医院生物治疗国家重点实验室干细胞与组织工程研究室,四川省成都市 610041
Notch signal pathway effect on receptor protein regulation by transforming growth factor beta in primary human keratinocytes
Xue Si-liang1, Wang Xiao-shan2, Li Dong-chuan3, Zhang Jue4, 5
- 1 Department of Dermatology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
2 Department of Oncology, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China
3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the 363 Hospital of Chengdu City, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
4 Zunyi Medical and Pharmaceutical College, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
5 Division of Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
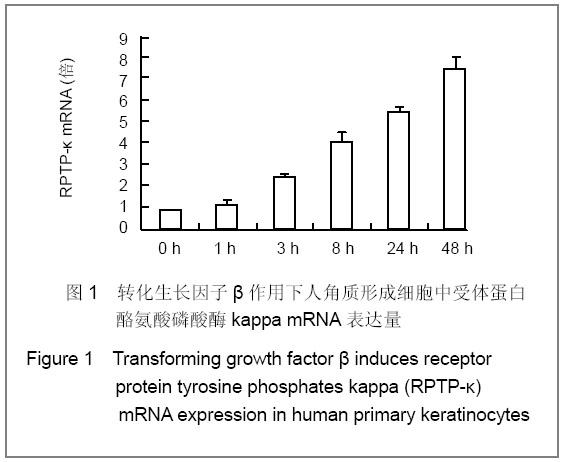
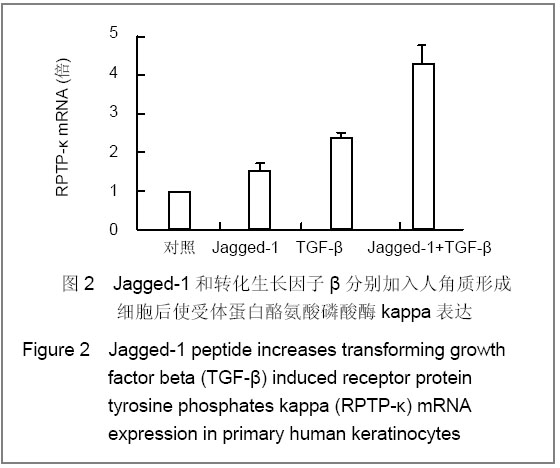
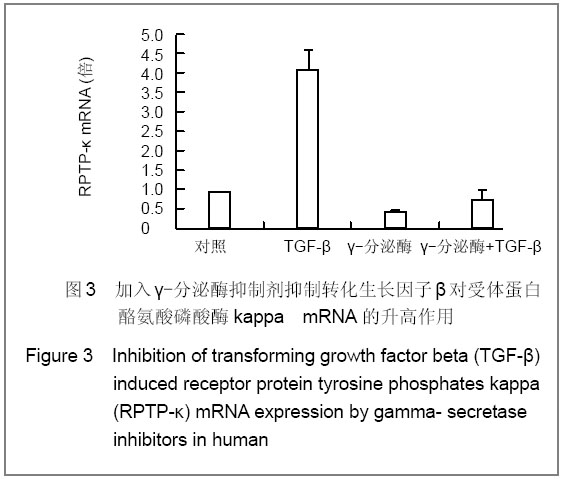
背景:在皮肤中受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa的调控至关重要,而转化生长因子β似乎是其调控的上游因子,既然Notch信号和转化生长因子β信号通道如此相关,那么Notch是不是也参加了转化生长因子β信号对受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa的调控呢? 目的:探讨Notch信号通道在人角质形成细胞中对转化生长因子β调控受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa的作用的影响。 方法:在分别用Jagged-1激活和用Γ-分泌酶抑制剂抑制Notch信号通道后,加入转化生长因子β,同时设立对照组,用Real-time PCR测试人角质形成细胞中受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa mRNA表达量。 结果与结论:覆盖率为40%的角质形成细胞在加入了转化生长因子β后,受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa mRNA量在各时间点均高于对照组。在用Jagged-1激活Notch通道的角质形成细胞中,单独加入Jagged-1、转化生长因子β及两者都加入时均高于对照组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01)。在用γ-分泌酶抑制剂抑制Notch通道的角质形成细胞中,只加入转化生长因子β显著高于对照组(P < 0.01),只加入γ-分泌酶抑制剂和两者均加入时与对照组比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。说明加入转化生长因子β导致角质形成细胞中受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa表达增加,而分别对Notch信号进行激活和抑制后发现,受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa信号分别显著增加和显著被抑制。所以在转化生长因子β升高受体蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶kappa表达过程中Notch信号通道是非常重要且不可或缺的。
中图分类号: