2.1 Notch信号通路 Notch信号通路是一种多细胞生物发育过程中进化上保守的信号传导途径,在许多生物的胚胎和出生后的发育中起重要作用,该途径具有高度的多效性,影响器官发育的过程以及成人干细胞自我更新的调节,从而维持组织稳态。然而,由于其多功能性,该途径易受信号分子异常激活的影响,并且与多种人类疾病相关,包括各种发育综合征和恶性肿瘤[9]。近年来,Notch信号通路已成为开发新型治疗策略最重要的潜在目标之一。
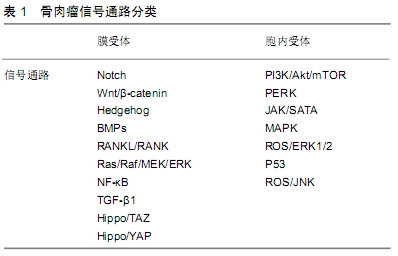
Notch信号通路家族由4个受体组成,称为Notch-1至Notch-4,以及5个Delta样配体,分别为Jagged-1,Jagged-2和Delta-like-1,Delta-like-3,Delta-like-4。Notch受体在与相邻细胞表面上呈现的同源配体结合后经历2次连续的蛋白水解切割。配体和Notch受体之间的相互作用导致金属蛋白酶肿瘤坏死因子α转换酶(TACE)在受体细胞外区域的切割,然后由早老素1组成的γ-分泌酶复合物切割跨膜结构域。因此,Notch细胞内结构域(Notch ICD,NICD)从质膜释放并易位至细胞核。在细胞核中,NICD与RBPJ和Mastermind-Like(MAML)相互作用,取代由RBPJ结合的共抑制因子复合物,将RBPJ转化为转录激活因子[5],见图1。
在人和动物的研究中已经证实Notch信号传导与肿瘤进展的关键步骤相关联。在骨肉瘤样本中分析Notch通路基因的表达,与正常人相比,其中NOTCH2、JAG1、HEY1和HEY2上调而NOTCH1和DLL1下调。同样,与人成骨细胞相比,人骨肉瘤细胞中NOTCH1、JAG1、HES1和HEY1的表达显著升高。来自p53杂合小鼠的骨肉瘤肿瘤的转录分析显示,Jag2,Hes1,Hey1和Dll4表达明显升高[10]。
大约30%的局限性骨肉瘤患者和80%的转移性骨肉瘤患者会复发。与正常成骨细胞或非转移性骨肉瘤细胞相比,Notch通路基因表达分析显示,在转移性骨肉瘤细胞系中鉴定出Notch1、Notch2、Dll1和Hes1高表达[11]。一项关于HES1在人骨肉瘤标本上表达的回顾性研究显示,HES1水平与患者生存率呈负相关[12]。
研究已经证明了Notch信号通路与骨肉瘤的耐药性、侵袭性和转移潜能的关联性,该关联已经在各种实验模型中得到验证,包括骨肉瘤人或小鼠细胞系,体内小鼠或犬模型,以及患者样本。所有这些研究表明,具有较高转移潜能的骨肉瘤细胞具有较高的Notch受体基础水平,尤其是Notch-1、Notch-2、Notch配体(Dll-1/ Jagged-1)和Notch靶基因,例如hey-1与正常成骨细胞或非转移性骨肉瘤细胞系相比表达更高[13]。这些Notch信号传导相关基因或蛋白质的较高表达水平显示与侵袭性和转移相关,影响骨肉瘤患者存活。还有报道Notch信号传导与醛脱氢酶(ALDH)活性增加有关,其导致鼠骨肉瘤细胞系(K7M2和K12)中的侵袭性转移表型增加,通过抑制Notch信号通路从而消除K7M2细胞中升高的醛脱氢酶活性,从而减少转移的发生。因此,通过使用γ-分泌酶抑制剂来消除hey-1、hes-1、Notch-1和Jagged-1的表达,也消除了它们对骨肉瘤的存活、骨转移和侵袭性的直接或间接影响。这些发现表明,在各个节点抑制Notch信号可能是预防骨肉瘤侵袭和转移的新型治疗策略[14]。
Notch还影响骨肉瘤的生长,已经发现Notch1受体、Jagged-1配体以及Notch靶转录因子HES-1和HEY-2在骨肉瘤原发性肿瘤中上调,通过使用γ-分泌酶抑制剂抑制Notch蛋白水解切割,减少SaOS-2骨肉瘤细胞的增殖,并且Notch抑制也减少了体内裸鼠移植瘤的生长。Notch抑制已被证实促进G1停滞,下调细胞周期启动子和上调p21,特别是Notch改变似乎影响骨肉瘤的侵袭和转移,Notch抑制也通过γ-分泌酶阻断,降低骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭性,且呈剂量依赖性[15]。
Notch信号通路还与骨肉瘤干细胞相关,通过体内外实验研究发现,顺铂可通过Notch信号传导诱导骨肉瘤干细胞样细胞的富集,靶向失活Notch信号通路可用于消除骨肉瘤干细胞和降低耐药性。
Notch信号的激活有助于了解人类骨肉瘤的发病机制,其抑制可能为骨肉瘤或相关的间充质肿瘤提供特异性治疗。尽管主要信号通路中存在这些成分,但许多其他基因的异常表达与人骨肉瘤有关,并最终可用于作为诊断和评估预后的标志物。值得注意的是,目前关于骨肉瘤的研究大多是使用人类骨肉瘤细胞系和/或骨肉瘤组织,其在晚期诊断已经累积了复杂的分子细胞遗传学改变[16]。将来,在基因工程小鼠模型中研究骨肉瘤将使人们更清楚地了解人类骨肉瘤的分子发病机制。
目前对骨肉瘤患者进行个体化Notch信号通路靶向治疗方案认知还不完善,随着人们研究的深入,Notch信号通路作为骨肉瘤治疗的新靶点将具有广阔的应用前景。
目前已经发现Notch信号通路和BMPs信号通路均在骨发育及重建中发挥重要的作用,两种信号通路相互关联、相互作用,Notch信号可通过促进BMP2/4/9表达诱导的间充质干细胞早晚期成骨分化。迄今已鉴定出20多种BMP,它们属于细胞因子的转化生长因子β超家族,BMP具有不同的细胞功能,但主要与骨生成有关,特别是与骨的分化有关。BMP信号传导成分与骨肉瘤发展和预后相关。体外研究表明,大多数骨肉瘤细胞系表达多种BMP配体,然而骨肉瘤组织中BMP配体的差异表达,与骨肉瘤组织学亚型之间尚未检测出显著相关性[17]。研究表明,过表达BMP家族成分和受体,与骨肉瘤肿瘤中的转移表型及不良预后之间有相关性。另一方面,对高级别骨肉瘤的不同研究显示BMP信号活性受限,这与低生存率具有相关性[18]。BMP-2的升高与骨肉瘤干细胞中VEGF、EMMPRIN和MMP-9的过度表达有关;相反,BMP-2下调Oct3/4、Sox2和Nanog在骨肉瘤细胞中的表达,致瘤性降低,可能与其抑制骨肉瘤干细胞的增殖有关。总体而言,BMP的确切作用(包括它作为骨肉瘤的预测指标)尚未明确,还需进一步深入研究。
2.2 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 Wnt是一种高度保守的信号通路,在人类发育和肿瘤发生中起重要作用,Wnt信号传导的异常激活与许多常见的人类肿瘤有关,且与骨肉瘤的发生发展密切相关。Wnt信号传导激活细胞存在许多转导级联,这些级联包括Wnt/β-catenin依赖性途径和β-catenin非依赖性途径。
在人骨肉瘤主要组织和细胞系中已经报道了Wnt/β-catenin途径的改变,特别是涉及β-catenin。在人类骨肉瘤组织中,β-catenin的表达显著高于正常组织、骨样骨瘤、成骨细胞瘤或新生骨。与人胎儿成骨细胞相比,人类骨肉瘤细胞系中Wnt/β-catenin途径的主要成分(包括Wnt3a,β-catenin和Lef1)表达上调[19]。经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中成分的异常表达表明Wnt/β-catenin信号传导在骨肉瘤发生中发挥着作用。
Wnt/β-catenin信号传导途径将来自细胞外受体的信号传递,通过细胞质并最终传递至细胞核,从而导致靶基因的表达[20]。通过Wnt配体与卷曲蛋白(FZL)受体和低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/6(LRP5/6)受体形成复合物结合激活该途径,散乱蛋白(Dsh)抑制这种多蛋白复合物的活性,该复合物还含有轴抑制蛋白质(Axin)、APC和糖原合成酶激酶3β(GSK3β),在细胞内传递配体-受体相互作用。在不存在合适配体的情况下,该复合物促进细胞内信号分子β-catenin的蛋白降解。β-catenin是经典Wnt途径中必需的,也是唯一的非多余成分,参与控制干细胞的增殖、分化和迁移[21]。
Wnt/β-catenin途径参与骨肉瘤的转移性机制。在骨肉瘤的转移过程中,Wnt/β-catenin途径促进骨肉瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移,并且β-catenin充当骨肉瘤的生物标志物,具有转移至肺的潜力。Wnt/β-catenin通路在骨肉瘤发生和转移过程中受多种因素的调节,包括激素和碱性磷酸酶。Wnt受体LRP5的表达与骨肉瘤的转移性相关,并且使用该受体的显性失活形式抑制LRP5,也可抑制肿瘤细胞的运动和侵袭[22]。因此,LRP5在促进骨肉瘤转移中起重要作用。
Wnt/β-catenin通路可作为骨肉瘤预后、转移的生物学标志物,80%的骨肉瘤患者发生复发和/或转移,局限性疾病的5年生存率约为80%,但如果存在转移性病变则下降至约30%。因此,转移性预测在设计治疗策略中是非常重要的。β-catenin被用作骨肉瘤向肺转移潜能的生物学标记[23]。
Wnt/β-catenin途径参与骨肉瘤化疗耐药性,尤其是对标准化疗中使用的所有3种药物的耐药性,即阿霉素、顺铂和甲氨蝶呤(MTX)。总之,这些发现表明Wnt/β-catenin途径在骨肉瘤发展和化疗反应中的作用是显著的,它可以促进骨肉瘤发展、转移和对化疗的耐药性[24]。因此,抑制或调节该途径将是新骨肉瘤治疗的有希望的靶标。
Wnt/β-catenin途径的激活还与肿瘤干细胞相关,可能导致骨肉瘤的复发,特别是Wnt/β-catenin的激活不仅与肿瘤干细胞群的存在相关,而且与化疗后骨肉瘤细胞中肿瘤细胞表型的转变相关,从而暗示该机制赋予药物耐药性。
对于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的分子靶向治疗还有待进一步研究,但随着人们对Wnt/β-catenin信号通路研究的深入,靶向干预Wnt信号通路将成为治疗肿瘤的新希望。
2.3 Hedgehog信号通路 最近研究显示hedgehog信号通路参与骨肉瘤的发病机制,靶向hedgehog信号传导抑制剂作为新的分子靶向药物引起了极大的关注。
现有数据表明,异常hedgehog信号传导具有促迁移作用,并导致成骨细胞向骨肉瘤的发展。已经在骨肉瘤细胞系中以及在原发性人骨肉瘤样本中观察到hedgehog信号传导的激活[25]。新的数据表明,抑制剂对hedgehog信号转导的干预可以抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖和肿瘤生长,从而防止骨肉瘤发生[26]。近年来,hedgehog信号通路已成为许多类型肿瘤发生、发展和转移的关键决定因素。异常激活hedgehog信号传导影响关键的致瘤过程,如肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭和进展[27]。
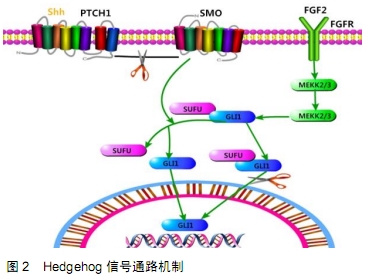
Hedgehog被发现是多种癌症发展和进展的关键因素,该途径是独特的,因为它由肿瘤抑制基因和癌基因组成。该信号通路的组成元件主要包括HH配体(SHH,IHH,DHH)、十二跨膜蛋白Patched(PTCH1和PTCH2)和七跨膜蛋白Smoothed(SMO)组成的受体复合物、核转录因子GLI家族(GLI1,GLI2,GLI3)和下游靶基因等。在经典途径中,配体将与PTCH1结合,从而激活SMO;SMO反过来可以激活GLI家族锌指蛋白的下游转录因子。如果不存在配体,PTCH将阻止SMO的进入,SMO不能在功能上抑制蛋白激酶,包括PKA,GSK-3β和CK1。因此,蛋白激酶可以使与SUFU复合的GLI蛋白磷酸化并引起GLI的蛋白水解切割。GLI的切割导致形成抑制形式的GLI,其将易位至细胞核并关闭信号传导[28],见图2。
研究表明,SMO和GLI激活对骨肉瘤进展至关重要。HIROTSU等[29]确定SHH、DHH、PTCH1、GLI1、GLI2和SMO在5种不同的骨肉瘤细胞系中过表达,推测GLI1的启动子在人骨肉瘤标本中失活,GLI2介导下游SMO的活性,因此,GLI1在骨肉瘤中下调,而GLI2上调。SATO等[30]研究表明GLI2参与了肿瘤的侵袭和转移,与没有GLI2被敲低的小鼠相比,通过转染GLI2-shRNA而被敲低的小鼠中肿瘤生长受到抑制。
高表达Hedgehog可能导致肿瘤体积更大,这是骨肉瘤的预后因素,从而表明Hedgehog信号激活是骨肉瘤进展所需的。最近的研究表明SMO和GLI活化是骨肉瘤进展中的重要组成部分[31]。
Hedgehog通路已被证明可参与骨肉瘤干细胞的调节,它们与干细胞的启动和调节有关,通过膜受体激活GLI来调节下游基因的表达,例如PTCH和Smoothened。
在不同类别的Hedgehog抑制剂中,最近的药物开发集中于SMO抑制剂影响骨肉瘤发展中的作用。尽管已经开发了许多Hedgehog途径抑制剂,但它们都没有成功地进入临床治疗骨肉瘤。由于激活Hedgehog途径不是恶性肿瘤的主要驱动因素,临床试验可能需要与其他信号传导通路抑制剂联合治疗。Hedgehog抑制剂有可能成为一种有前景的药物选择,但是为了探索靶向Hedgehog信号传导途径在骨肉瘤中的治疗潜力,仍然需要了解Hedgehog途径抑制的生物学效应。
2.4 PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路 PI3K/Akt/mTOR途径对细胞稳态非常重要,在调节细胞生长、自噬、增殖和细胞生理学等方面发挥重要作用,它被认为是人类肿瘤中最重要的致癌途径之一。这种级联的蛋白激酶已经涉及各种肿瘤类型,并且还有越来越多的证据表明PI3K/Akt/mTOR对骨肉瘤的进展和治疗有靶向作用。该途径在骨肉瘤中经常过度活化并且有助于疾病的发生和发展,包括肿瘤发生、增殖、侵袭、细胞周期进展、细胞凋亡的抑制、血管生成、转移和化学耐药性。通过小分子化合物抑制该途径,是一种很有吸引力的潜在治疗骨肉瘤的方法[32]。探索PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路在骨肉瘤发生和发展中的作用,将有助于进一步了解骨肉瘤的发病机制并设计后续治疗策略。
PI3K/Akt/mTOR途径的失调对肿瘤细胞特性可产生多效作用,它能影响肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭和转移,还能影响细胞的凋亡和周期调节;除此之外,还对肿瘤的血管生成和化疗药耐药有作用[33]。PERRY等[33]对9个肿瘤与正常对照组全基因组测序显示,PI3K/Akt/mTOR是骨肉瘤中发生改变最常见的途径,观察到PTEN,TSC2,PI3KCA,PDPK1,AKT1和EIF4B基因突变,而在体内全基因组汇集的shRNA筛选分析表明mTOR和PI3KCA对于骨肉瘤增殖和存活至关重要。此外,mTOR抑制剂雷帕霉素可减轻骨肉瘤细胞增殖,但与单独靶向PI3K或mTOR相比,原代小鼠和人类骨肉瘤细胞培养物中PI3K和mTOR的双重抑制能够诱导细胞凋 亡[34]。研究表明,通过抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路,可诱导骨肉瘤干细胞中G0/G1细胞周期停滞和凋亡。靶向PI3K/Akt/mTOR途径可能对骨肉瘤具有促凋亡和抗增殖作用,然而还需要进一步的临床研究。
2.5 RANKL/RANK信号通路 RANK信号传导对于通过旁分泌与成骨细胞产生的配体RANKL相互作用调节破骨细胞分化,这种特殊的信号通路在病理机制中很重要,并且已经在骨肉瘤中发挥作用[35]。RANK在人类骨肉瘤细胞系和人体组织中表达,并且在RANKL刺激后诱导激活下游信号分子。RANKL表达增加也与患者术前化疗反应差、降低无癌生存率有关[36]。另一方面,RANK在转基因小鼠骨肉瘤模型的肿瘤组织中表现出多重表达。RANK信号传导不影响细胞增殖,但在小鼠模型的原代骨肉瘤细胞中可诱导细胞运动和促进非依赖性生长[37]。
在模拟人骨肉瘤的基因组小鼠模型中,有38%的肿瘤中鉴定出含有Prkar1a基因的11qE1缺失,Prkar1a是骨肉瘤中下调的肿瘤抑制因子,从而驱动RANKL过表达;进一步实验证明RANKL介导的信号传导促进骨肉瘤的发展,而仅在破骨细胞中对RANKL的特异性抑制消除了这种效应[38]。目前靶向RANKL/RANK信号通路药物已在临床试验中观察到疗效,包括绝经后骨质疏松症、多发性骨髓瘤和转移性骨病等,然而对RANKL的长期抑制是否有不良反应仍有待阐明。
2.6 Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK信号通路 Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK和PI3/AKT是实体瘤恶性肿瘤中改变最多的信号传导途径。YE等[39]支持MEK在骨肉瘤侵袭性中的作用,MEK的过表达与骨肉瘤的生长和转移有关。免疫组化染色显示小鼠原发性肿瘤中AKT、p38 MAPK、IGF-1R和MEK的总蛋白阳性表达。然而,在原发性和转移性肿瘤中仅通过免疫组织化学观察到磷酸化的MEK。此外,当MEK途径用MAPK/ERK抑制剂U0126靶向时,骨肉瘤细胞的体外侵袭能力降低。因此,新的靶向治疗可能与Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK信号通路有关,这可能会减弱骨肉瘤的侵袭性。YU等[40]通过免疫组织化学检测原位143B小鼠骨肉瘤模型样品中信号因子的变化,用Matrigel测定法评估干扰下的细胞侵袭能力。结果显示:与对照相比,用MEK/ERK抑制剂U0126处理的143B细胞具有更低的体外侵袭能力,Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK可能在骨肉瘤肺转移中起重要作用,并且其特异性抑制剂靶向MEK/ERK可能在骨肉瘤的治疗中具有潜在用途。Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK信号通路在骨肉瘤的发生和发展中起重要作用,在信号传导途径中关键信号的抑制剂是治疗骨肉瘤的新策略,这些抑制剂的筛选及其体外和体内研究已成为该治疗领域的热点。