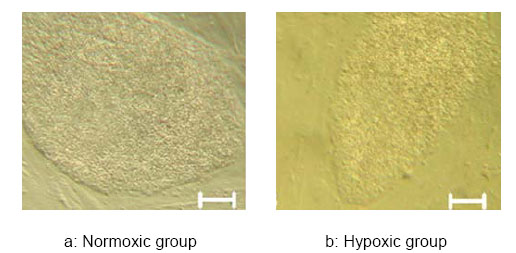
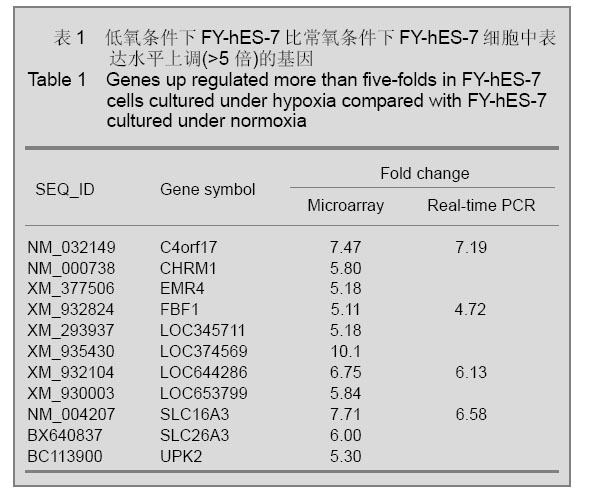
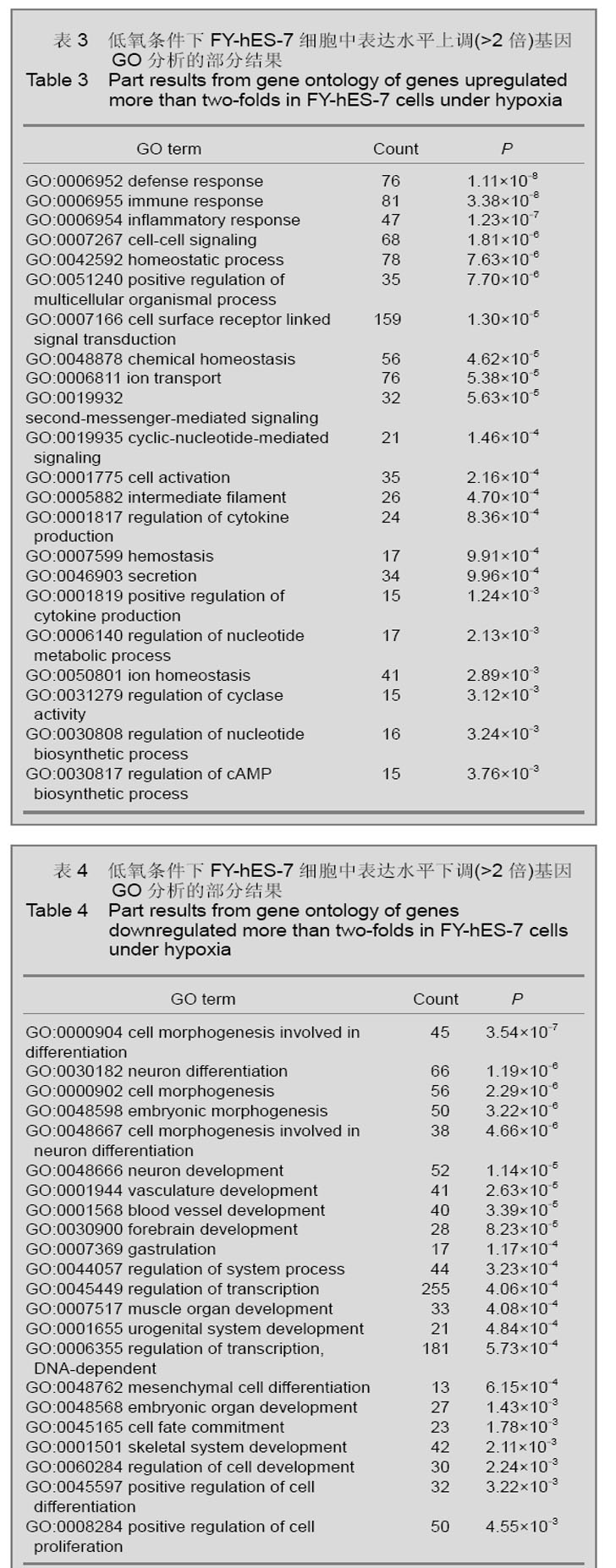
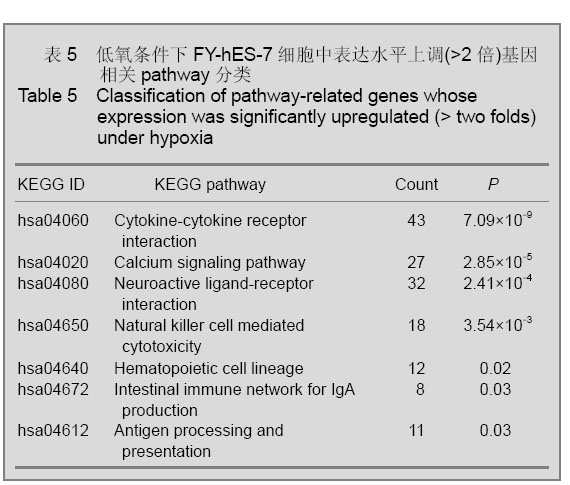
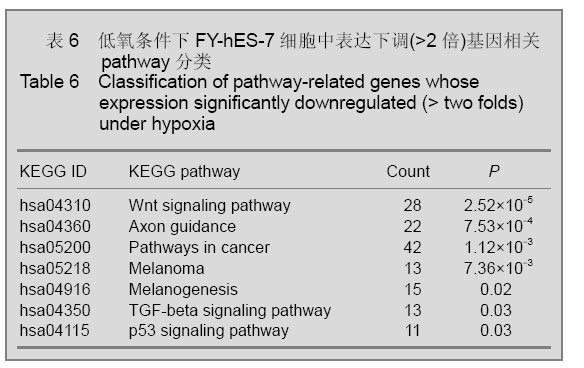
| [1] Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282(5391):1145-1147.[2] Westfall SD, Sachdev S, Das P, et al. Identification of oxygen-sensitive transcriptional programs in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(5):869-881.[3] Forristal CE, Wright KL, Hanley NA, et al. Hypoxia inducible factors regulate pluripotency and proliferation in human embryonic stem cells cultured at reduced oxygen tensions. Reproduction. 2010;139(1):85-97.[4] Cowan CA, Klimanskaya I, McMahon J, et al. Derivation of embryonic stem-cell lines from human blastocysts. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(13):1353-1356.[5] Forsyth NR, Musio A, Vezzoni P, et al. Physiologic oxygen enhances human embryonic stem cell clonal recovery and reduces chromosomal abnormalities. Cloning Stem Cells. 2006;8(1):16-23.[6] Lim HJ, Han J, Woo DH, et al. Biochemical and morphological effects of hypoxic environment on human embryonic stem cells in long-term culture and differentiating embryoid bodies. Mol Cells. 2011;31(2):123-132.[7] Millman JR, Tan JH, Colton CK. The effects of low oxygen on self-renewal and differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2009;14(6):694-700.[8] Zachar V, Prasad SM, Weli SC, et al. The effect of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) long-term normoxic and hypoxic cultures on the maintenance of pluripotency. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010;46(3-4):276-283.[9] Ezashi T, Das P, Roberts RM. Roberts, Low O2 tensions and the prevention of differentiation of hES cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(13):4783-4788.[10] Prasad SM, Czepiel M, Cetinkaya C, et al. Continuous hypoxic culturing maintains activation of Notch and allows long-term propagation of human embryonic stem cells without spontaneous differentiation. Cell Prolif. 2009;42(1):63-74.[11] Forsyth NR, Kay A, Hampson K, et al. Transcriptome alterations due to physiological normoxic (2% O2) culture of human embryonic stem cells. Regen Med. 2008;3(6): 817-833.[12] Simon MC, Keith B. The role of oxygen availability in embryonic development and stem cell function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(4):285-296.[13] Sun X, Long X, Yin Y, et al. Similar biological characteristics of human embryonic stem cell lines with normal and abnormal karyotypes. Hum Reprod. 2008;23(10):2185-2193.[14] Chen HF, Kuo HC, Chen W, et al. A reduced oxygen tension (5%) is not beneficial for maintaining human embryonic stem cells in the undifferentiated state with short splitting intervals. Hum Reprod. 2009;24(1):71-80.[15] Huang da W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44-57.[16] Moon SH, Kim SW, Kim JS, et al. Gene expression profiles in CHA3 and CHA4 human embryonic stem cells and embryoid bodies. Mol Cells. 2011;31(4):315-326.[17] Zhao M, Ren CP, Yang H, et al. Shengming Kexue Yanjiu. 2008;12(1):61-65.赵明,任彩萍,杨红,等.人胚胎干细胞和拟胚体基因表达谱的初步分析[J].生命科学研究,2008,12(1):61-65.[18] Rocha S. Gene regulation under low oxygen: holding your breath for transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32(8): 389-397. |