中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 736-740.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1928
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
老年糖尿病患者的足底压力及步态特征
卜月丽1,王 芳1,2,张建国1,2,李晓林1,曹子君1,李雪梅3
- 1天津科技大学机械工程学院,天津市 300222;2天津市轻工与食品工程机械装备集成设计与在线监控重点实验室,天津市 300222;3天津医科大学代谢病医院,天津市 300070
Plantar pressure and gait characteristics in older adult patients with diabetes
Bu Yueli1, Wang Fang1, 2, Zhang Jianguo1, 2, Li Xiaolin1, Cao Zijun1, Li Xuemei3
- 1College of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University of Science & Technology, Tianjin 300222, China; 2Tianjin Key Laboratory of Integrated Design and Online Monitoring for Light Industry & Food Machinery and Equipment, Tianjin 300222, China; 3Metabolic Disease Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
摘要:

文题释义:
老年糖尿病患者:糖尿病指以慢性高血糖为特征的代谢性疾病,是一种广泛流行于全世界的慢性疾病。老年糖尿病患者是指年龄≥60周岁的糖尿病患者。
足底压力:具体指当人体处于静止站立或动态行走的状态时,足部受到一个在竖直方向上来自地面的反作用力,这个力就被称为足底压力。
背景:研究表明,足底压力是糖尿病足溃疡的主要危险因素之一。
目的:探讨老年糖尿病患者自然步态下足底压力特征及差异性,为老年患者足部的监测和足部减压产品设计提供数据支撑。
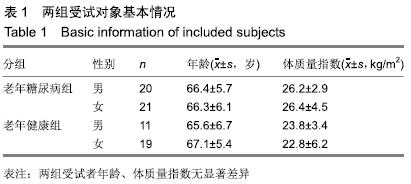
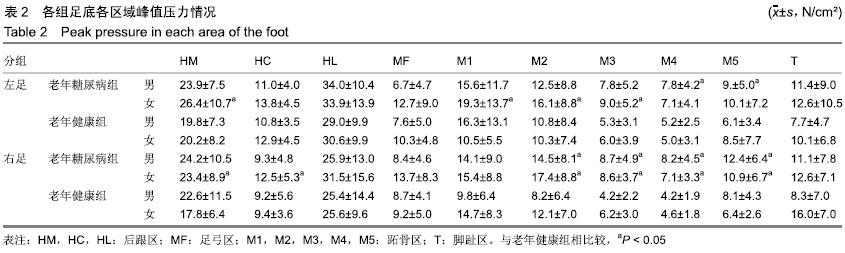
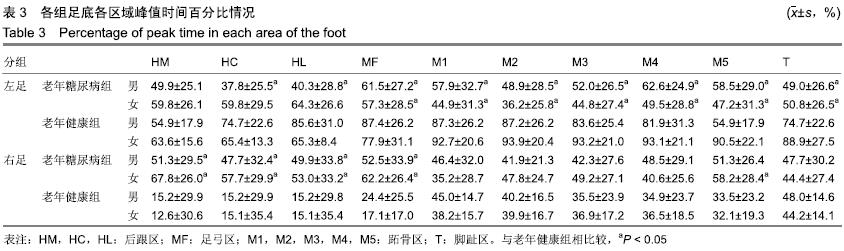
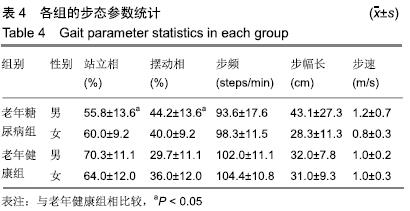
方法:研究方案的实施符合天津医科大学代谢病医院对研究的相关伦理要求,所有受试者均对试验过程完全知情同意。通过鞋垫式足底压力检测系统对年龄≥60周岁的41位老年糖尿病患者和30位老年健康者自然步态下的足底压力进行检测。观察足部峰值压力、峰值时间百分比、X偏移量、Y偏移量、包络压力中心点95%椭圆置信面积、步频、步速、步幅长、站立相、摆动相。
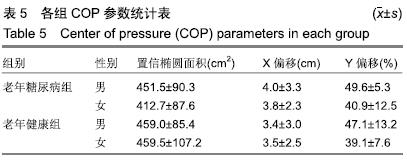
结果与结论:①与老年健康组相比,老年糖尿病组峰值压力集中在第2-4跖骨区显著增大,左足多数足区峰值时间百分比减小,右足足跟区、中足区峰值时间百分比增大(P < 0.05);②与老年健康组相比,老年糖尿病组站立相降低,摆动相升高,步频降低,男性步幅长增大,步速加快,女性步幅长减小,步速减慢;③老年糖尿病组包络压力中心点95%椭圆置信面积较老年健康组呈减小趋势,老年糖尿病组X、Y偏移量大于老年健康组;④结果说明:老年糖尿病患者身体稳定性和灵活性较正常老年人降低,足底压力明显由足跟向跖骨部位转移,在足部护理中需加强对跖骨区足底压力的重视。ORCID: 0000-0001-5815-4684(卜月丽)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: