| [1] Fan B, Wei Z, Yao X, et al. Microenvironment Imbalance of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):853-866.[2] Ahuja CS, Nori S, Tetreault L, et al. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury- Repair and Regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80(3S):S9-S22.[3] Furlan JC, Fehlings MG. The impact of age on mortality, impairment, and disability among adults with acute traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(10):1707-1717.[4] Wu Q, Li YL, Ning GZ, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic cervical spinal cord injury in Tianjin, China. Spinal Cord. 2012;50(10): 740-744.[5] Raspa A, Pugliese R, Maleki M, et al. Recent therapeutic approaches for spinal cord injury. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2016;113(2): 253-259.[6] Lee N, Rydyznski CE, Rasch MS, et al. Adult ciliary neurotrophic factor receptors help maintain facial motor neuron choline acetyltransferase expression in vivo following nerve crush. J Comp Neurol. 2017;525(5): 1206-1215.[7] Cen LP, Liang JJ, Chen JH, et al. AAV-mediated transfer of RhoA shRNA and CNTF promotes retinal ganglion cell survival and axon regeneration. Neuroscience. 2017;343:472-482.[8] Yin DP, Chen QY, Liu L.Synergetic effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor and olfactory ensheathing cells on optic nerve reparation (complete translation).Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(6):1006-1012.[9] Lee N, Serbinski CR, Braunlin MR, et al. Muscle and motor neuron ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor α together maintain adult motor neuron axons in vivo. Eur J Neurosci. 2016;44(12):3023-3034.[10] Gu Y, Wang J, Ding F, et al. Neurotrophic actions of bone marrow stromal cells on primary culture of dorsal root ganglion tissues and neurons. J Mol Neurosci. 2010;40(3):332-341.[11] Wen SY, Li AM, Mi KQ, et al.In vitro neuroprotective effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor on dorsal root ganglion neurons with glutamate- induced neurotoxicity.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(10):1716-1723.[12] Feng GY, Liu J, Wang YC, et al. Effects of Alpha-Synuclein on Primary Spinal Cord Neurons Associated with Apoptosis and CNTF Expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(5):817-829.[13] Yao R, Murtaza M, Velasquez JT, et al. Olfactory Ensheathing Cells for Spinal Cord Injury: Sniffing Out the Issues. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6): 879-889.[14] Wright AA, Todorovic M, Tello-Velasquez J, et al. Enhancing the Therapeutic Potential of Olfactory Ensheathing Cells in Spinal Cord Repair Using Neurotrophins. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):867-878.[15] Haggerty AE, Maldonado-Lasunción I, Oudega M. Biomaterials for revascularization and immunomodulation after spinal cord injury. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(4):044105.[16] Nakhjavan-Shahraki B, Yousefifard M, Rahimi-Movaghar V, et al. Transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells on functional recovery and neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury; systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):325.[17] Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC, et al. MASCIS evaluation of open field locomotor scores: effects of experience and teamwork on reliability. Multicenter Animal Spinal Cord Injury Study. J Neurotrauma. 1996;13(7): 343-359.[18] 岳妍,谭波涛,刘媛,等. FTY720对急性脊髓损伤大鼠神经功能及血脊髓屏障的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2015,40(3): 200-205.[19] Stevens RD, Bhardwaj A, Kirsch JR, et al. Critical care and perioperative management in traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2003;15(3):215-229.[20] Lang-Lazdunski L, Heurteaux C, Mignon A, et al. Ischemic spinal cord injury induced by aortic cross-clamping: prevention by riluzole. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2000;18(2):174-181.[21] Yu WR, Liu T, Fehlings TK, et al. Involvement of mitochondrial signaling pathways in the mechanism of Fas-mediated apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;29(1):114-131.[22] Manthorpe M, Skaper SD, Williams LR, et al. Purification of adult rat sciatic nerve ciliary neuronotrophic factor. Brain Res.1986; 367(1-2): 282-286.[23] 习杨彦彬,王廷华. CNTF基因在正常大鼠和猫脊髓组织中的表达[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2006, 27(6):34-37.[24] 曾洪艳,李力燕,郭小兵,等. 神经营养因子、凋亡相关因子和轴突导向因子在大鼠神经管畸形发育中的表达[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2012, 33(11):13-18.[25] Tripathi RB, McTigue DM. Chronically increased ciliary neurotrophic factor and fibroblast growth factor-2 expression after spinal contusion in rats. J Comp Neurol. 2008;510(2):129-144.[26] Yetiser S, Kahraman E. An analysis of time-dependent changes of neurotrophic factors (BDNF, CNTF) in traumatic facial nerve injury of a nerve-cut and nerve-crush model in rats. Otol Neurotol. 2008; 29(3): 392-396.[27] Santos MD, Yasuike M, Kondo H, et al. A novel type-1 cytokine receptor from fish involved in the Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (Jak/STAT) signal pathway. Mol Immunol. 2007;44(13): 3355-3363.[28] 陈珊珊,郭小兵,金华.动脉移植BMSCs对大鼠缺血再灌注损伤脊髓CNTF和STAT3的影响[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志,2014, 31(6):492-496.[29] 李越,余化霖,陈莉发,等. 嗅球成鞘细胞植入大鼠挫伤脊髓内的迁移分布特征[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2011, 27(1):78-82.[30] 姜泳,迟晓飞,邹喜军,等. 重复经颅磁刺激联合嗅鞘细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(1):98-102.[31] 布林,郑鸿,姜汉国,等. 移植神经生长因子和脑衍生神经生长因子基因修饰的嗅鞘细胞对脊髓损伤后细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2005, 9(18):124-125. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
睫状神经营养因子:作为一种神经营养因子,对颅内损伤后视神经纤维的再生具有关键作用,可通过释放有丝分裂因子,促进有丝分裂后神经元的存活以及未成熟背根神经节神经元的发生与分化;此外,过表达睫状神经营养因子对于脊髓损伤也具有一定的保护作用。
嗅鞘细胞:是一种特殊的胶质细胞,具有神经营养、抑制胶质增生等作用,为轴突生长提供了适宜的环境,能够促进中枢神经元再生。嗅鞘细胞移植用于治疗脊髓损伤已经多有报道,但其效果有限以及作用机制尚不清晰,同时也存在一些不足之处,如目前无论是动物实验或是临床试验主要都是嗅球源性嗅鞘细胞,需要加大嗅黏膜源性嗅鞘细胞的研究应用力度,解决来源问题或者建立嗅鞘细胞系为后续的研究提供便捷。
文题释义:
睫状神经营养因子:作为一种神经营养因子,对颅内损伤后视神经纤维的再生具有关键作用,可通过释放有丝分裂因子,促进有丝分裂后神经元的存活以及未成熟背根神经节神经元的发生与分化;此外,过表达睫状神经营养因子对于脊髓损伤也具有一定的保护作用。
嗅鞘细胞:是一种特殊的胶质细胞,具有神经营养、抑制胶质增生等作用,为轴突生长提供了适宜的环境,能够促进中枢神经元再生。嗅鞘细胞移植用于治疗脊髓损伤已经多有报道,但其效果有限以及作用机制尚不清晰,同时也存在一些不足之处,如目前无论是动物实验或是临床试验主要都是嗅球源性嗅鞘细胞,需要加大嗅黏膜源性嗅鞘细胞的研究应用力度,解决来源问题或者建立嗅鞘细胞系为后续的研究提供便捷。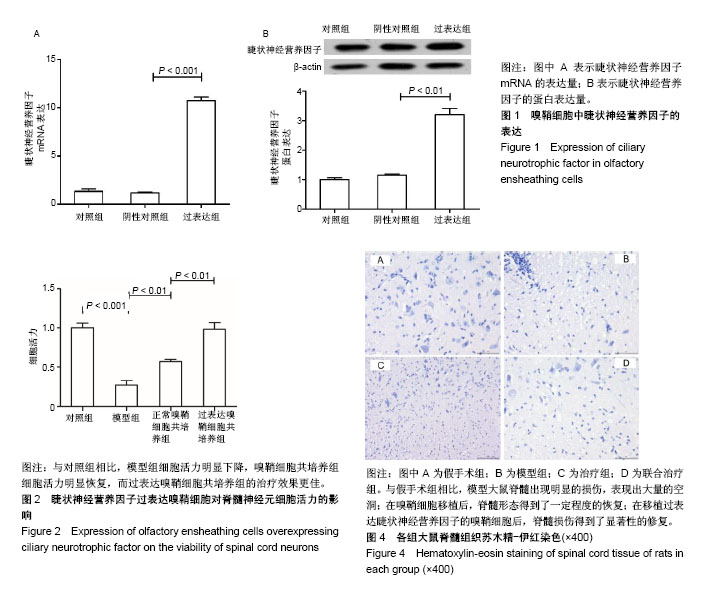
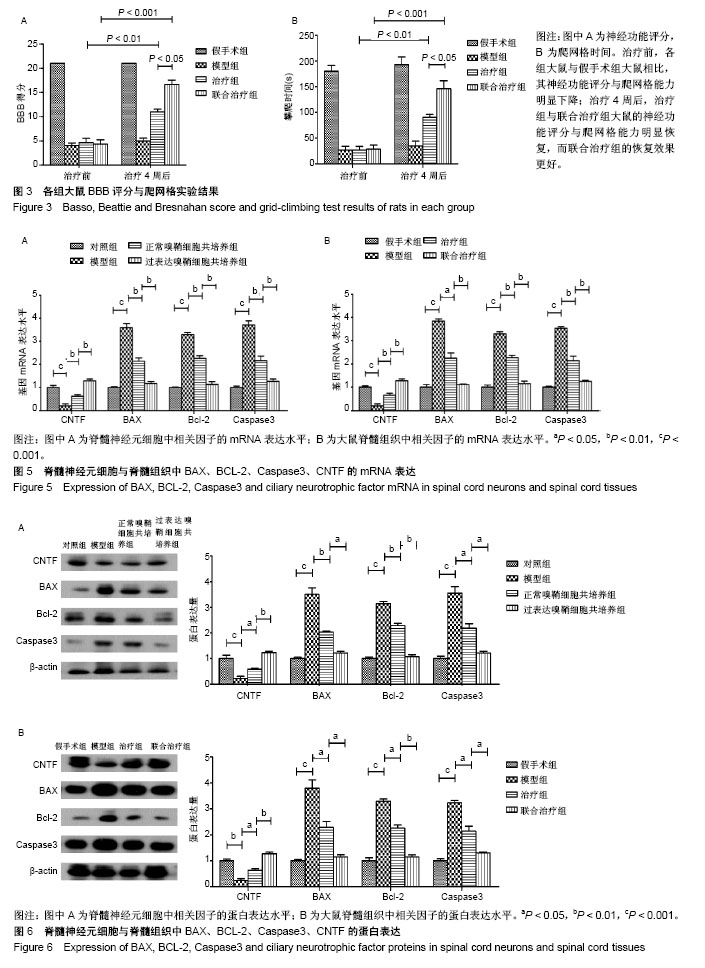
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
睫状神经营养因子:作为一种神经营养因子,对颅内损伤后视神经纤维的再生具有关键作用,可通过释放有丝分裂因子,促进有丝分裂后神经元的存活以及未成熟背根神经节神经元的发生与分化;此外,过表达睫状神经营养因子对于脊髓损伤也具有一定的保护作用。
嗅鞘细胞:是一种特殊的胶质细胞,具有神经营养、抑制胶质增生等作用,为轴突生长提供了适宜的环境,能够促进中枢神经元再生。嗅鞘细胞移植用于治疗脊髓损伤已经多有报道,但其效果有限以及作用机制尚不清晰,同时也存在一些不足之处,如目前无论是动物实验或是临床试验主要都是嗅球源性嗅鞘细胞,需要加大嗅黏膜源性嗅鞘细胞的研究应用力度,解决来源问题或者建立嗅鞘细胞系为后续的研究提供便捷。
文题释义:
睫状神经营养因子:作为一种神经营养因子,对颅内损伤后视神经纤维的再生具有关键作用,可通过释放有丝分裂因子,促进有丝分裂后神经元的存活以及未成熟背根神经节神经元的发生与分化;此外,过表达睫状神经营养因子对于脊髓损伤也具有一定的保护作用。
嗅鞘细胞:是一种特殊的胶质细胞,具有神经营养、抑制胶质增生等作用,为轴突生长提供了适宜的环境,能够促进中枢神经元再生。嗅鞘细胞移植用于治疗脊髓损伤已经多有报道,但其效果有限以及作用机制尚不清晰,同时也存在一些不足之处,如目前无论是动物实验或是临床试验主要都是嗅球源性嗅鞘细胞,需要加大嗅黏膜源性嗅鞘细胞的研究应用力度,解决来源问题或者建立嗅鞘细胞系为后续的研究提供便捷。