中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (13): 2055-2060.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1689
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
白藜芦醇联合内皮祖细胞移植修复镉致大鼠的肾损伤
贺立娟1,马春磊2,申玉兰1,赵国红3
- 1北京市密云区医院肾内科,北京市 101500;2南开大学附属第四中心医院泌尿外科,天津市 300140;3北京市密云区中医医院内二病房,北京市 101500
Resveratrol combined with endothelial progenitor cell transplantation for treatment of cadmium-induced renal injury in rats
He Lijuan1, Ma Chunlei2, Shen Yulan1, Zhao Guohong3
- 1Department of Nephrology, Miyun District Hospital of Beijing, Beijing 101500, China; 2Department of Urinary Surgery, Tianjin 4th Centre Hospital, Nankai University, Tianjin 300140, China; 3Second Ward of Internal Medicine, Miyun District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 101500, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 镉:是环境中常见的重金属污染元素之一,因而镉导致的肾脏损伤发病率较高。 内皮祖细胞应用前景:内皮祖细胞取材方便,在血管再生和心血管疾病的细胞治疗和基因治疗中具有广阔的应用前景。例如,利用内皮祖细胞修复心肌梗死患者的心脏,治疗临床肢体缺血,治疗冠状动脉疾病,改善血管移植物的通畅率,改善糖尿病患者的血管形成能力,定向抑制肿瘤血管生成,作为基因治疗导向载体和靶细胞等。应用内皮细胞治疗心血管疾病将是很有前途的新方法。
摘要
背景:研究表明白藜芦醇能有效提高大鼠近曲小管上皮细胞存活率,抑制细胞凋亡,对肾小管上皮细胞损伤具有保护作用,但白藜芦醇治疗大鼠肾损伤的具体机制尚有待进一步明确。
目的:探讨白藜芦醇联合内皮祖细胞移植对慢性镉暴露致大鼠肾脏损伤的保护作用及机制。
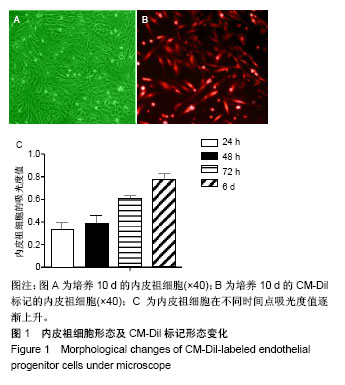
方法:体外复苏培养中国医学科学院提供的大鼠内皮祖细胞,并制备其细胞悬液,对内皮祖细胞行CM-Dil荧光标记。将购自北京维通利华动物实验技术有限公司的Wistar大鼠随机分5组,对照组皮下注射生理盐水,其他4组均皮下注射6 μmol/kg的CdCl2,每日1次,连续染毒6周,建立肾损伤大鼠模型。建模后模型组大鼠尾静脉注射0.5 mL的L-DMEM,内皮祖细胞组大鼠尾静脉注射0.5 mL的1×1010 L-1内皮祖细胞组悬液;白藜芦醇组大鼠灌胃120 mg/kg白藜芦醇,联合组大鼠同时给予以上2种干预,每日1次,连续治疗7 d。
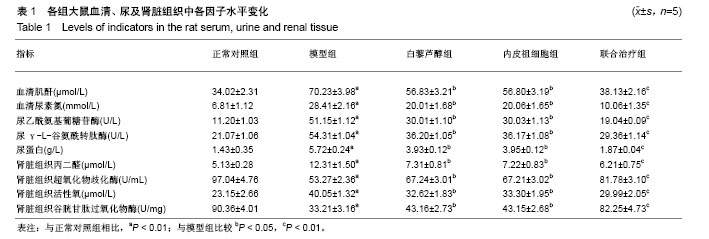
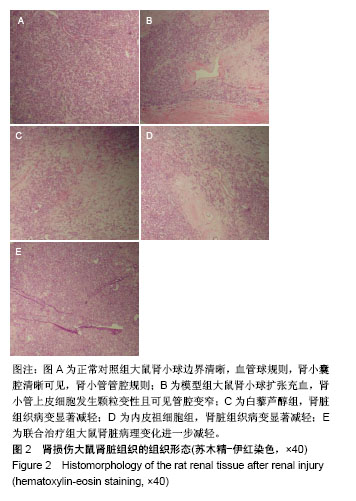
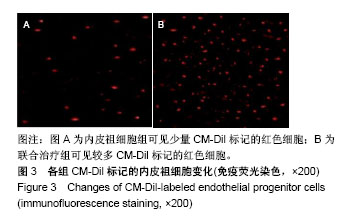
结果与结论:①血清及尿液指标检测:与模型组比较,白藜芦醇组、内皮祖细胞组及联合组尿素氮、肌酐、尿乙酰氨基葡糖苷酶、尿γ-L-谷氨酰转肽酶及尿蛋白水平均降低(P < 0.05),联合组降低更明显(P < 0.01);②肾脏组织指标检测:与模型组比较,白藜芦醇组、内皮祖细胞组及联合组肾皮质中活性氧及丙二醛水平降低(P < 0.05),超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活力升高(P < 0.05),联合组上述指标变化更为明显(P < 0.01);③肾脏组织病理变化:联合组的肾脏组织病理改善情况明显优于内皮祖细胞组、白藜芦醇及模型组,荧光显微镜观察显示,联合组CM-Dil标记的内皮祖细胞多于内皮祖细胞组(P < 0.05);④结果证实,白藜芦醇联合内皮祖细胞移植对慢性镉暴露致大鼠肾脏损伤具有保护作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-7139-6482(贺立娟)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)