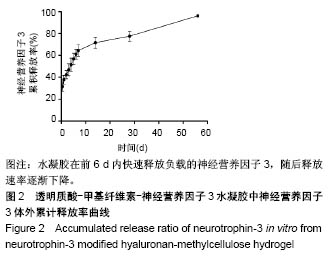
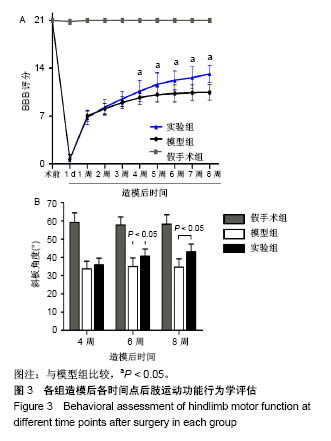
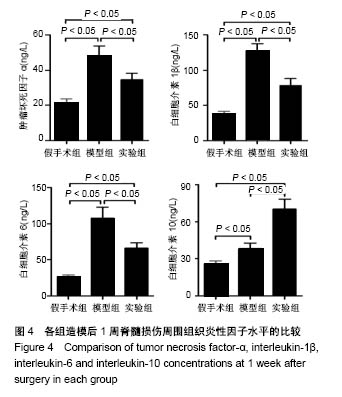
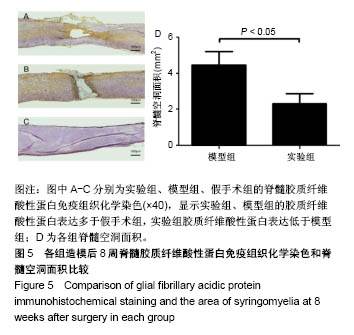
| [1] Ackery A,Tator C,Krassioukov A.A global perspective on spinal cord injury epidemiology.J Neurotrauma. 2004;21(10):1355-1370.[2] Mothe AJ,Tam RY,Zahir T,et al.Repair of the injured spinal cord by transplantation of neural stem cells in a hyaluronan-based hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2013;34(15):3775-3783.[3] Moon YJ,Lee JY,Oh MS,et al.Inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress by Angelica dahuricae radix extract decreases apoptotic cell death and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci Res. 2012;90(1):243-256.[4] An Y,Tsang KK,Zhang H.Potential of stem cell based therapy and tissue engineering in the regeneration of the central nervous system.Biomed Mater.2006;1(2):R38-344.[5] Blesch A,Tuszynski MH.Spinal cord injury: plasticity, regeneration and the challenge of translational drug development.Trends Neurosci. 2009; 32(1):41-47.[6] Cregg JM,DePaul MA,Filous AR,et al.Functional regeneration beyond the glial scar.Exp Neurol.2014;253:197-207.[7] Li G,Che MT,Zeng X,et al.Neurotrophin-3 released from implant of tissue-engineered fibroin scaffolds inhibits inflammation, enhances nerve fiber regeneration, and improves motor function in canine spinal cord injury.J Biomed Mater Res A.2018;106(8):2158-2170.[8] Shibayama M,Hattori S,Himes BT,et al.Neurotrophin-3 prevents death of axotomized Clarke's nucleus neurons in adult rat.J Comp Neurol. 1998; 390(1):102-111.[9] McMahon SS,Nikolskaya N,Choileain SN,et al.Thermosensitive hydrogel for prolonged delivery of lentiviral vector expressing neurotrophin-3 in vitro. J Gene Med.2011;13(11):591-601.[10] Elliott Donaghue I,Tator CH,Shoichet MS.Sustained delivery of bioactive neurotrophin-3 to the injured spinal cord.Biomater Sci.2015;3(1):65-72.[11] Li G,Che MT,Zhang K,et al.Graft of the NT-3 persistent delivery gelatin sponge scaffold promotes axon regeneration, attenuates inflammation, and induces cell migration in rat and canine with spinal cord injury. Biomaterials.2016;83:233-248.[12] Ejstrup R,Kiilgaard JF,Tucker BA,et al.Pharmacokinetics of intravitreal glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor: experimental studies in pigs. Exp Eye Res.2010;91(6):890-895.[13] Baumann MD,Kang CE,Tator CH,et al.Intrathecal delivery of a polymeric nanocomposite hydrogel after spinal cord injury.Biomaterials. 2010; 31(30):7631-7639.[14] Tam RY,Cooke MJ,Shoichet MS.A covalently modified hydrogel blend of hyaluronan–methyl cellulose with peptides and growth factors influences neural stem/progenitor cell fate.J Mater Chem.2012;22(37):19402.[15] Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats.J Neurotrauma.1995;12(1):1-21.[16] Liu S,Sandner B,Schackel T,et al.Regulated viral BDNF delivery in combination with Schwann cells promotes axonal regeneration through capillary alginate hydrogels after spinal cord injury.Acta Biomater. 2017; 60:167-180.[17] Bartus K,James ND,Didangelos A,et al.Large-scale chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan digestion with chondroitinase gene therapy leads to reduced pathology and modulates macrophage phenotype following spinal cord contusion injury.J Neurosci.2014;34(14):4822-4836.[18] Fouad K,Ghosh M,Vavrek R,et al.Dose and chemical modification considerations for continuous cyclic AMP analog delivery to the injured CNS.J Neurotrauma. 2009;26(5):733-740.[19] Oh JS,An SS,Gwak SJ,et al.Hypoxia-specific VEGF-expressing neural stem cells in spinal cord injury model.Neuroreport.2012;23(3):174-178.[20] Hong LTA,Kim YM,Park HH,et al.An injectable hydrogel enhances tissue repair after spinal cord injury by promoting extracellular matrix remodeling. Nat Commun.2017;8(1):533.[21] 卫巍,刘燕飞,何洋,等.β折叠型自组装短肽水凝胶特性及在神经组织工程中的应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(10):1586-1592.[22] Cigognini D, Silva D, Paloppi S, et al.Evaluation of mechanical properties and therapeutic effect of injectable self-assembling hydrogels for spinal cord injury.J Biomed Nanotechnol.2014;10(2): 309-323.[23] Liu Y, Ye H, Satkunendrarajah K, et al.A self-assembling peptide reduces glial scarring, attenuates post-traumatic inflammation and promotes neurological recovery following spinal cord injury.Acta Biomater. 2013; 9(9):8075-8088.[24] Saghazadeh A,Rezaei N.The role of timing in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother.2017;92:128-139.[25] Coll-Miro M,Francos-Quijorna I,Santos-Nogueira E,et al.Beneficial effects of IL-37 after spinal cord injury in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(5):1411-1416.[26] Wakao N,Imagama S,Zhang H,et al.Hyaluronan oligosaccharides promote functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats.Neurosci Lett. 2011;488(3):299-304.[27] Wang CX, Olschowka JA, Wrathall JR. Increase of interleukin-1beta mRNA and protein in the spinal cord following experimental traumatic injury in the rat.Brain Res.1997;759(2):190-196.[28] Lacroix S,Chang L,Rose-John S,et al.Delivery of hyper-interleukin-6 to the injured spinal cord increases neutrophil and macrophage infiltration and inhibits axonal growth. J Comp Neurol.2002;454(3):213-228.[29] Ropper AE,Ropper AH.Acute Spinal Cord Compression.N Engl J Med. 2017;376(14):1358-1369.[30] 秦茂林,杨卫兵,李红丽,等.小鼠胚胎干细胞NT3基因转染后移植对脊髓损伤的恢复作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2008,12(12):2263-2266.[31] 邓兴力,梁袁昕,杨智勇,等.神经营养因子3基因修饰神经干细胞移植脊髓损伤的相关蛋白表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2010,14(36):6751-6754.[32] Anderson MA,Burda JE,Ren Y,et al.Astrocyte scar formation aids central nervous system axon regeneration. Nature. 2016;532(7598):195-200. |
.jpg)

.jpg)