| [1] Sheikh Z, Najeeb S, Khurshid Z, et al. Biodegradable Materials for Bone Repair and Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials(Basel).2015;8(9):5744-5794.[2] 岑超德,罗聪.可降解组织工程骨材料及其血管化研究:问题与应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(21):3391-3397.[3] Song R,Murphy M,Li C, et al. Current development of biodegradable polymeric materials for biomedical applications. Drug Des Devel Ther.2018;12:3117-3145.[4] 李君涛,陈周煜.可降解生物医用材料研究现状与展望[J].新材料产业,2016,18(1):32-35.[5] Ginebra MP,Espanol M,Maazouz Y,et al.Bioceramics and bone healing.EFORT Open Rev.2018;3(5):173-183.[6] 医用高分子材料及其相关产品的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(47):8877-8878.[7] Yoshii H,Futsusaka H,Tsuchigame N,et al.An in-vitro test of thyroid function by T3 Uptake (MAA) Kit (author's transl). Horumon To Rinsho.1980;28(4):443-446.[8] Bertesteanu S,Chifiriuc MC,Grumezescu AM,et al.Biomedical applications of synthetic, biodegradable polymers for the development of anti-infective strategies.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(29):3383-3390.[9] Seitz JM,Durisin M,Goldman J,et al.Recent advances in biodegradable metals for medical sutures: a critical review.Adv Healthc Mater.2015;4(13):1915-1936.[10] Prakasam M,Locs J,Salma-Ancane K,et al. Biodegradable materials and metallic implants - a review. J Funct Biomater. 2017;8(4):44.[11] Fukunaka A, Fujitani Y.Role of Zinc Homeostasis in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes and Obesity.Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2).pii: E476. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020476.[12] Suzuki T,Kajita Y,Katsumata S,et al. Zinc Deficiency Increases Serum Concentrations of Parathyroid Hormone through a Decrease in Serum Calcium and Induces Bone Fragility in Rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2015;61(5): 382-390.[13] Liu H,Li W,Jia S,et al.Puerarin and zinc additively prevent mandibular bone loss through inhibiting osteoclastogenesis in ovariectomized rats.Histol Histopathol.2017;32(8):851-860.[14] Zhao L, Zhang Z, Song Y, et al. Mechanical properties and in vitro biodegradation of newly developed porous Zn scaffolds for biomedical applications.Mater Design.2016;108:136-144.[15] 冯相蓺,周超,张海军.生物可降解锌基金属材料研究进展[J].材料导报,2018,32(z1):188-191,195.[16] Zackular JP,Moore JL, Jordan AT, et al.Dietary zinc alters the microbiota and decreases resistance to Clostridium difficile infection.Nat Med.2016;22(11):1330-1334.[17] Murphy RA, Okoli O, Essien I, et al. Multidrug-resistant surgical site infections in a humanitarian surgery project. Epidemiol Infect.2016;144(16):3520-3526.[18] 贾曼,金文姬,李娜,等.骨科患者手术植入物感染的相关因素分析与预防[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2017,27(23):5391-5394.[19] Murray CK,Obremskey WT,Hsu JR,et al.Prevention of infections associated with combat-related extremity injuries.J Trauma.2011;71(2 Suppl 2):S235-S257.[20] Zberg B,Uggowitzer PJ, Loffler JF. MgZnCa glasses without clinically observable hydrogen evolution for biodegradable implants.Nat Mater.2009;8(11):887-891.[21] Bowen PK,Guillory RN, Shearier ER,et al.Metallic zinc exhibits optimal biocompatibility for bioabsorbable endovascular stents.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015; 56:467-472.[22] Wang X,Lu HM,Li XL,et al.Effect of cooling rate and composition on microstructures and properties of Zn-Mg alloys.Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China.2007;(S1):122-125.[23] Murni NS,Dambatta MS, Yeap SK,et al.Cytotoxicity evaluation of biodegradable Zn-3Mg alloy toward normal human osteoblast cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;49: 560-566.[24] Bowen PK,Seitz JM,Guillory RN,et al.Evaluation of wrought Zn-Al alloys (1, 3, and 5 wt % Al) through mechanical and in vivo testing for stent applications.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2018;106(1):245-258.[25] Sikora-Jasinska M,Mostaed E,Mostaed A,et al.Fabrication, mechanical properties and in vitro degradation behavior of newly developed ZnAg alloys for degradable implant applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77: 1170-1181.[26] Tang Z,Niu J,Huang H,et al.Potential biodegradable Zn-Cu binary alloys developed for cardiovascular implant applications.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2017;72:182-191.[27] Li HF,Xie XH,Zheng YF,et al.Development of biodegradable Zn-1X binary alloys with nutrient alloying elements Mg, Ca and Sr.Sci Rep.2015;5:10719.[28] 项荣,丁栋博,范亮亮,等.氧化锌的抗菌机制及其安全性研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(3):470-475.[29] 张波,周潘宇,邱超,等.医用可降解锌合金材料抗菌性能及细胞相容性的体外实验研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2016, 11(3):191-197.[30] Tapiero H,Tew KD.Trace elements in human physiology and pathology: zinc and metallothioneins. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;57(9):399-411.[31] Redmile-Gordon M,Chen L. Zinc toxicity stimulates microbial production of extracellular polymers in a copiotrophic acid soil.Int Biodeterior Biodegradation.2017;119:413-418.[32] Vojtech D,Kubasek J,Serak J,et al.Mechanical and corrosion properties of newly developed biodegradable Zn-based alloys for bone fixation.Acta Biomater.2011;7(9):3515-3522. |
.jpg)
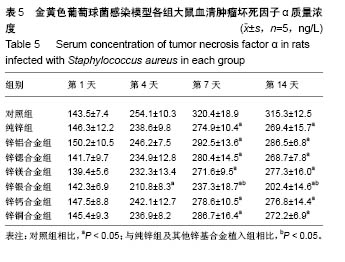
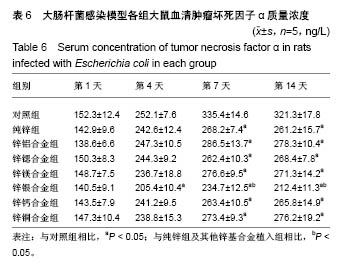

.jpg)