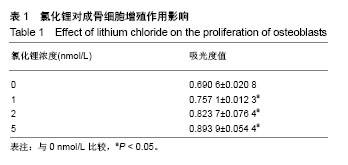
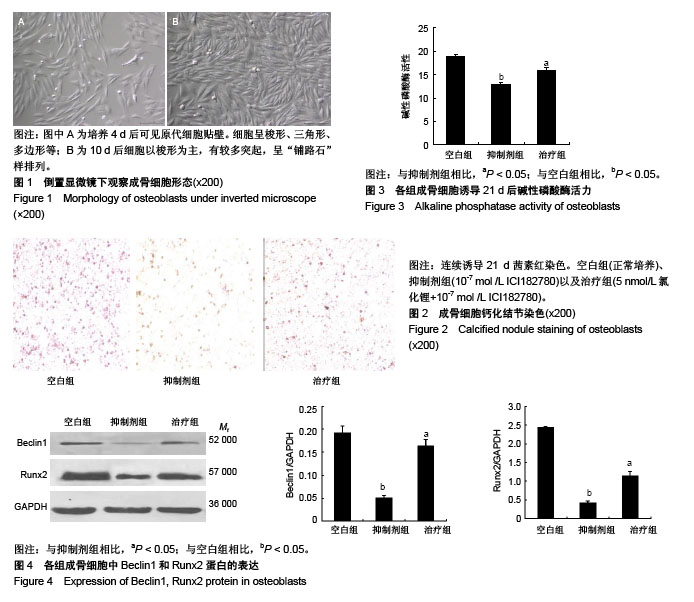
| [1] Cunningham TD, Martin BC, Deshields SC, et al. The impact of osteoporotic fractures compared with other health conditions in older adults living in Virginia, United States. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(10):1-10. [2] 杨宇,凯赛尔江•艾合买提.自噬现象与骨类疾病的关系[J].临床军医杂志,2015,43(2):196-199.[3] She C, Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, et al. Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH maintenance: new implications for osteonecrosis treatment. Cell Signal. 2014; 26(1):1-8. [4] Bonnelye E, Chabadel A, Saltel F, et al. Dual effect of strontium ranelate: stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro. Bone. 2008 42(1):129-138. [5] 王伟舟,郭皓,袁勇.自噬在绝经后骨质疏松中作用的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017(12):1675-1680.[6] Han SY, Lee KH, Kim YK. Poligoni Multiflori Radix enhances osteoblast formation and reduces osteoclast differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(1):331-345. [7] Inokondo A, Hotokezaka H, Kondo T, et al. Lithium chloride reduces orthodontically induced root resorption and affects tooth root movement in rats. Angle Orthod. 2018;88(4): 474-482. [8] Lin FX, Zheng GZ, Chang B, et al. Connexin 43 modulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through GSK-3beta/Beta-Catenin signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(1):161-175. [9] Pan J, He S, Yin X, et al. Lithium enhances alveolar bone formation during orthodontic retention in rats. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2017; 20(3):146-151. [10] Liu J, Wen J, Kai M, et al. Elevated risk of subsequent endometrial cancer after first primary breast cancer according to estrogen and progesterone receptor status: a SEER analysis. Meeting of the American-Society-Of-Breast-Surgeons. 2015: 72-73. [11] 王双利,查振刚,刘宁,等.改进酶消化法培养SD大鼠成骨细胞及其鉴定[J].实用医学杂志,2008,24(6):915-918.[12] 李启活.补骨脂素激活MAPK-NF-κB信号通路促进成骨细胞增殖的研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2016.[13] 隋国良,彭依群,翟木绪,等.17β-雌二醇下调人成骨细胞CTGF表达的信号转导机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2006,12(5): 443-446.[14] 包倪荣,赵建宁,李芳秋,等.小鼠颅骨成骨样细胞体外分离方法的改进[J].医学研究生学报,2003,16(4):260-261.[15] 闫娟丽,陈克明,周建,等.脉冲电磁场与正弦交变电磁场对成骨细胞增殖与成熟矿化的比较研究[J].解放军医药杂志, 2015,27(3): 6-10.[16] 余帮兴,梁文斌,王文.Western blot在大鼠心肌缺血炎性因子研究中的应用[J].实验动物科学,2018,35(2):69-73.[17] Tanaka S. Development of osteoporosis drugs -the past, the present and the future-. Clin Calcium. 2017;27(1):137-141. [18] Chen XX, Yang T. Roles of leptin in bone metabolism and bone diseases. J Bone Miner Metab. 2015;33(5):474-485. [19] Hart NH, Nimphius S, Rantalainen T, et al. Mechanical basis of bone strength: influence of bone material, bone structure and muscle action. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017 ;17(3): 114-139. [20] Nguyen HTT, Bo VS, Nguyen TV, et al. Sex hormone levels as determinants of bone mineral density and osteoporosis in Vietnamese women and men. J Bone Miner Metab. 2015;33(6): 658-665. [21] Black DM, Rosen CJ. Clinical practice. postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(6):595-603. [22] 李继钢.骨质疏松药物治疗研究进展[J].中国处方药, 2018,16(4): 17-18.[23] 陶亚军.骨质疏松药物治疗的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2016,22(9): 1715-1718.[24] Gennari L, Rotatori S, Bianciardi S, et al. Treatment needs and current options for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016;17(8):1141-1152. [25] Horák P, Skácelová M. Current treatment options for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Klinicka Farmakologie A Farmacie. 2014;28(3):99-104. [26] 吴智鸿,赵水平.他汀类药物抗骨质疏松作用的研究进展[J].中华老年医学杂志, 2005, 24(1):64-66. [27] 田发明,张柳.他汀类药物抗骨质疏松作用的实验研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(5):419-422.[28] Arioka M, TakahashiYanaga F, Sasaki M, Acceleration of bone regeneration by local application of lithium: Wnt signal-mediated osteoblastogenesis and Wnt signal-independent suppression of osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;90(4):397-405. [29] Zhu Z, Yin J, Guan J, et al. Lithium stimulates human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell proliferation through GSK‐3β‐dependent β‐catenin/Wnt pathway activation. FEBS J. 2015; 281(23):5371-5389. [30] Pan J, He S, Yin X, et al. Lithium enhances alveolar bone formation during orthodontic retention in rats. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2017; 20(3):146-151. [31] 陈天钢,勾禹,田发明,等.雌激素及选择性雌激素受体调节剂对骨关节炎作用的研究进展[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2018(1):73-76.[32] Lee WY, Ji HY, Lee DH, et al. 2B24 application of vibration signal processing for gear fault detection(the 12th international conference on motion and vibration control)[c] dynamics and design conference. The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers. 2017:385-385. [33] Hori YS, Hosoda R, Akiyama Y, et al. Chloroquine potentiates temozolomide cytotoxicity by inhibiting mitochondrial autophagy in glioma cells. J Neurooncol. 2015;122(1):11-20. [34] 郭鑫,杨俊.Beclin1调控自噬、凋亡与炎症反应的分子机制[J].中国老年学,2014(18):5289-5291.[35] 唐欢,许海甲,侯煜东,等.Runx2基因对骨代谢调控的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014(12):1501-1505. |
.jpg)
.jpg)