| [1] 魏燕华,刘桂桃.肺纤维化的治疗进展[J].临床肺科杂志, 2014,19(2): 336-339.[2] Kumagai S, Marumo S, Yamanashi K, et al. Prognostic significance of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema in patients with resected non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;46(6):e113-119.[3] 何爱明,金美芳,叶瑞洪.肺成纤维细胞在博来霉素致肺纤维化中的作用机制[J].心肺血管病杂志,2015,34(11):863-866.[4] Pan Y, Fu H, Kong Q, et al. Prevention of pulmonary fibrosis with salvianolic acid a by inducing fibroblast cell cycle arrest and promoting apoptosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;155(3):1589-1596.[5] 肖梦.姜黄素对肺纤维化大鼠内皮祖细胞的影响[D]. 重庆:重庆医科大学, 2015.[6] 陈玉凤.骨髓间充质干细胞对百草枯中毒导致肺纤维化的影响及机制[D]. 福州:福建医科大学,2015.[7] 刘哲,张晓梅,尹婷,等.肺纤方提取物干预肺纤维化模型大鼠肺微血管内皮细胞新生血管形成的体外研究[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2015,38(4):233-235.[8] 刘哲,张晓梅,秦慧慧,等.肺纤方提取物干预肺纤维化模型大鼠微血管内皮细胞黏附及游走迁移作用研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2015,30(11):4042-4044.[9] Mahmoudi T, Fathi F, Rezaei MJ, et al. Transgenic Mice Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Congress of Immunology & Allergy of Iran, 2016.[10] Zhou MI, Chen DL, Jiang T, et al. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transfected with survivin on pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10(5):1857-1864.[11] Fikry EM, Safar MM, Hasan WA, et al. Bone Marrow and Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Methotrexate-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rat: Comparison with Dexamethasone. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2015;29(7):321-329.[12] 龚如.内皮祖细胞在缺血性脑血管疾病治疗中的研究进展[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2014,41(2):130-133.[13] 李文华,张群辉,戎浩,等.内皮祖细胞与高血压病的应用研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(15):2273-2280.[14] 毛梅,王健瑜,汪丽,等.内皮祖细胞对急性损伤肺组织的抗炎作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(24):2444-2447.[15] Li C, Wilson PB, Levine E, et al. TGF-beta1 levels in pre-treatment plasma identify breast cancer patients at risk of developing post-radiotherapy fibrosis. Int J Cancer. 1999;84(2):155-159.[16] Lu C, Zhang J, Zhang D, et al. EPCs in vascular repair: how can we clear the hurdles between bench and bedside. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014;19:34-48.[17] Rurali E, Bassetti B, Perrucci GL, et al. BM ageing: Implication for cell therapy with EPCs. Mech Ageing Dev. 2016;159:4-13.[18] Chong MS, Ng WK, Chan JK. Concise Review: Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Regenerative Medicine: Applications and Challenges. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(4):530-538.[19] Sun K, Zhou Z, Ju X, et al. Combined transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells for tissue engineering: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):151.[20] Salmina AB, Morgun AV, Kuvacheva NV, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in cerebral endothelium development and repair (review). Sovremennye Tehnologii. 2015;6(4):213-221.[21] Ikutomi M, Sahara M, Nakajima T, et al. Diverse contribution of bone marrow-derived late-outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells to vascular repair under pulmonary arterial hypertension and arterial neointimal formation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;86:121-135.[22] Doyle MF, Tracy RP, Parikh MA, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emphysema. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0173446.[23] Xu BJ, Chen J, Chen X, et al. High shear stress-induced pulmonary hypertension alleviated by endothelial progenitor cells independent of autophagy. World J Pediatr. 2015;11(2):171-176.[24] 孙宏,刘显东,吕迪宇,等.转化生长因子-β/Smad信号通路对 急性肺损伤小鼠免疫平衡的影响[J].中华危重病急救医学, 2016,28(11):967-972.[25] Ji H, Li Y, Jiang F, et al. Inhibition of transforming growth factor beta/SMAD signal by MiR-155 is involved in arsenic trioxide-induced anti-angiogenesis in prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(12): 1541-1549.[26] 顾刘宝,卞茸文,涂玥,等.虫草素调控eIF2α/TGF-β/Smad信号通路改善肾间质纤维化的机制[J].中国中药杂志, 2014,39(21):4096-4101.[27] 邵笑,祝骥,赵峻峰,等.丹参酮ⅡA对大鼠肺纤维化细胞TGF-β1/Smads信号通路的影响[J].浙江中西医结合杂志, 2016,26(5):414-417. |
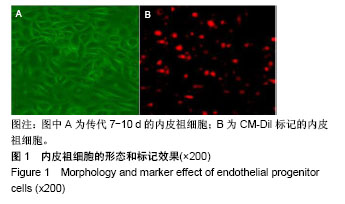
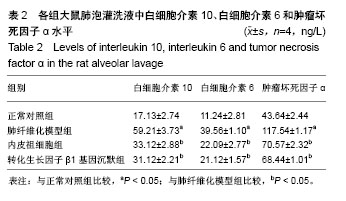
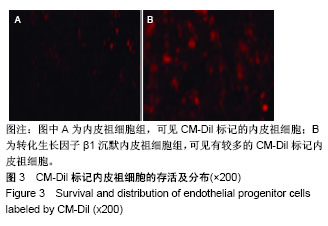
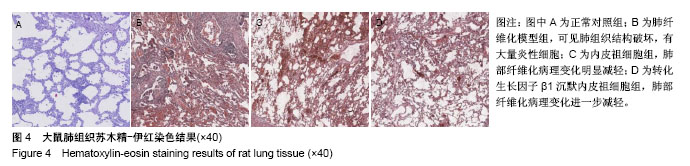
.jpg)

.jpg)