中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (26): 4101-4108.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1346
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 下一篇
钴铬颗粒刺激成骨细胞前体细胞可能加重假体周围的炎症反应
- 1滨州医学院附属医院创伤骨科,山东省滨州市256600;2美国堪萨斯州堪萨斯大学威寄托骨科中心,美国堪萨斯州威寄托市;3美国堪萨斯州威寄托州立大学生物系,美国堪萨斯州威寄托市
-
通讯作者:杨淑野,博士,主治医师,山东省内滨州市滨州医学院附属医院创伤骨科,山东省滨州市 256600 -
作者简介:姜建浩,男,1984年生,山东省海阳市人,汉族,2015年山东大学毕业,博士,主治医师,主要从事人工关节置换假体松动方向的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(81241061),项目负责人:张锴;山东省医药卫生科技发展项目(2016WS0023),项目负责人:杨淑野;滨州医学院科研启动资金(BY2016KYQD19),项目负责人:杨淑野
Cobalt-chromium particles inducing preosteoblasts may aggravate periprosthetic inflammation
- 1Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Wichita, KS, USA; 3Department of Biological Sciences, Wichita State University, Wichita, KS, USA
-
Contact:Yang Shuye, MD, Attending physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Binzhou Medical University Hopital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Jiang Jianhao, MD, Attending physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81241061 (to ZK); the Medical and Health Technology Development Project of Shandong Province, No. 2016WS0023 (to YSY); the Science Research Startup Foundation of Binzhou Medical University, No. BY2016KYQD19 (to YSY)
摘要:
文题释义:
无菌性假体松动:人工关节置换后,由于骨与假体磨损产生金属磨损颗粒,这些磨损颗粒被巨噬细胞吞噬,但是巨噬细胞不可能将金属颗粒清除,因而产生一系列的炎症刺激反应,导致白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12、肿瘤坏死因子、干扰素等表达增高,刺激成纤维细胞增殖,在假体周围形成炎性假膜,随着时间的延长,产生假体的微动。
中图分类号:
引用本文
姜建浩,李 朋,杜刚强,刘宏智,王 辉,张 锴,杨上游,杨淑野. 钴铬颗粒刺激成骨细胞前体细胞可能加重假体周围的炎症反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(26): 4101-4108.
Jiang Jianhao, Li Peng, Du Gangqiang, Liu Hongzhi, Wang Hui, Zhang Kai, Yang Shangyou, Yang Shuye. Cobalt-chromium particles inducing preosteoblasts may aggravate periprosthetic inflammation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4101-4108.
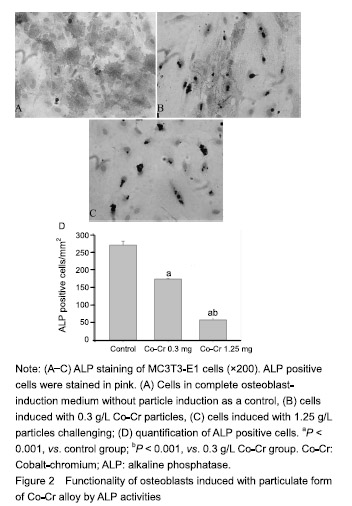
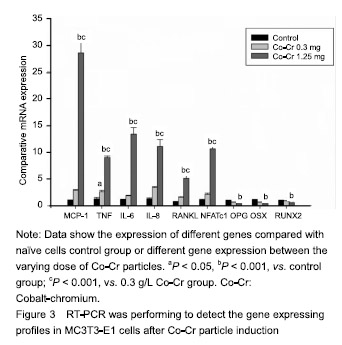
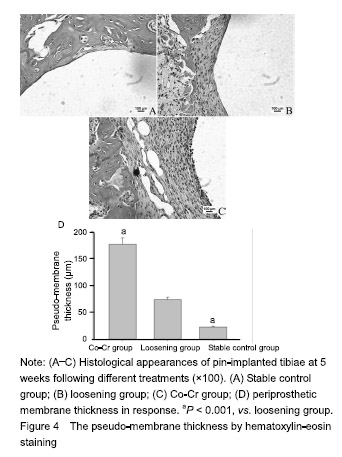
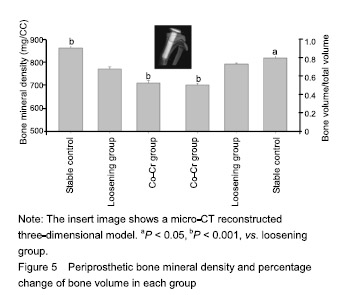
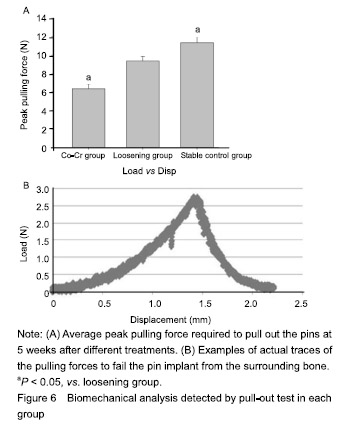
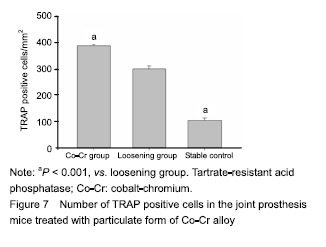
| [1]Pajarinen J, Lin TH, Nabeshima A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in the aseptic loosening of total joint replacements. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(4): 1195-1207. [2]Goodman SB, Gibon E, Pajarinen J, et al. Novel biological strategies for treatment of wear particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis of orthopaedic implants for joint replacement. J R Soc Interface. 2014;11(93):20130962. [3]Lombardi AV Jr, Barrack RL, Berend KR, et al. The Hip Society: algorithmic approach to diagnosis and management of metal-on-metal arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(11 Suppl A):14-18. [4]Marti A. Cobalt-base alloys used in bone surgery. Injury. 2000;31 Suppl 4:18-21.[5]Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, et al. Effects of Ti, PMMA, UHMWPE, and Co-Cr wear particles on differentiation and functions of bone marrow stromal cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(10):2817-2825. [6]Kadoya Y, Revell PA, Kobayashi A, et al. Wear particulate species and bone loss in failed total joint arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(340):118-129.[7]Yang SY, Zhang K, Bai L, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate and titanium alloy particles activate peripheral monocytes during periprosthetic inflammation and osteolysis. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):781-786.[8]Zhao YP, Wei JL, Tian QY, et al. Progranulin suppresses titanium particle induced inflammatory osteolysis by targeting TNFα signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20909.[9]An S, Han F, Hu Y, et al. Curcumin Inhibits Polyethylene- Induced Osteolysis via Repressing NF-κB Signaling Pathway Activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3): 1100-1112. [10]Man K, Jiang LH, Foster R, et al. Immunological Responses to Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Funct Biomater. 2017;8(3):E33. [11]Dyskova T, Gallo J, Kriegova E. The Role of the Chemokine System in Tissue Response to Prosthetic By-products Leading to Periprosthetic Osteolysis and Aseptic Loosening. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1026. [12]Wang Z, Liu N, Liu K, et al. Autophagy mediated CoCrMo particle-induced peri-implant osteolysis by promoting osteoblast apoptosis. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2358-2369. [13]Pajarinen J, Nabeshima A, Lin TH, et al. Murine Model of Progressive Orthopedic Wear Particle-Induced Chronic Inflammation and Osteolysis. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2017;23(12):1003-1011. [14]Terkawi MA, Hamasaki M, Takahashi D, et al. Transcriptional profile of human macrophages stimulated by ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene particulate debris of orthopedic implants uncovers a common gene expression signature of rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:417-425. [15]Ollivere B, Wimhurst JA, Clark IM, et al. Current concepts in osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(1):10-15.[16]Wooley PH, Morren R, Andary J, et al. Inflammatory responses to orthopaedic biomaterials in the murine air pouch. Biomaterials. 2002;23(2):517-526.[17]Zhang K, Jia TH, McQueen D, et al. Circulating blood monocytes traffic to and participate in the periprosthetic tissue inflammation. Inflamm Res. 2009;58(12):837-844. [18]Yang SY, Nasser S, Markel DC, et al. Human periprosthetic tissues implanted in severe combined immunodeficient mice respond to gene transfer of a cytokine inhibitor. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(5):1088-1097.[19]Thomas P, Thomsen M. Allergy diagnostics in implant intolerance. Orthopade. 2008;37(2):131-135. [20]Nakamura-Ota M, Hamanaka R, Yano H, et al. A new murine osteoblastic cell line immortalized with the SV40 large T antigen. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014;15(3):373-380.[21]Bauer TW. Particles and periimplant bone resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(405):138-143.[22]Au A, Ha J, Hernandez M, et al. Nickel and vanadium metal ions induce apoptosis of T-lymphocyte Jurkat cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;79(3):512-521.[23]Cadosch D, Sutanto M, Chan E, et al. Titanium uptake, induction of RANK-L expression, and enhanced proliferation of human T-lymphocytes. J Orthop Res. 2010; 28(3):341-347. [24]Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, et al. Titanium particle-challenged osteoblasts promote osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis in a murine model of periprosthestic osteolysis. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7564-7572.[25]Jacobs JJ, Gilbert JL, Urban RM. Corrosion of metal orthopaedic implants. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(2): 268-282.[26]Sunderman FW Jr, Hopfer SM, Swift T, et al. Cobalt, chromium, and nickel concentrations in body fluids of patients with porous-coated knee or hip prostheses. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(3):307-315.[27]Purdue PE, Koulouvaris P, Potter HG, et al. The cellular and molecular biology of periprosthetic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;454:251-261.[28]Hirakawa K, Jacobs JJ, Urban R, et al. Mechanisms of failure of total hip replacements: lessons learned from retrieval studies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(420):10-17.[29]Tucci M, Tsao A, Hughes J Jr. Analysis of capsular tissue from patients undergoing primary and revision total hip arthroplasty. Biomed Sci Instrum. 1996;32:119-125.[30]Chang YS, Kobayashi M, Li ZL, et al. Significance of peak value and duration of the interfacial shear load in evaluation of the bone-implant interface. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(8):773-779.[31]Goodman S, Ma T, Trindade M, et al. COX-2 selective NSAID decreases bone ingrowth in vivo. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(6):1164-1169.[32]El-Warrak AO, Olmstead M, Schneider R, et al. An experimental animal model of aseptic loosening of hip prostheses in sheep to study early biochemical changes at the interface membrane. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2004;5:7.[33]Warme BA, Epstein NJ, Trindade MC, et al. Proinflammatory mediator expression in a novel murine model of titanium-particle-induced intramedullary inflammation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;71(2):360-366. |
| [1] | 王秋霏, 顾 叶, 彭育沁, 薛 峰, 巨 荣, 朱 锋, 王熠军, 耿德春, 徐耀增. 人工假体磨损颗粒作用下Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对成骨细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3894-3901. |
| [2] | 杨彩会, 刘启成, 董 明, 王丽娜, 左美娜, 陆 颖, 牛卫东. 丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶促进慢性根尖周炎模型小鼠的骨破坏[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [3] | 霍 花, 程余婷, 周 倩, 齐昱晗, 伍 超, 石前会, 杨童景, 廖 健, 洪 伟. 种植体表面药物涂层对骨结合的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [4] | 蒋昇源, 李 丹, 姜建浩, 杨上游, 杨淑野. 假体无菌性松动过程中Co2+对成骨前体细胞的生物学反应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [5] | 李啸群, 徐凯航, 纪 方. 补骨脂异黄酮抑制破骨细胞分化缓解小鼠去卵巢骨质疏松[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(2): 186-190. |
| [6] | 辛鹏飞, 柯梦楠 , 张海涛, 乌日莎娜, 李子祺, 庄至坤, 魏秋实, 何 伟. 活血化瘀中药治疗股骨头坏死共同作用机制的网络药理学数据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(17): 2727-2733. |
| [7] | 张 为, 崔帅帅, 周志超, 胡小华, 杨晓红. 微小RNA调控组蛋白去乙酰化酶治疗骨相关疾病的发展现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(17): 2767-2774. |
| [8] | 范思奇, 曾 平, 农 焦, 刘金富, 钱晓芬. 通络生骨胶囊含药血清对破骨细胞及Toll样受体4/核因子κB信号通路的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(14): 2155-2160. |
| [9] | 吴钰坤, 韩 杰, 温帅波. 骨折愈合过程中Runx2基因的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(14): 2274-2279. |
| [10] | 李冬冬, 廖红兵. miR-214参与骨组织代谢的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(11): 1779-1784. |
| [11] | 李啸群, 徐凯航, 纪 方. 补骨脂异黄酮抑制破骨细胞分化缓解小鼠去卵巢骨质疏松[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(在线): 4-. |
| [12] | 许 诺, 曹 蓁, 李晓杰, 史 春. MiR-21可调控牙周炎破骨细胞的增殖[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(8): 1225-1230. |
| [13] | 葛均成, 马金辉, 王佰亮, 岳德波, 孙 伟, 王卫国, 郭万首, 李子荣. 股骨头缺血性坏死中双膦酸盐的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(5): 753-759. |
| [14] | 张亚楠, 严 霞, 孟增东. Zn、Mg增强羟基磷灰石骨修复材料临床应用与机制:生物活性及成骨诱导的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(4): 606-611. |
| [15] | 宋世雷, 陈跃平, 章晓云. PI3K/AKT信号通路调控股骨头坏死的相关机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(3): 408-415. |


| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||