中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3609-3772.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1304
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
不同分期骨关节炎关节液中相关降解酶的表达差异
王海英1,2,丁 晓1,2,杨 立3,韩 飞1,2,蒲沛东1,2,马青源1,2,史晨辉1,王维山1
- 1石河子大学医学院第一附属医院骨科,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832008;2石河子大学医学院,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832008;3新疆军区总医院北京路临床部药剂科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Differences in the expression of related degrading enzymes in joint fluids of different stages of osteoarthritis
Wang Haiying1, 2, Ding Xiao1, 2, Yang Li3, Han Fei1, 2, Pu Peidong1, 2, Ma Qingyuan1, 2, Shi Chenhui1, Wang Weishan1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of the Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Pharmacy, Beijing Road Clinical Department, General Hospital of Xinjiang Military Region of Chinese PLA, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞外调节蛋白激酶:主要包括细胞外调节蛋白激酶1和细胞外调节蛋白激酶2,分子质量分别为44 kD和42 kD,是MAPK 家族成员之一,是将信号从表面受体传导至细胞核的关键。细胞外调节蛋白激酶的主要作用是调节细胞增殖、分化和分裂及神经细胞的学习和记忆,可通过调节关节软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡活性参与骨关节炎发病的整个过程。
人类含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(adisintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin-like motifs,ADAMTS):该家族由19个蛋白水解酶组成,具有多种生理、病理学作用,如止血、器官生成、骨关节炎和肿瘤等,是一类在结构上不同于MMPs的金属蛋白酶。其中ADAMT4及ADAMT5以聚蛋白聚糖为降解底物,是关节软骨内另一类成分聚蛋白多糖的降解酶,在骨关节炎发生发展上有重要作用。
文题释义:
细胞外调节蛋白激酶:主要包括细胞外调节蛋白激酶1和细胞外调节蛋白激酶2,分子质量分别为44 kD和42 kD,是MAPK 家族成员之一,是将信号从表面受体传导至细胞核的关键。细胞外调节蛋白激酶的主要作用是调节细胞增殖、分化和分裂及神经细胞的学习和记忆,可通过调节关节软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡活性参与骨关节炎发病的整个过程。
人类含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(adisintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin-like motifs,ADAMTS):该家族由19个蛋白水解酶组成,具有多种生理、病理学作用,如止血、器官生成、骨关节炎和肿瘤等,是一类在结构上不同于MMPs的金属蛋白酶。其中ADAMT4及ADAMT5以聚蛋白聚糖为降解底物,是关节软骨内另一类成分聚蛋白多糖的降解酶,在骨关节炎发生发展上有重要作用。
.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞外调节蛋白激酶:主要包括细胞外调节蛋白激酶1和细胞外调节蛋白激酶2,分子质量分别为44 kD和42 kD,是MAPK 家族成员之一,是将信号从表面受体传导至细胞核的关键。细胞外调节蛋白激酶的主要作用是调节细胞增殖、分化和分裂及神经细胞的学习和记忆,可通过调节关节软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡活性参与骨关节炎发病的整个过程。
人类含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(adisintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin-like motifs,ADAMTS):该家族由19个蛋白水解酶组成,具有多种生理、病理学作用,如止血、器官生成、骨关节炎和肿瘤等,是一类在结构上不同于MMPs的金属蛋白酶。其中ADAMT4及ADAMT5以聚蛋白聚糖为降解底物,是关节软骨内另一类成分聚蛋白多糖的降解酶,在骨关节炎发生发展上有重要作用。
文题释义:
细胞外调节蛋白激酶:主要包括细胞外调节蛋白激酶1和细胞外调节蛋白激酶2,分子质量分别为44 kD和42 kD,是MAPK 家族成员之一,是将信号从表面受体传导至细胞核的关键。细胞外调节蛋白激酶的主要作用是调节细胞增殖、分化和分裂及神经细胞的学习和记忆,可通过调节关节软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡活性参与骨关节炎发病的整个过程。
人类含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(adisintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin-like motifs,ADAMTS):该家族由19个蛋白水解酶组成,具有多种生理、病理学作用,如止血、器官生成、骨关节炎和肿瘤等,是一类在结构上不同于MMPs的金属蛋白酶。其中ADAMT4及ADAMT5以聚蛋白聚糖为降解底物,是关节软骨内另一类成分聚蛋白多糖的降解酶,在骨关节炎发生发展上有重要作用。摘要
背景:目前对骨关节患者滑膜、关节软骨中相关降解酶的研究较多,对关节液中相关因子的检测亦有报道,但有关不同病变分期相关因子表达情况的报道较少,且其与病变程度相关性研究报道亦相对较少。
目的:检测不同分期骨关节炎患者关节液中细胞外调节蛋白激酶、基质金属蛋白酶13和人类含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶4/5(a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin-like motifs,ADAMTS4/5)的表达。
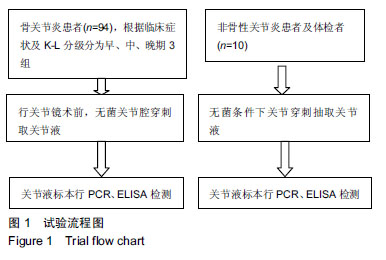
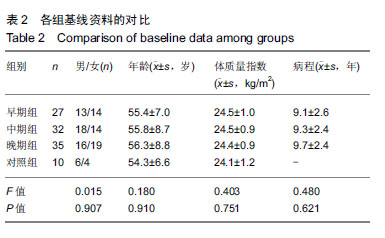
方法:选择2016年10月至2017年12月在石河子大学医学院第一附属医院骨科行关节镜手术的骨关节炎患者94例,根据临床症状与K-L X射线分级分为早期组(n=27)、中期组(n=32)、晚期组(n=35);选择行截肢的健康患者、单纯膝外伤行关节镜检查者及自愿参与试验的门诊体检者10例,作为对照组。采集4组受试者关节液,采用荧光定量PCR法和ELISA法检测细胞外调节蛋白激酶、基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMTS4/5的表达情况。试验经石河子大学医学院第一附属医院医学伦理委员会批准,批准号:2017-052-01。
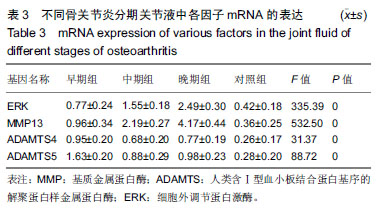
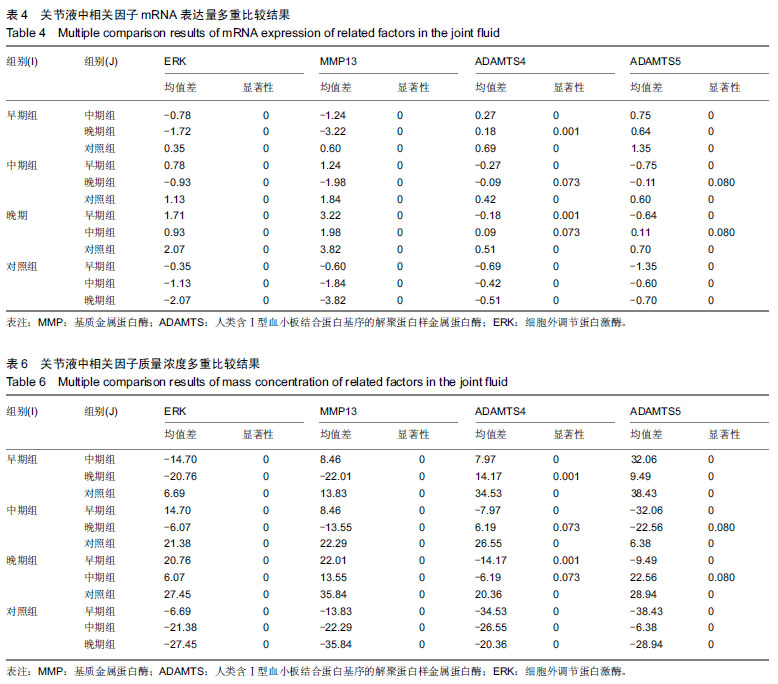
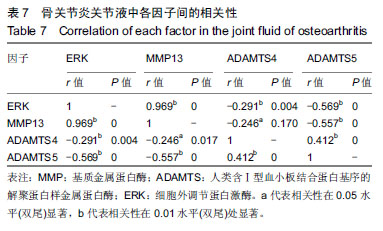
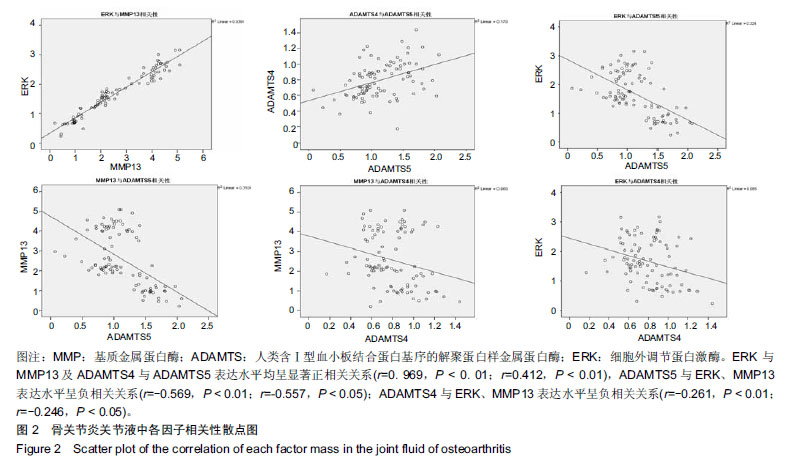
结果与结论:①荧光定量PCR检测:早、中、晚期组的各基因表达均高于对照组(P < 0.001),早、中、晚期组的细胞外调节蛋白激酶、基质金属蛋白酶13基因表达呈逐渐上升趋势(P < 0.01),早期组ADAMTS4/5基因表达高于中、晚期组(P < 0.01);②ELISA检测:早、中、晚期组的关节液中各因子表达均高于对照组(P < 0.001),早、中、晚期组的细胞外调节蛋白激酶、基质金属蛋白酶13表达呈逐渐上升趋势(P < 0.01),早期组ADAMTS4/5表达高于中、晚期组(P < 0.01);③相关性分析:细胞外调节蛋白激酶与基质金属蛋白酶13表达水平呈正相关关系(P < 0.01),ADAMTS4与ADAMTS5表达呈正相关关系(P < 0.01),ADAMTS4、ADAMTS5与细胞外调节蛋白激酶、基质金属蛋白酶13表达水平呈负相关关系(P < 0.05);④结果表明:细胞外调节蛋白激酶、基质金属蛋白酶13及ADAMTS4/5的表达与膝骨性关节炎临床症状较为密切,研究这些因子在骨性关节炎不同分期中的分子机制,有望为临床诊断及预后判定提供一定的依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0002-0209-2522(王海英)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
细胞外调节蛋白激酶:主要包括细胞外调节蛋白激酶1和细胞外调节蛋白激酶2,分子质量分别为44 kD和42 kD,是MAPK 家族成员之一,是将信号从表面受体传导至细胞核的关键。细胞外调节蛋白激酶的主要作用是调节细胞增殖、分化和分裂及神经细胞的学习和记忆,可通过调节关节软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡活性参与骨关节炎发病的整个过程。
人类含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(adisintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin-like motifs,ADAMTS):该家族由19个蛋白水解酶组成,具有多种生理、病理学作用,如止血、器官生成、骨关节炎和肿瘤等,是一类在结构上不同于MMPs的金属蛋白酶。其中ADAMT4及ADAMT5以聚蛋白聚糖为降解底物,是关节软骨内另一类成分聚蛋白多糖的降解酶,在骨关节炎发生发展上有重要作用。
文题释义:
细胞外调节蛋白激酶:主要包括细胞外调节蛋白激酶1和细胞外调节蛋白激酶2,分子质量分别为44 kD和42 kD,是MAPK 家族成员之一,是将信号从表面受体传导至细胞核的关键。细胞外调节蛋白激酶的主要作用是调节细胞增殖、分化和分裂及神经细胞的学习和记忆,可通过调节关节软骨细胞的增殖、凋亡活性参与骨关节炎发病的整个过程。
人类含Ⅰ型血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(adisintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin-like motifs,ADAMTS):该家族由19个蛋白水解酶组成,具有多种生理、病理学作用,如止血、器官生成、骨关节炎和肿瘤等,是一类在结构上不同于MMPs的金属蛋白酶。其中ADAMT4及ADAMT5以聚蛋白聚糖为降解底物,是关节软骨内另一类成分聚蛋白多糖的降解酶,在骨关节炎发生发展上有重要作用。