中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3092-3096.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1256
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
早期不同负荷运动对后期2型糖尿病大鼠成模率及血糖水平的影响
金山虎,胡亚哲
- (华中师范大学体育学院,湖北省武汉市 430079)
Effect of early different intensities of exercise on the modelling rate and blood glucose level of rats with late-stage type 2 diabetes
Jin Shanhu, Hu Yazhe
- (School of Physical Education, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China)
摘要:
.jpg) 文题释义:
糖化血清蛋白:是血液中的葡萄糖与白蛋白和其他蛋白分子N末端发生非酶促糖化反应,形成糖化血清蛋白。由于血清中白蛋白的半衰期约21 d,糖化血清蛋白测定可有效反映患者过去1-3周内平均血糖水平。
口服葡萄糖耐量试验:是一种葡萄糖负荷试验,用以了解胰岛β细胞功能和机体对血糖的调节能力,是目前公认的诊断糖尿病的金标准,在血糖异常增高但尚未达到糖尿病诊断标准时,为明确是否为糖尿病可以采用口服葡萄糖耐量试验。
文题释义:
糖化血清蛋白:是血液中的葡萄糖与白蛋白和其他蛋白分子N末端发生非酶促糖化反应,形成糖化血清蛋白。由于血清中白蛋白的半衰期约21 d,糖化血清蛋白测定可有效反映患者过去1-3周内平均血糖水平。
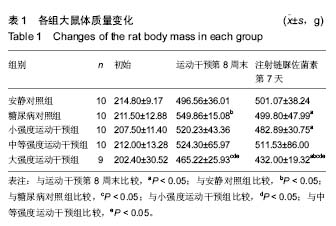
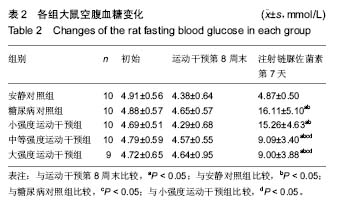
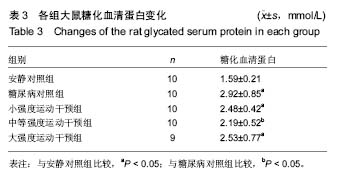
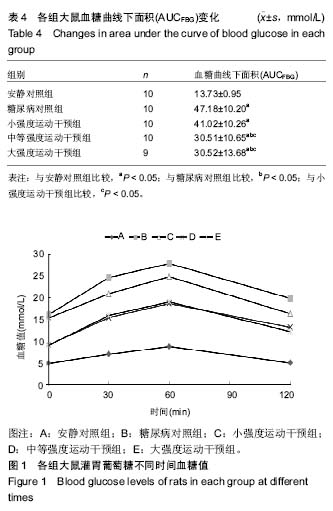
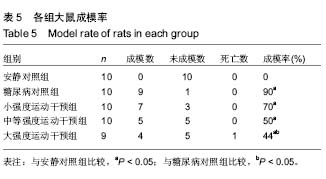
口服葡萄糖耐量试验:是一种葡萄糖负荷试验,用以了解胰岛β细胞功能和机体对血糖的调节能力,是目前公认的诊断糖尿病的金标准,在血糖异常增高但尚未达到糖尿病诊断标准时,为明确是否为糖尿病可以采用口服葡萄糖耐量试验。摘要 背景:糖代谢紊乱是糖尿病的主要临床表现,运动是治疗糖尿病的主要方法之一,早期不同负荷运动对后期2型糖尿病大鼠模型成模率及血糖水平的影响尚不明确。 目的:探究不同负荷运动对高糖高脂膳食联合注射链脲佐菌素建立大鼠2型糖尿病模型的影响。 方法:50只SD雄性大鼠(购自湖北省实验动物研究中心),随机分为安静对照组、糖尿病对照组、小强度运动干预组、中等强度运动干预组和大强度运动干预组5组,每组10只。安静对照组普通饲料喂养;糖尿病对照组高糖高脂饲料喂养,均笼中自由活动;小、中、大强度运动干预组高糖高脂喂养,期间分别进行8周不同强度的跑台运动。运动第8周末,检测各组大鼠的体质量和空腹血糖,然后隔夜禁食不禁水12 h,安静对照组一次性腹腔注射柠檬酸缓冲液,其余4组一次性腹腔注射2%链脲佐菌素溶液。注射链脲佐菌素第7天再次检测大鼠体质量、空腹血糖和糖化血清蛋白水平。 结果与结论:不同强度运动干预组的体质量、空腹血糖、糖化血清蛋白、血糖曲线下面积均较糖尿病对照组有所改善,中等、大强度运动干预可更有效地调节2型糖尿病血糖水平,改善糖耐量,而大强度运动干预对于降低2型糖尿病的发病率更为有效。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0001-7302-8758(金山虎)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
糖化血清蛋白:是血液中的葡萄糖与白蛋白和其他蛋白分子N末端发生非酶促糖化反应,形成糖化血清蛋白。由于血清中白蛋白的半衰期约21 d,糖化血清蛋白测定可有效反映患者过去1-3周内平均血糖水平。
口服葡萄糖耐量试验:是一种葡萄糖负荷试验,用以了解胰岛β细胞功能和机体对血糖的调节能力,是目前公认的诊断糖尿病的金标准,在血糖异常增高但尚未达到糖尿病诊断标准时,为明确是否为糖尿病可以采用口服葡萄糖耐量试验。
文题释义:
糖化血清蛋白:是血液中的葡萄糖与白蛋白和其他蛋白分子N末端发生非酶促糖化反应,形成糖化血清蛋白。由于血清中白蛋白的半衰期约21 d,糖化血清蛋白测定可有效反映患者过去1-3周内平均血糖水平。
口服葡萄糖耐量试验:是一种葡萄糖负荷试验,用以了解胰岛β细胞功能和机体对血糖的调节能力,是目前公认的诊断糖尿病的金标准,在血糖异常增高但尚未达到糖尿病诊断标准时,为明确是否为糖尿病可以采用口服葡萄糖耐量试验。