| [1]Loeser RF,Collins JA,Diekman BO.Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(7):412-420.[2]Carames B,Olmer M,Kiosses WB,et al.The relationship of autophagy defects to cartilage damage during joint aging in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheumatol.2015;67(6):1568-1576.[3]López de Figueroa P, Lotz MK, Blanco FJ, Caramés B.Autophagy activation and protection from mitochondrial dysfunction in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(4):966-976.[4]Loeser RF.Aging and osteoarthritis: the role of chondrocyte senescence and aging changes in the cartilage matrix.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2009;17(8):971-979.[5]Meckes JK,Carames B,Olmer M,et al.Compromised autophagy precedes meniscus degeneration and cartilage damage in mice. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(11):1880-1889.[6]Almonte-Becerril M,Navarro-Garcia F,Gonzalez-Robles A,et al.Cell death of chondrocytes is a combination between apoptosis and autophagy during the pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis within an experimental model.Apoptosis. 2010;15(5):631-638.[7]Huang ZM, Du SH, Huang LG, et al. Leptin promotes apoptosis and inhibits autophagy of chondrocytes through upregulating lysyl oxidase-like 3 during osteoarthritis pathogenesis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2016;24(7):1246-1253.[8]Ribeiro M, López de Figueroa P, Blanco FJ, et al.Insulin decreases autophagy and leads to cartilage degradation.Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2016,24(4):731-739.[9]Martinez-Lopez N,Athonvarangkul D,Singh R.Autophagy and aging. Adv Exp Med Biol.2015;847:73-87.[10]Loeser RF,Collins JA,Diekman BO.Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2016;12(7):412-420.[11]Lotz MK,Carames B.Autophagy and cartilage homeostasis mechanisms in joint health, aging and OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol.2011; 7(10):579-587.[12]Ansari MY,Khan NM,Ahmad I,et al.Parkin clearance of dysfunctional mitochondria regulates ROS levels and increases survival of human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(8):1087-1097.[13]Zhang Y,Vasheghani F,Li YH, et al.Cartilage-specific deletion of mTOR upregulates autophagy and protects mice from osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.2015;74(7):1432-1440.[14]Carames B,Hasegawa A,Taniguchi N,et al.Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces severity of experimental osteoarthritis.Ann Rheum Dis.2012;71(4):575-581.[15]Vasheghani F,Zhang Y,Li YH,et al.PPARgamma deficiency results in severe, accelerated osteoarthritis associated with aberrant mTOR signalling in the articular cartilage.Ann Rheum Dis.2015;74(3): 569-578.[16]Zhang H,Wang H,Zeng C,et al.mTORC1 activation downregulates FGFR3 and PTH/PTHrP receptor in articular chondrocytes to initiate osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2017;25(6):952-963.[17]Ito M,Yurube T,Kakutani K,et al.Selective interference of mTORC1/RAPTOR protects against human disc cellular apoptosis, senescence, and extracellular matrix catabolism with Akt and autophagy induction. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2017;25(12): 2134-2146.[18]Cravedi P,Ruggenenti P,Remuzzi G.Sirolimus to replace calcineurin inhibitors? Too early yet. Lancet. 2009;373(9671):1235-1236.[19]Zhao Y, Hu J, Miao G, et al.Transmembrane protein 208: a novel ER-localized protein that regulates autophagy and ER stress.PLoS One.2013;8(5):e64228.[20]Hosseinzadeh A, Kamrava SK,Joghataei MT,et al.Apoptosis signaling pathways in osteoarthritis and possible protective role of melatonin.J Pineal Res.2016;61(4):411-425.[21]Yorimitsu T,Nair U,Yang Z,et al.Endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers autophagy.J Biol Chem,2006,281(40):30299-30304.[22]Deegan S,Saveljeva S,Gorman AM,et al.Stress-induced self-cannibalism: on the regulation of autophagy by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Mol Life Sci.2013;70(14):2425-2441.[23]Levine B,Kroemer G.Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease.Cell. 2008;132(1):27-42.[24]Shapiro IM, Layfield R,Lotz M,et al.Boning up on autophagy: the role of autophagy in skeletal biology.Autophagy.2014;10(1):7-19.[25]Sasaki H,Takayama K,Matsushita T,et al.Autophagy modulates osteoarthritis-related gene expression in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum.2012;64(6):1920-1928.[26]Barranco C.Osteoarthritis: Activate autophagy to prevent cartilage degeneration? Nat Rev Rheumatol.2015;11(3):127.Harrison DE, Strong R,Sharp ZD,et al.Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice.Nature.2009; 460(7253):392-395. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
跨膜蛋白208(Transmembrane protein 208,TMEM208):是一个自噬抑制基因,可能通过对细胞内质网应激的抑制达到抑制自噬的作用。内质网能识别并降解未正确折叠的蛋白,内质网应激是指各种原因引起的细胞内质网发生功能紊乱, 导致错误折叠和未折叠蛋白在内质网腔内聚集以及Ca2+平衡紊乱的病理状态。
自噬:是一种通过溶酶体途径进行细胞质组分(蛋白质、细胞器)降解的过程,降解产物被用于能量供应及物质合成。同时,自噬也已被认为是维持软骨细胞功能正常的重要机制。自噬不仅可以调节软骨细胞生命周期的最后阶段,还可以调节软骨细胞进入成熟过程的速度。细胞的自噬水平和机体年龄、局部刺激都有关系。
文题释义:
跨膜蛋白208(Transmembrane protein 208,TMEM208):是一个自噬抑制基因,可能通过对细胞内质网应激的抑制达到抑制自噬的作用。内质网能识别并降解未正确折叠的蛋白,内质网应激是指各种原因引起的细胞内质网发生功能紊乱, 导致错误折叠和未折叠蛋白在内质网腔内聚集以及Ca2+平衡紊乱的病理状态。
自噬:是一种通过溶酶体途径进行细胞质组分(蛋白质、细胞器)降解的过程,降解产物被用于能量供应及物质合成。同时,自噬也已被认为是维持软骨细胞功能正常的重要机制。自噬不仅可以调节软骨细胞生命周期的最后阶段,还可以调节软骨细胞进入成熟过程的速度。细胞的自噬水平和机体年龄、局部刺激都有关系。.jpg) 文题释义:
跨膜蛋白208(Transmembrane protein 208,TMEM208):是一个自噬抑制基因,可能通过对细胞内质网应激的抑制达到抑制自噬的作用。内质网能识别并降解未正确折叠的蛋白,内质网应激是指各种原因引起的细胞内质网发生功能紊乱, 导致错误折叠和未折叠蛋白在内质网腔内聚集以及Ca2+平衡紊乱的病理状态。
自噬:是一种通过溶酶体途径进行细胞质组分(蛋白质、细胞器)降解的过程,降解产物被用于能量供应及物质合成。同时,自噬也已被认为是维持软骨细胞功能正常的重要机制。自噬不仅可以调节软骨细胞生命周期的最后阶段,还可以调节软骨细胞进入成熟过程的速度。细胞的自噬水平和机体年龄、局部刺激都有关系。
文题释义:
跨膜蛋白208(Transmembrane protein 208,TMEM208):是一个自噬抑制基因,可能通过对细胞内质网应激的抑制达到抑制自噬的作用。内质网能识别并降解未正确折叠的蛋白,内质网应激是指各种原因引起的细胞内质网发生功能紊乱, 导致错误折叠和未折叠蛋白在内质网腔内聚集以及Ca2+平衡紊乱的病理状态。
自噬:是一种通过溶酶体途径进行细胞质组分(蛋白质、细胞器)降解的过程,降解产物被用于能量供应及物质合成。同时,自噬也已被认为是维持软骨细胞功能正常的重要机制。自噬不仅可以调节软骨细胞生命周期的最后阶段,还可以调节软骨细胞进入成熟过程的速度。细胞的自噬水平和机体年龄、局部刺激都有关系。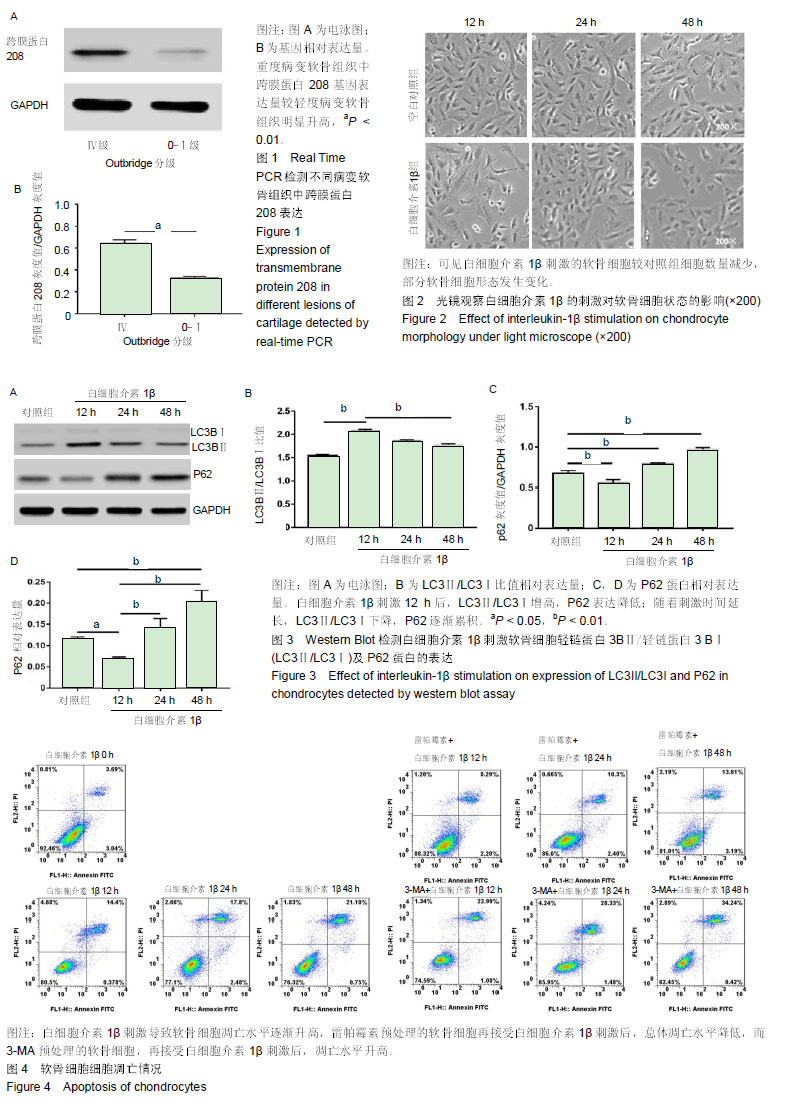
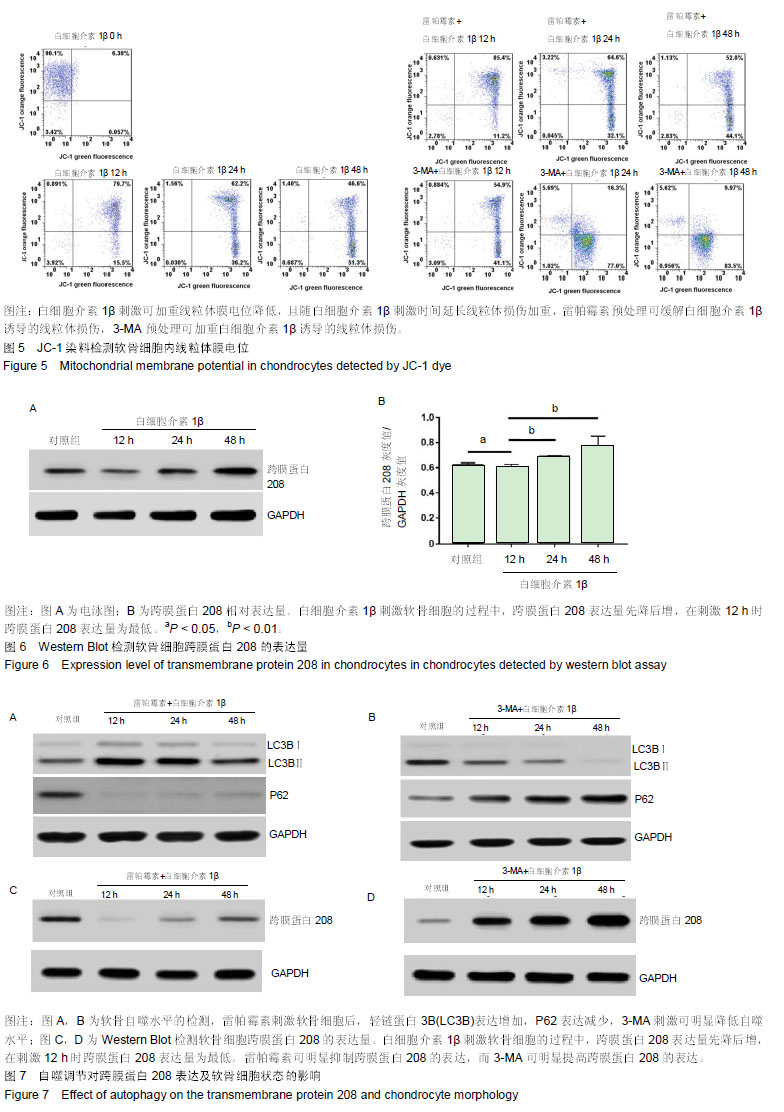
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
跨膜蛋白208(Transmembrane protein 208,TMEM208):是一个自噬抑制基因,可能通过对细胞内质网应激的抑制达到抑制自噬的作用。内质网能识别并降解未正确折叠的蛋白,内质网应激是指各种原因引起的细胞内质网发生功能紊乱, 导致错误折叠和未折叠蛋白在内质网腔内聚集以及Ca2+平衡紊乱的病理状态。
自噬:是一种通过溶酶体途径进行细胞质组分(蛋白质、细胞器)降解的过程,降解产物被用于能量供应及物质合成。同时,自噬也已被认为是维持软骨细胞功能正常的重要机制。自噬不仅可以调节软骨细胞生命周期的最后阶段,还可以调节软骨细胞进入成熟过程的速度。细胞的自噬水平和机体年龄、局部刺激都有关系。
文题释义:
跨膜蛋白208(Transmembrane protein 208,TMEM208):是一个自噬抑制基因,可能通过对细胞内质网应激的抑制达到抑制自噬的作用。内质网能识别并降解未正确折叠的蛋白,内质网应激是指各种原因引起的细胞内质网发生功能紊乱, 导致错误折叠和未折叠蛋白在内质网腔内聚集以及Ca2+平衡紊乱的病理状态。
自噬:是一种通过溶酶体途径进行细胞质组分(蛋白质、细胞器)降解的过程,降解产物被用于能量供应及物质合成。同时,自噬也已被认为是维持软骨细胞功能正常的重要机制。自噬不仅可以调节软骨细胞生命周期的最后阶段,还可以调节软骨细胞进入成熟过程的速度。细胞的自噬水平和机体年龄、局部刺激都有关系。