中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4286-4290.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1159
• 脊柱组织构建 spinal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
持续压力负荷离体兔脊柱运动节段软骨终板的应力变化
韩 涛1,2,展嘉文1,2,朱立国1,2,冯敏山1,2,尹逊路1,2
- (1中国中医科学院望京医院,北京市 100102;2中医正骨技术北京市重点实验室,北京市 100700)
Stress changes of cartilage endplate in isolated rabbit spinal motion segment under continuous pressure load
Han Tao1, 2, Zhan Jiawen1, 2, Zhu Liguo1, 2, Feng Minshan1, 2, Yin Xunlu1, 2
- (1Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China; 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Chinese Manipulative Technique, Beijing 100700, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
软骨终板:主要组成成分是蛋白多糖、胶原和水。椎间盘可以有效的维持椎间隙的高度,抵抗外界的压力,并限制相邻两椎体的相对活动,发挥生物力学功能。
椎体终板:具有极强的承载能力,在生理情况下椎间盘主要受到身体所给予的垂直静压力和运动过程中产生的水平剪切力,而软骨终板主要承载脊柱轴向的压力,并通过终板传递至纤维环和髓核,以分散和消化人体及其以外的压力负荷对脊柱的作用,使脊柱具有一定的刚韧性,从而保证脊柱的运动及抗负压能力,所以椎体终板的退变可以破坏椎间盘应力的分布。
文题释义:
软骨终板:主要组成成分是蛋白多糖、胶原和水。椎间盘可以有效的维持椎间隙的高度,抵抗外界的压力,并限制相邻两椎体的相对活动,发挥生物力学功能。
椎体终板:具有极强的承载能力,在生理情况下椎间盘主要受到身体所给予的垂直静压力和运动过程中产生的水平剪切力,而软骨终板主要承载脊柱轴向的压力,并通过终板传递至纤维环和髓核,以分散和消化人体及其以外的压力负荷对脊柱的作用,使脊柱具有一定的刚韧性,从而保证脊柱的运动及抗负压能力,所以椎体终板的退变可以破坏椎间盘应力的分布。
.jpg) 文题释义:
软骨终板:主要组成成分是蛋白多糖、胶原和水。椎间盘可以有效的维持椎间隙的高度,抵抗外界的压力,并限制相邻两椎体的相对活动,发挥生物力学功能。
椎体终板:具有极强的承载能力,在生理情况下椎间盘主要受到身体所给予的垂直静压力和运动过程中产生的水平剪切力,而软骨终板主要承载脊柱轴向的压力,并通过终板传递至纤维环和髓核,以分散和消化人体及其以外的压力负荷对脊柱的作用,使脊柱具有一定的刚韧性,从而保证脊柱的运动及抗负压能力,所以椎体终板的退变可以破坏椎间盘应力的分布。
文题释义:
软骨终板:主要组成成分是蛋白多糖、胶原和水。椎间盘可以有效的维持椎间隙的高度,抵抗外界的压力,并限制相邻两椎体的相对活动,发挥生物力学功能。
椎体终板:具有极强的承载能力,在生理情况下椎间盘主要受到身体所给予的垂直静压力和运动过程中产生的水平剪切力,而软骨终板主要承载脊柱轴向的压力,并通过终板传递至纤维环和髓核,以分散和消化人体及其以外的压力负荷对脊柱的作用,使脊柱具有一定的刚韧性,从而保证脊柱的运动及抗负压能力,所以椎体终板的退变可以破坏椎间盘应力的分布。摘要
背景:研究表明软骨组织的改变将会影响椎间盘的功能。
目的:观察持续压力负荷对离体兔脊柱运动节段软骨终板的影响。
方法:将16只新西兰白兔处死后在无菌条件下取出脊柱运动节段,随机分为对照组(无压力)与压力组(持续29.4 N压力),利用离体加载和培养装置进行离体培养,于培养前及培养后第3,7,14天,取2组兔终板软骨组织各10个样本,苏木精-伊红染色进行组织学观察,免疫组织化学检测基质金属蛋白酶13、Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白多糖表达。
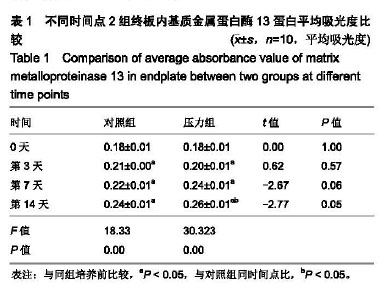
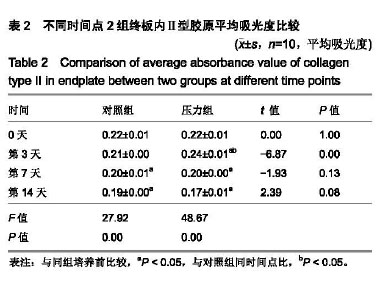
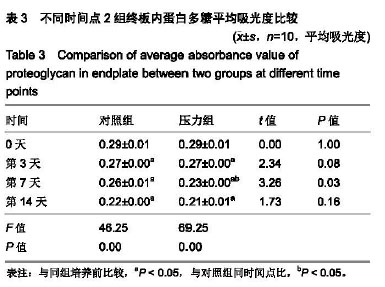
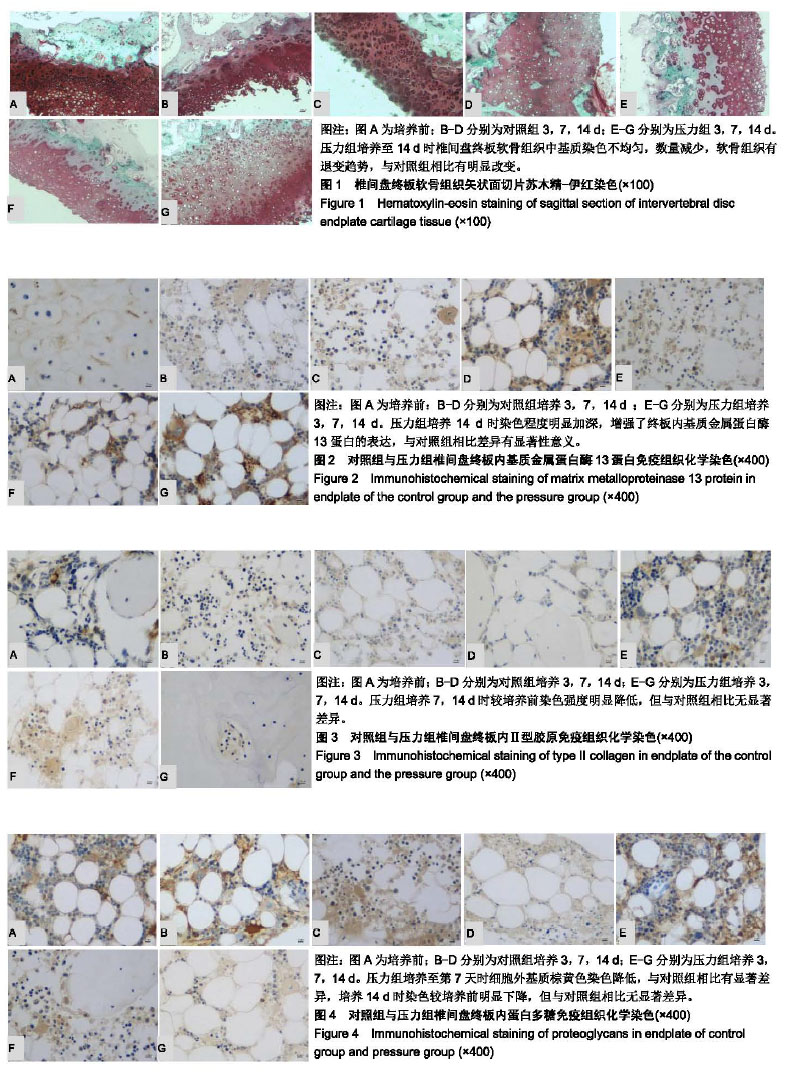
结果与结论:①压力组培养至14 d时椎间盘终板软骨组织中基质染色不均匀,数量减少,软骨组织有退变趋势,与对照组相比有明显改变;②培养14 d,与培养前相比压力组增强了终板内基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白的表达,基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白平均吸光度值显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);③培养3 d,压力组Ⅱ型胶原平均吸光度值显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);培养7,14 d,压力组Ⅱ型胶原染色较培养前强度明显降低,但与对照组相比无显著差异;④培养3,7,14 d,2组蛋白多糖染色变浅(P < 0.05);培养7 d压力组蛋白多糖平均吸光度值显著低于对照组(P < 0.05);⑤结果说明,持续压力会导致离体培养椎间盘模型终板退变,这一结果会为椎间盘退变过程中软骨损伤及早期防治提供有意义的数据。
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
软骨终板:主要组成成分是蛋白多糖、胶原和水。椎间盘可以有效的维持椎间隙的高度,抵抗外界的压力,并限制相邻两椎体的相对活动,发挥生物力学功能。
椎体终板:具有极强的承载能力,在生理情况下椎间盘主要受到身体所给予的垂直静压力和运动过程中产生的水平剪切力,而软骨终板主要承载脊柱轴向的压力,并通过终板传递至纤维环和髓核,以分散和消化人体及其以外的压力负荷对脊柱的作用,使脊柱具有一定的刚韧性,从而保证脊柱的运动及抗负压能力,所以椎体终板的退变可以破坏椎间盘应力的分布。
文题释义:
软骨终板:主要组成成分是蛋白多糖、胶原和水。椎间盘可以有效的维持椎间隙的高度,抵抗外界的压力,并限制相邻两椎体的相对活动,发挥生物力学功能。
椎体终板:具有极强的承载能力,在生理情况下椎间盘主要受到身体所给予的垂直静压力和运动过程中产生的水平剪切力,而软骨终板主要承载脊柱轴向的压力,并通过终板传递至纤维环和髓核,以分散和消化人体及其以外的压力负荷对脊柱的作用,使脊柱具有一定的刚韧性,从而保证脊柱的运动及抗负压能力,所以椎体终板的退变可以破坏椎间盘应力的分布。