| [1] Okada S, Hara M, Kobayakawa K, et al. Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res. 2018; 126:39-43.[2] Anwar MA, Ai STS, Eid AH. Inflammogenesis of secondary spinal cord injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:98.[3] Liu X, Huang S, Liu C, et al. PPP1CC is associated with astrocyte and microglia proliferation after traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. Pathol Res Pract. 2017;213(11): 1355-1364.[4] Wang Y, Li W, Wang M, et al. Quercetin reduces neural tissue damage and promotes astrocyte activation after spinal cord injury in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(2):2298-2306.[5] Casula M, Iyer AM, Spliet WG, et al. Toll-like receptor signaling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord tissue. Neuroscience. 2011;179:233-243.[6] Ahmed A, Patil AA, Agrawal DK. Immunobiology of spinal cord injuries and potential therapeutic approaches. Mol Cell Biochem.2017.doi:10.1007/s11010-017-3184-9.[7] Wang H, Li W, Goldstein R, et al. HMGB1 as a potential therapeutic target. Novartis Found Symp. 2007;280:73-85.[8] Park JS, Gamboni-Robertson F, He Q, et al. High mobility group box 1 protein interacts with multiple Toll-like receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;290(3):C917-924.[9] Taguchi A, Blood DC, del TG, et al. Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and metastases. Nature. 2000;405(6784):354-360.[10] Kikuchi K, Uchikado H, Miura N, et al. HMGB1 as a therapeutic target in spinal cord injury: A hypothesis for novel therapy development. Exp Ther Med. 2011;2(5):767-770.[11] Gong G, Yuan LB, Hu L, et al. Glycyrrhizin attenuates rat ischemic spinal cord injury by suppressing inflammatory cytokines and HMGB1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012;33(1): 11-18.[12] 沈劲松,徐伟杰,武绍远,等.星形胶质细胞在脊髓损伤中的研究展望[J].生命科学,2017,29(02):170-173.[13] Buffo A, Rolando C, Ceruti S. Astrocytes in the damaged brain: molecular and cellular insights into their reactive response and healing potential. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010; 79(2):77-89.[14] Kerstetter AE, Miller RH. Isolation and culture of spinal cord astrocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;814:93-104.[15] Takebayashi H, Nabeshima Y, Yoshida S, et al. The basic helix-loop-helix factor olig2 is essential for the development of motoneuron and oligodendrocyte lineages. Curr Biol. 2002; 12(13):1157-1163.[16] Jian Z, Ding S, Deng H, et al. Probenecid protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation injury in primary astrocytes by regulating inflammasome activity. Brain Res. 2016;1643: 123-129.[17] Ouyang L, Liu Y, Wang BY, et al. Carnosine suppresses oxygen-glucose deprivation/recovery-induced proliferation and migration of reactive astrocytes of rats in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(1):24-34.[18] Wang D, Wang S, Ji B, et al. Spatiotemporal expression of FOXA1 correlates with reactive gliosis after spinal cord injury. Neuropeptides.2017;66:36-44.[19] Burda JE, Sofroniew MV. Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease. Neuron. 2014;81(2):229-248.[20] Gabriel C, Ali C, Lesné S, et al. Transforming growth factor alpha-induced expression of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in astrocytes rescues neurons from excitotoxicity. FASEB J. 2003;17(2):277-279.[21] van Beijnum JR, Buurman WA, Griffioen AW. Convergence and amplification of toll-like receptor (TLR) and receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) signaling pathways via high mobility group B1 (HMGB1). Angiogenesis. 2008; 11(1):91-99.[22] Zhang Y, Zhu T, Zhang X, et al. Role of high-mobility group box 1 in methamphetamine-induced activation and migration of astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:156.[23] Luan G, Gao Q, Zhai F, et al. Upregulation of HMGB1, toll-like receptor and RAGE in human Rasmussen's encephalitis. Epilepsy Res. 2016;123:36-49[24] Chiavegato A, Zurolo E, Losi G, et al. The inflammatory molecules IL-1β and HMGB1 can rapidly enhance focal seizure generation in a brain slice model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:155.[25] Hayakawa K, Miyamoto N, Seo JH, et al. High-mobility group box 1 from reactive astrocytes enhances the accumulation of endothelial progenitor cells in damaged white matter. J Neurochem. 2013;125(2):273-280.[26] Zurolo E, Iyer A, Maroso M, et al. Activation of Toll-like receptor, RAGE and HMGB1 signalling in malformations of cortical development.Brain.2011;134(Pt 4):1015-1032.[27] Qiu J, Xu J, Zheng Y, et al. High-mobility group box 1 promotes metalloproteinase-9 upregulation through Toll-like receptor 4 after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2010;41(9): 2077-2082.[28] Kawabata H, Setoguchi T, Yone K, et al. High mobility group box 1 is upregulated after spinal cord injury and is associated with neuronal cell apoptosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35(11):1109-1115.[29] Kang N, Hai Y, Yang J, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen intervention reduces secondary spinal cord injury in rats via regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(2):1141-1153.[30] Bi Y, Zhu Y, Zhang M, et al. Effect of shikonin on spinal cord Injury in rats via regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(2):481-491. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
高迁移率族蛋白1:HMGB1是一种广泛存在于真核生物细胞核内,结合于DNA的非组蛋白。当细胞损伤或坏死后,HMGB1会被动释放到细胞外,而胞外的HMGB1具有较强的促炎作用,它能和多种受体结合,引起等多种炎症因子的大量释放,从而在多种炎性疾病中发挥着重要作用。
氧糖剥夺/复氧:体外培养大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞,首先,细胞在含有体积分数10%的胎牛血清星形胶质细胞培养基中培养,氧糖剥夺时细胞加入到无血清的DMEM无糖培养基,并置于体积分数1%O2、5%CO2、94%N2的三气培养箱中孵育,复氧时,再换回原来的培养基及培养条件下进行培养。
文题释义:
高迁移率族蛋白1:HMGB1是一种广泛存在于真核生物细胞核内,结合于DNA的非组蛋白。当细胞损伤或坏死后,HMGB1会被动释放到细胞外,而胞外的HMGB1具有较强的促炎作用,它能和多种受体结合,引起等多种炎症因子的大量释放,从而在多种炎性疾病中发挥着重要作用。
氧糖剥夺/复氧:体外培养大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞,首先,细胞在含有体积分数10%的胎牛血清星形胶质细胞培养基中培养,氧糖剥夺时细胞加入到无血清的DMEM无糖培养基,并置于体积分数1%O2、5%CO2、94%N2的三气培养箱中孵育,复氧时,再换回原来的培养基及培养条件下进行培养。.jpg) 文题释义:
高迁移率族蛋白1:HMGB1是一种广泛存在于真核生物细胞核内,结合于DNA的非组蛋白。当细胞损伤或坏死后,HMGB1会被动释放到细胞外,而胞外的HMGB1具有较强的促炎作用,它能和多种受体结合,引起等多种炎症因子的大量释放,从而在多种炎性疾病中发挥着重要作用。
氧糖剥夺/复氧:体外培养大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞,首先,细胞在含有体积分数10%的胎牛血清星形胶质细胞培养基中培养,氧糖剥夺时细胞加入到无血清的DMEM无糖培养基,并置于体积分数1%O2、5%CO2、94%N2的三气培养箱中孵育,复氧时,再换回原来的培养基及培养条件下进行培养。
文题释义:
高迁移率族蛋白1:HMGB1是一种广泛存在于真核生物细胞核内,结合于DNA的非组蛋白。当细胞损伤或坏死后,HMGB1会被动释放到细胞外,而胞外的HMGB1具有较强的促炎作用,它能和多种受体结合,引起等多种炎症因子的大量释放,从而在多种炎性疾病中发挥着重要作用。
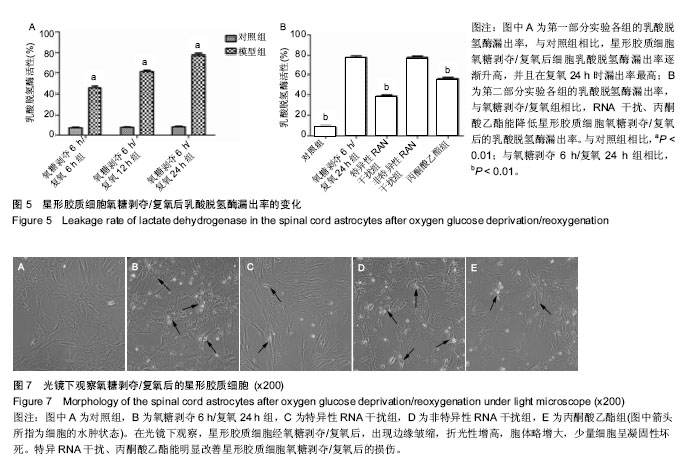
氧糖剥夺/复氧:体外培养大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞,首先,细胞在含有体积分数10%的胎牛血清星形胶质细胞培养基中培养,氧糖剥夺时细胞加入到无血清的DMEM无糖培养基,并置于体积分数1%O2、5%CO2、94%N2的三气培养箱中孵育,复氧时,再换回原来的培养基及培养条件下进行培养。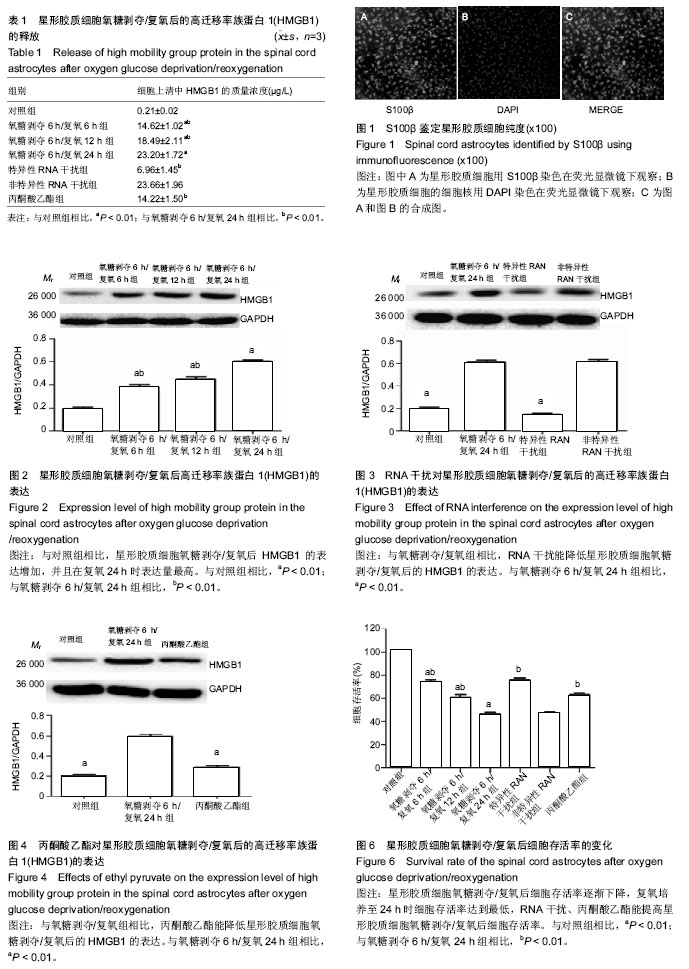
.jpg) 文题释义:
高迁移率族蛋白1:HMGB1是一种广泛存在于真核生物细胞核内,结合于DNA的非组蛋白。当细胞损伤或坏死后,HMGB1会被动释放到细胞外,而胞外的HMGB1具有较强的促炎作用,它能和多种受体结合,引起等多种炎症因子的大量释放,从而在多种炎性疾病中发挥着重要作用。
氧糖剥夺/复氧:体外培养大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞,首先,细胞在含有体积分数10%的胎牛血清星形胶质细胞培养基中培养,氧糖剥夺时细胞加入到无血清的DMEM无糖培养基,并置于体积分数1%O2、5%CO2、94%N2的三气培养箱中孵育,复氧时,再换回原来的培养基及培养条件下进行培养。
文题释义:
高迁移率族蛋白1:HMGB1是一种广泛存在于真核生物细胞核内,结合于DNA的非组蛋白。当细胞损伤或坏死后,HMGB1会被动释放到细胞外,而胞外的HMGB1具有较强的促炎作用,它能和多种受体结合,引起等多种炎症因子的大量释放,从而在多种炎性疾病中发挥着重要作用。
氧糖剥夺/复氧:体外培养大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞,首先,细胞在含有体积分数10%的胎牛血清星形胶质细胞培养基中培养,氧糖剥夺时细胞加入到无血清的DMEM无糖培养基,并置于体积分数1%O2、5%CO2、94%N2的三气培养箱中孵育,复氧时,再换回原来的培养基及培养条件下进行培养。