1.1 设计 基因学实验。
1.2 时间及地点 于2017年1月至7月在广东省第二中医院中药药理(毒理)研究室完成。
1.3 材料
引物设计:ULK1基因的3'UTR全长引物,利用NCBI数据库,采用Primer Premier 5软件设计,由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成;在5'-端载入XhoⅠ及NotⅠ(美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)酶切序列及其保护碱基。基因扩增长度为672 bp。
再根据ULK1基因3'UTR的序列,设计出点突变实验所用引物(由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成)。引物序列见表1。
表1 构建含人ULK1基因3'UTR的荧光素酶载体所用的引物序列
Table 1 Primers for constructing luciferase reporter gene vectors containing human ULK1 3'UTR area
|
|
引物名称
|
序列(5'-3')
|
|
ULK1-Xho ⅠF
|
CCG CTC GAG GGG GGG TGT CTC CCA TCT TTT AC
|
|
ULK1-NotⅠR
|
ATT TGC GGC CGC CTC GCC CTC CCA AAA CCA AT
|
|
ULK1 MUT-F
|
GGA CAG GCA AGG GCC AAT TCA GGA AGC CGA CTC AAA G
|
|
ULK1 MUT-R
|
CTT TGA GTC GGC TTC CTG AAT TGG CCC TTG CCT GTC C
|
|
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 总RNA提取 用含体积分数10%胎牛血清的高糖DMEM培养基培养293T细胞(人胚肾上皮细胞系293T细胞为实验室保存),每天在倒置荧光显微镜(DMI8型倒置荧光显微镜,德国Leica公司)下观察生长情况,每隔2 d换液1次,待细胞铺满瓶底后,用体积分数0.25%胰酶(美国Gibco公司)进行消化和传代。
实验以1×105细胞种植于6孔板,培养至细胞融合度达到约90%时,每孔加入Trigol(北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司)1 mL,振荡混匀,室温下静置5 min;加入0.2 mL氯仿,剧烈震荡2 min,静置2 min;4 ℃、10 000 r/min条件下将混合液离心10 min,取上层水相液体至一新的 1.5 mL EP管中;加入等体积异丙醇,-20 ℃条件下放置30 min,4 ℃、10 000 r/min条件下将混合液离心10 min (5424型小型高速离心机,德国Eppendorf公司),弃去上清液;加体积分数75%无水乙醇1 mL洗涤沉淀,4 ℃、 5 000 r/min条件下离心5 min,弃上清,静置于室温下,使充分晾干,接着加入ddH2O(美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)25 μL溶解RNA,于超低温冰箱(702型-80 ℃超低温冰箱,美国Thermo Scientific公司)冻存备用。
1.4.2 反转录及PCR 取新的0.2 mL PCR管进行反转录。反应的体系和条件:总RNA 1 μg;随机引物(上海英潍捷基贸易有限公司)和Oligo(dT)15的等体积混合物为反转录引物,共2 μL,在72 ℃条件处理5 min后,立即放在冰上冷却2 min。然后加入RT buffer 4 μL,dNTP 2 μL,RT反转录酶1 μL,42 ℃下反应1 h,94 ℃变性5 min;PCR (ViiA7型实时荧光定量PCR系统,美国Thermo Scientific公司)扩增反应体系和条件为:反转录所得的cDNA 1 μL,特异性引物(终浓度1 μmol/L)各1 μL,5×PrimerSTAR buffer 5 μL,dNTP 2 μL,dd H2O 14 μL,共25 μL反应体系,94 ℃预变性5 min, 94 ℃ 30 s,60 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 1 min,30个循环,72 ℃ 5 min。
1.4.3 重组载体的构建 在120 V,25 min条件下,将上述PCR产物进行1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳(PowerPac Basic电泳仪,美国Bio-Rad公司;JY-SPC水平电泳槽,北京君意东方电泳设备有限公司;AlphaImager HP凝胶成像分析系统,美国Alpha Innotech公司)。用XhoⅠ与NotⅠ,对psiCHECK-2载体和ULK1基因3'UTR PCR回收产物进行双酶切反应,酶切体系和条件:PCR回收产物或载体10 μL,XhoⅠ1.5 μL,NotⅠ1.5 μL,10×buffer 5 μL,ddH2O 32 μL,混匀后37 ℃水浴2 h。用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳对酶切产物进行检测,并根据凝胶回收试剂盒(美国OMEGA公司)说明书,对ULK1基因3'UTR PCR产物进行回收。
1.4.4 目的片段与载体进行连接、连接产物的转化 在 0.2 mL EP管中配制连接体系:酶切回收的PCR产物7 μL,酶切回收的载体1.5 μL,T4 DNA Ligase 0.5 μL,10×T4 DNA Ligase buffer 1 μL,充分混匀后于22 ℃反应2 h。在100 μL大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞中加入10 μL连接产物,混匀;先将上述大肠杆菌细胞放置于冰上30 min,42 ℃热激90 s,再次置于冰上2 min;加入800 mL LB液体培养基,37 ℃,220 r/min下培养1 h;4 000 r/min条件下离心5 min,弃去大部分上清,其他上清用于重悬菌体;将菌液均匀涂布于含100 mg/L氨苄青霉素(广州捷倍斯生物科技有限公司)固体培养基上,37 ℃条件下倒置培养过夜。取800 μL含100 mg/L氨苄青霉素培养基加入一新的1.5 mL EP管中,挑取上述固体培养基上若干菌落,接种于该管,37 ℃下振荡培养5-8 h。取1 μL上述培养菌液为模板,进行PCR,反应条件和体系如前所述。
1.4.5 质粒的提取、重组质粒酶切鉴定 选取阳性克隆的菌液按1∶100的比例扩接至5 mL含100 mg/L氨苄青霉素的LB培养基中,37 ℃、220 r/min下培养过夜;收集菌液,按照质粒提取试剂盒(美国OMEGA公司)说明书步骤进行质粒提取。反应体系中质粒3 μL,XhoⅠ0.4 μL,Not Ⅰ0.4 μL,10×buffer 1 μL,ddH2O 5.2 μL,于37 ℃酶切2 h。采用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳对酶切产物进行检测,将酶切鉴定完毕的质粒进行测序(上海生工生物工程有限公司)。
1.4.6 基因点突变 将构建好的质粒稀释100倍,分别取 1 µL做模板进行PCR反应,体系如下:PrimeSTAR® HS DNA Polymerase(日本Takara公司)0.5 μL,5×PrimeSTAR buffer 5 μL,dNTP Mix(2.5 mmol/L each)2 μL,MUT-F (10 μmol/L)和MUT-R(10 μmol/L)各0.5 μL,模板1 μL。PCR反应条件如下:94 ℃预变性5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,65 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 7 min 30 s,连续18个循环;72 ℃ 10 min,于4 ℃保存。PCR产物用Dpn Ⅰ进行酶切,以消化掉模板DNA,反应体系如下:PCR产物17 μL,10×T buffer 2 μL,Dpn Ⅰ酶1 μL,37 ℃消化3.0-4.0 h。
1.4.7 酶切产物转化 在100 μL大肠杆菌DH5α感受态细胞中加入10 μL酶切产物,混匀;先将上述大肠杆菌细胞放置于冰上30 min,42 ℃热激90 s,再次置于冰上2 min; 加入800 mL LB 液体培养基,37 ℃,220 r/min下培养1 h;4 000 r/min条件下离心5 min,弃去大部分上清,其余上清用于重悬菌体;将菌液均匀涂布于含100 mg/L氨苄青霉素固体培养基上,37 ℃条件下倒置培养过夜。挑取1个上述固体培养基菌落,接种于含100 mg/L氨苄青霉素LB培养基上,在37 ℃,220 r/min条件下培养5 h,取200 μL菌液进行测序(由上海生工生物工程有限公司完成)。
1.4.8 质粒共转染采用双荧光素酶报告基因进行检测 实验分为4组:ULK1-WT+NC组用ULK1野生型质粒和NC进行共转染;ULK1-WT+140-5p mimics组用ULK1野生型质粒和miR-140-5p mimics进行共转染;ULK1-MUT+NC组用ULK1突变型质粒和NC进行共转染;ULK1-MUT+ 140-5p mimics组用ULK1突变型质粒和140-5p mimics进行共转染(NC和miR-140-5p mimics,上海吉玛制药技术有限公司)。
转染开始前1 d,先将293T细胞接种于24孔板上,2×104个/孔,培养基采用含10%FBS的高糖DMEM培养基;转染当天,取出长至80%的细胞,弃旧培养液;用PBS(美国Gibco公司)洗涤细胞一两次;加入胰酶,清洗培养皿底部,弃去胰酶,在37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱(3111型CO2细胞培养箱,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)中反应两三分钟后,在倒置荧光显微镜(DMI8型倒置荧光显微镜,德国Leica公司)下观察,当细胞即将脱离而变为圆粒状时,加入新鲜培养液,使均匀遍布皿底,制备成单细胞悬液;计数,并将细胞浓度调整为8×108 L-1;取出24孔板,接种浓度为8×108 L-1细胞悬液100 μL,置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱中过夜。次日,进行质粒与miRNA共转染:将30 pmol miRNA加入125 μL的无血清高糖DMEM培养基中,混匀;将4 μg质粒加入125 μL的无血清DMEM培养基(美国Gibco公司)中,混匀;在125 μL的无血清高糖DMEM培养基中加入5 μL Lipofectamine™ 2000 (Lipofectamine™ 2000转染试剂盒,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司),柔和混匀;在125 μL的无血清高糖DMEM培养基中加入10 μL Lipofectamine™ 2000,柔和混匀;室温放置5 min;分别将稀释好的miRNA与Lipofectamine™ 2000混合,柔和混匀,室温放置20 min,以便形成miRNA/Lipofectamine™ 2000复合物;将质粒稀释培养液与Lipofectamine™ 2000稀释培养液混匀,室温下放置 20 min,从而形成质粒/Lipofectamine™ 2000复合物;分别将250 μL质粒/Lipofectamine™ 2000复合物、miRNA/Lipofectamine™ 2000复合物加入到含细胞和培养基的培养板孔中,混匀;转染48 h后,进行后续检测;弃旧培养基,用PBS清洗2次,将100 μL的PLB(Passive Lysis Buffer)(美国Promega公司)分别加入每孔中,室温下振摇15 min,最后收集细胞裂解液;在发光板上加20 μL细胞裂解液,采用酶标仪(Varioskan Flash型全波长多功能酶标仪,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)读取背景值2 s;在每个样品中加入100 μL LARⅡ工作液(美国Promega公司),快速混匀后读值2 s;在每个样品中再加入100 μL Stop Glo® Reagent(美国Promega公司),快速混匀后再次读值 2 s;保存数据,进行数据分析。
1.4.9 Western blot检测 用miR-140-5p inhibitor(上海吉玛制药技术有限公司)干预6孔板中的细胞,inhibitor浓度为20 μmo/L,每孔加入5 μL。作用48 h后收集293T细胞,利用蛋白提取试剂盒提取细胞总蛋白,BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(Pierce® BCA蛋白定量分析试剂盒,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司)测浓度后进行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,下一步转印至PVDF膜,用体积分数5%牛奶封闭1 h,接着加入兔源ULK1蛋白(1∶1 000稀释)或兔源GAPDH蛋白(1∶1 000稀释),4 ℃孵育过夜;第2天用TBST洗膜后,分别加入辣根过氧化物酶标记羊抗兔IgG(1∶2 000稀释;ULK1蛋白一抗、GAPDH蛋白一抗、辣根过氧化物酶标记羊抗兔IgG,美国Proteintech公司),室温下孵育1 h,再次用TBST洗膜后加入ECL发光液进行显色。
结果蛋白条带采用多功能成像系统(Tanon 5200 Multi多功能成像系统,上海天能科技有限公司)拍照,并分析条带灰度值,以ULK1灰度值/内参GAPDH灰度值的结果作为ULK1蛋白相对表达量。
1.5 主要观察指标 各组荧光素酶的表达活性及ULK1蛋白表达。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 18.0软件对所得数据进行统计学分析,分析结果以x±s表示。两组间比较采用独立样本t 检验。采用单因素方差分析对多组间均数进行比较;组间均数两两比较采用SNK法或Dunnett’s T3法,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
.jpg) 文题释义:
荧光素酶报告基因:荧光素酶报告基因是指以荧光素(luciferin)为底物来检测萤火虫荧光素酶(fireflyluciferase)活性的一种报告系统。
荧光素酶:可催化荧光素氧化,在荧光素氧化的过程中,会发出生物荧光。荧光素和荧光素酶这一生物发光体系,可以极其灵敏、高效地检测基因的表达。是检测转录因子与目的基因启动子区DNA相互作用的一种检测方法。
文题释义:
荧光素酶报告基因:荧光素酶报告基因是指以荧光素(luciferin)为底物来检测萤火虫荧光素酶(fireflyluciferase)活性的一种报告系统。
荧光素酶:可催化荧光素氧化,在荧光素氧化的过程中,会发出生物荧光。荧光素和荧光素酶这一生物发光体系,可以极其灵敏、高效地检测基因的表达。是检测转录因子与目的基因启动子区DNA相互作用的一种检测方法。.jpg) 文题释义:
荧光素酶报告基因:荧光素酶报告基因是指以荧光素(luciferin)为底物来检测萤火虫荧光素酶(fireflyluciferase)活性的一种报告系统。
荧光素酶:可催化荧光素氧化,在荧光素氧化的过程中,会发出生物荧光。荧光素和荧光素酶这一生物发光体系,可以极其灵敏、高效地检测基因的表达。是检测转录因子与目的基因启动子区DNA相互作用的一种检测方法。
文题释义:
荧光素酶报告基因:荧光素酶报告基因是指以荧光素(luciferin)为底物来检测萤火虫荧光素酶(fireflyluciferase)活性的一种报告系统。
荧光素酶:可催化荧光素氧化,在荧光素氧化的过程中,会发出生物荧光。荧光素和荧光素酶这一生物发光体系,可以极其灵敏、高效地检测基因的表达。是检测转录因子与目的基因启动子区DNA相互作用的一种检测方法。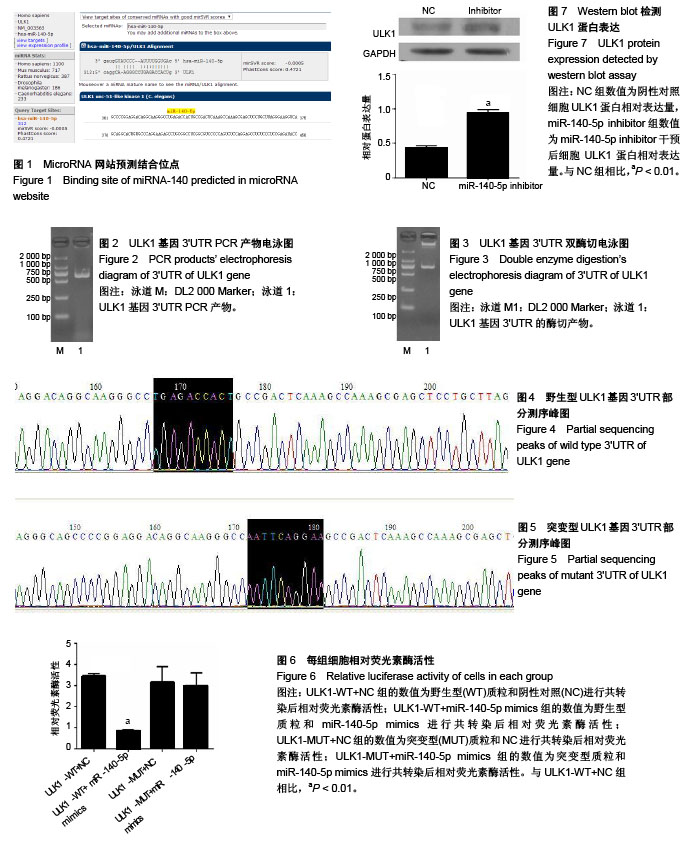
.jpg) 文题释义:
荧光素酶报告基因:荧光素酶报告基因是指以荧光素(luciferin)为底物来检测萤火虫荧光素酶(fireflyluciferase)活性的一种报告系统。
荧光素酶:可催化荧光素氧化,在荧光素氧化的过程中,会发出生物荧光。荧光素和荧光素酶这一生物发光体系,可以极其灵敏、高效地检测基因的表达。是检测转录因子与目的基因启动子区DNA相互作用的一种检测方法。
文题释义:
荧光素酶报告基因:荧光素酶报告基因是指以荧光素(luciferin)为底物来检测萤火虫荧光素酶(fireflyluciferase)活性的一种报告系统。
荧光素酶:可催化荧光素氧化,在荧光素氧化的过程中,会发出生物荧光。荧光素和荧光素酶这一生物发光体系,可以极其灵敏、高效地检测基因的表达。是检测转录因子与目的基因启动子区DNA相互作用的一种检测方法。