中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (24): 3837-3842.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0267
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
跑步运动结合摄取杜仲提取物对去卵巢大鼠骨密度和抗氧化能力的影响
程 林
- 重庆人文科技学院体育学院,重庆市 401524
Effects of the combination of running and Eucommia ulmoides extract on the bone mineral density and antioxidant capacity in ovariectomized rats
Cheng Lin
- Department of Sports, Chongqing College of Humanities, Science & Technology, Chongqing 401524, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
杜仲:又名木棉、思仙。从杜仲中提取的化学成分按其结构可分为木脂素类、环烯醚萜类、黄酮类、苯丙素类、萜类、多糖类等。杜仲具有降血压、降血脂、降血糖、抗肿瘤、抗菌抗病毒、抗炎、抗氧化、保肝护肾、防止骨量流失等药理作用。
运动氧化伤害:机体剧烈运动过程中及运动结束后, 组织代谢率的增加导致氧自由基产生增加, 引起机体氧自由基代谢失衡,进而引发红细胞、心肌及骨骼肌等细胞的细胞膜及细胞器结构损伤甚至凋亡,造成运动氧化伤害。
摘要
背景:研究显示运动导致骨密度增加,并可改善身体组成。但妇女停经后身体抗氧化能力大幅下降,所以预防运动造成的氧化伤害亦非常关键。杜仲具有对改善骨密度和抗氧化效果,利用运动搭配杜仲摄入,尝试既可以改善更年期骨密度又能减少运动氧化伤害的方案。
目的:探讨跑步运动结合摄取杜仲提取物和单纯摄入杜仲提取物对接受卵巢切除大鼠骨密度、血清雌激素、骨质代谢、抗氧化能力的影响。
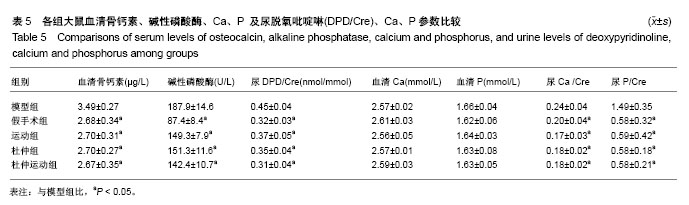
方法:先对大鼠进行1周适应性饲养,随机将大鼠分为2组,分别进行卵巢切除或假手术。大鼠恢复4周后,将切除卵巢大鼠随机分为模型组、杜仲组,杜仲运动组,进行12周干预,干预结束后,将所有大鼠置入代谢笼采集24 h尿样;隔日,所有大鼠进行力竭运动,之后采集大鼠腹腔血液。检测各组大鼠的氧化指标(包括血肌酸激酶、乳酸脱氢酶浓度、丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化酶活性),骨质代谢指标(包括血清骨钙素、碱性磷酸酶、Ca、P浓度以及尿液中的脱氧吡啶啉、Ca、P水平),同时记录大鼠的体质量变化、血清雌二醇水平和股骨骨密度值。
结果与结论:经12周干预后,杜仲组和杜仲运动组大鼠体质量、丙二醛、骨钙、碱性磷酸酶、磷浓度显著低于模型组(P < 0.05);血清雌二醇、股骨骨密度显著高于模型组(P < 0.05)。杜仲运动组各项指标均优于杜仲组和运动组,但未达到显著性差异(P > 0.05)。说明长期进行跑步运动并结合摄取杜仲提取物或单纯摄取杜仲提取物均可以显著提升切除卵巢骨质疏松大鼠的骨密度、血清雌激素水平,并可以促进骨代谢平衡,降低骨转换率和因卵巢功能降低导致的体质量增加,能够起到维护骨量、防止骨质疏松作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5362-4894(程林)
中图分类号:
.jpg)