| [1] Kirchberger I, Sinnott A, Charlifue S, et al. Functioning and disability in spinal cord injury from the consumer perspective: an international qualitative study using focus groups and the ICF. Spinal Cord.2010;48:603-613.[2] Burke DA, Linden RD, Zhang YP, et al. Incidence rates and populations at risk for spinal cord injury: a regional study.Spinal Cord.2001;39(5):274-278.[3] Devivo MJ. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury: trends and future implications.Spinal Cord. 2012;50(5):365-372.[4] 杨枭雄,于前进,秦江,等.脊髓损伤住院患者1027例流行病学分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(5):301-305.[5] Pickett GE,Campos-Benitez M, Keller JL,et al.Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury in Canada.Spine.2006;31(7):799-805. [6] Bauchet L,Lonjon N, Perrin FE, et al. Strategies for spinal cord repair after injury: A review of the literature and information.Ann Phys Rehabil Med.2009; 52(4):330-351.[7] Rowland JW,Hawryluk GW,Kwon B,et al.Current status of acute spinal cord injury pathophysiology and emerging therapies: promise on the horizon. Neurosurg Focus.2008;25(5):E2.[8] McDonald JW, Sadowsky C.Spinal-cord injury.Lancet.2002; 359: 417-425.[9] Dumont RJ,Okonkwo DO,Verma S,et al.Acute spinal cord injury, part I: pathophysiologic mechanisms. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2001;24:254-264.[10] Kwon BK, Tetzlaff W, Grauer JN,et al. Pathophysiology and pharmacologic treatment of acute spinal cord injury.Spine J. 2004;4:451-464.[11] Allen AR. Surgery of experimental lesion of spinal cord equivalent to crush injury of fracture dislocation of spinal column: A preliminary report.JAMA.1911;57:878-880.[12] Oyinbo CA. Secondary injury mechanisms in traumatic spinal cord injury: a nugget of this multiply cascade. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars).2011;71:281-299.[13] Hausmann ON.Post-traumatic inflammation following spinal cord injury.Spinal Cord.2003;41:369-378.[14] Hayashi M, Ueyama T, Nemoto K, et al. Sequential mRNA expression for immediate early genes, cytokines, and neurotrophins in spinal cord injury.J Neurotrauma.2000;17: 203-218.[15] Bastien D, Lacroix S. Cytokine pathways regulating glial and leukocyte function after spinal cord and peripheral nerve injury. Exp Neurol.2014;258:62-77.[16] Pan JZ, Ni L, Sodhi A, et al. Cytokine activity contributes to induction of inflammatory cytokine mRNAs in spinal cord following contusion. J Neurosci Res.2002;68:315-322.[17] 李建军,王方永.脊髓损伤神经学分类国际标准(2011 年修订)[J].中国康复理论与实践,2011,17(10):963-972.[18] American Spinal Injury Association. Standard neurological classification of spinal cord injury. Continuum.2011;17(3): 644-645. [19] 李珂珂,宗少晖.脊髓损伤中的免疫炎性细胞因子[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(53):8646.[20] Behtea JR, Dleitreh WD.Targeting the host inflammatory response in traumatic spinal cord injury. Curr Opin Neurol.2002; 15(3):355-360.[21] 郭宗铎,孙晓川.白介素-6与颅脑损伤[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2006,32(3):282-283.[22] 庄志,顾红兵,朱灿宏. IL-1和IL-6在脊髓损伤大鼠神经细胞中的表达及其动态变化[J]. 医药论坛杂志,2010,31(23):38-40.[23] Frei K,Nadal D,Fontana A,et al.Intracerebral Synthesis of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-6 in Infectious Meningitisa. Ann NY Acad Sci.1990; 594(1):326-335.[24] 宗少晖,方晔,彭金珍,等.急性不完全脊髓损伤模型大鼠相关炎症因子的表达[J].中国国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2806-2811.[25] 郑晶晶,姚安会,刘芳芳,等.小鼠脊髓损伤早期不同炎症因子的表达变化[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2012,28(4):391-394.[26] Song Y, Liu J, Zhang F, et al. Antioxidant effect of quercetin against acute spinal cord injury in rats and its its correlation with the p38MAPK/iNOS signaling pathway. Life Sci.2013;92(24-26): 1215-1221.[27] Wang CX, Shuaib A.Involvement of inflammatory cytokines in central nervous system injury. Prog Neurobiol.2002;67(2):161-172.[28] Pan W, Zhang L, Liao J, et al. Selective increase in TNF-α permeation across the blood-spinal cord barrier after SCI.J Neuroimmunol.2003;134(1-2):111-117.[29] 毕爱华.医学免疫学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,1997:71-72.[30] Gebhard F,Pfetsch H, Steinbach G, et al. Is interleukin6 an early marker of injury severity following major traumain humans?. Arch Surg.2000;135(3):291 -295.[31] Wang Q,Fang CH,Hasselgren P.Intestinal permeability is reduced and IL-10 levels are increased in septic IL-6 knockout mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.2001;281:R1013-1023.[32] Meng ZH, Dyer K, Billiar TR,et al. Essential role for IL-6 in postresuscitation inflammation in hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2001;280(2):C343-C351.[33] Leon LR, White AA, Kluger MJ. Role of IL-6 and TNF in thermoregulation and survival during sepsis in mice. Am J Physiol.1998;275:R269-277.[34] Kanemoto M, Hukuda S, Komiya Y, et al.Immunohistochemical study of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 human intervertebral discs.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1996;21(1):1-8.[35] Tuna M, Polat S, Erman T, et al. Effect of anti-rat interleukin-6 antibody after spinal cord injury in the rat: inducible nitric oxide synthase expression, sodium- and potassium-activated, magnesium-dependent adenosine-5′-triphosphatase and superoxide dismutase activation, and ultrastructural changes. J Neurosurg. 2001;95(1):64-73.[36] Kollias HD,McDermott JC.Transforming growth factor-β and myostatin signaling in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol.2008; 104(3):579-587.[37] Keski-Oja J, Koli K, von Melchner H.TGF-beta activation by traction? Trends Cell Biol.2004;14: 657-659.[38] Buss A, Pech K, Kakulas BA, et al.TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 expression after traumatic human spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2008;46:364-371.[39] Yang L, Blumbergs PC, Jones NR, et al. Early expression and cellular localization of prion flammatory cytokines interleukin-beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human traumatic spinal cord injury.Spine.2004;29:966-971.[40] Sporn MB, Roberts AB.Transforming growth factor-beta: Recent progress and new challenges.Cell Biol. 1992;119:1017-1021.[41] Moses HL,Yang EY,Pietenpol JA.TGF-beta stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation: new mechanistic insights.Cell.1990; 63:245-247.[42] Roelen BA,Dijke P.Controlling mesenchymal stem cell differentiation by TGFBeta family members.J Orthop Sci.2003;8: 740-748.[43] 冯均伟,王跃,吕波,等.骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导成软骨细胞的动态观察[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(36):6409-6416.[44] Ritz MF, Graumann U, Gutierrez B,et al.Traumatic spinal cord injury alters angiogenic factors and TGF-beta1 that may affect vascular recovery. Curr Neurovasc Res.2010;7(4):301-310.[45] Aigner L, Bogdahn U. TGF‐beta in neural stem cells and in tumors of the central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res.2008; 331:225-241.[46] Tyor WR, Avgeropoulos N, Ohlandt G, et al. Treatment of spinal cord impact injury in the rat with transforming growth factor-beta.J Neurol Sci.2002;200:33-41.[47] Ihn H. Autocrine TGF-beta signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis.J Dermatol Sci.2008;49:103-113.[48] Mittaud P,Labourdette G,Zingg H,et al.Neurons modulate oxytocin receptor expression in rat cultured astrocytes: involvement of TGF-beta and membrane components.Glia.2002;37:169-177.[49] Letterio JJ,Roberts AB.Regulation of immune responses by TGF-beta.Annu Rev Immunol.1998;16:137-161.[50] Wahl SM,Hunt DA,Wakefield LM,et al.Transforming growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1987;84:5788-5792.[51] Werner F, Jain MK, Feinberg MW, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibition of macrophage activation is mediated via Smad3.J Biol Chem.2000;275:36653-36658.[52] Feinberg MW, Shimizu K, Lebedeva M, et al. Essential role for Smad3 in regulating MCP-1 expression and vascular inflammation. Circ Res.2004;94:601-608.[53] Kohta M, Kohmura E,Yamashita T. Inhibition of TGF-beta1 promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res.2009;65(4):393-401. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
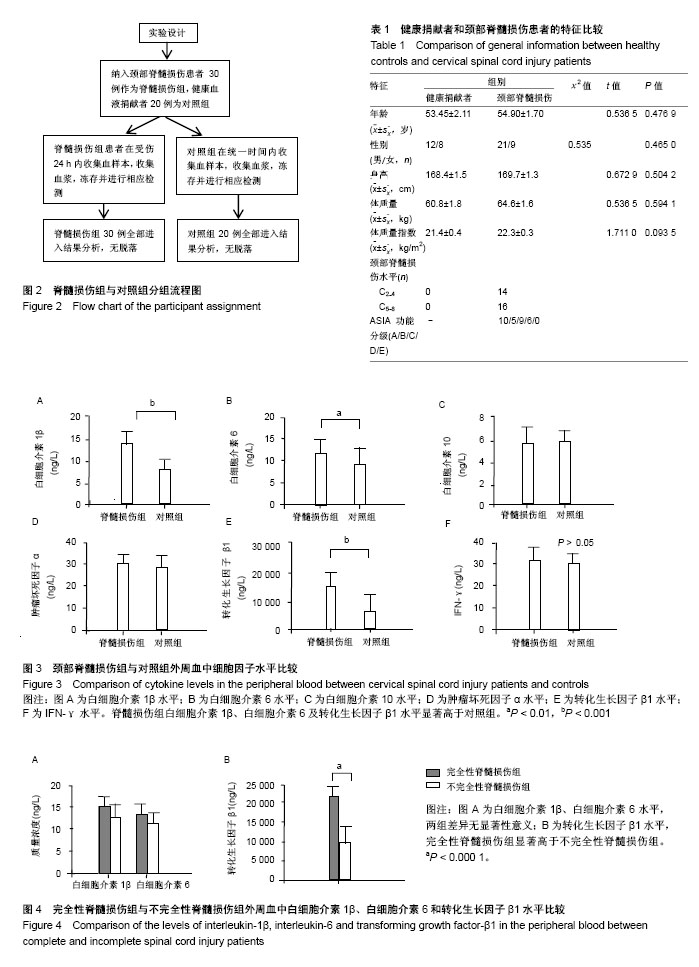
.jpg)
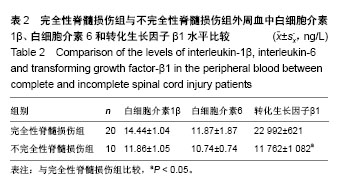
.jpg)