| [1]Lozano R,Naghavi M,Foreman K,et al.Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (vol 380, pg 2095, 2012). Lancet.2013;381(9867): 628-628.[2]Amezcua R,Shirolkar A,Fraze C,et al.Nanomaterials for Cardiac Myocyte Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials.2016;6(7):133.[3]Chan V,Raman R,Cvetkovic C,et al.Enabling Microscale and Nanoscale Approaches for Bioengineered Cardiac Tissue.Acs Nano.2013;7(3):1830-1837.[4]Liu Y,Lu J,Xu G,et al.Tuning the conductivity and inner structure of electrospun fibers to promote cardiomyocyte elongation and synchronous beating.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69: 865-874.[5]Zhou J,Chen J,Sun H,et al.Engineering the heart: evaluation of conductive nanomaterials for improving implant integration and cardiac function.Sci Rep.2014;4:3733.[6]Chen YS,Tsou PC,Lo JM,et al.Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with interpenetrating multiwalled carbon nanotubes for cell sheet engineering.Biomaterials.2013;34(30):7328-7334.[7]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon nanotubes promote growth and spontaneous electrical activity in cultured cardiac myocytes.Nano Lett.2012;12(4):1831-1838.[8]Pok S,Vitale F,Eichmann SL,et al.Biocompatible Carbon Nanotube-Chitosan Scaffold Matching the Electrical Conductivity of the Heart.Acs Nano.2014;8(10):9822-9832.[9]Hopley EL,Salmasi S,Kalaskar DM,et al.Carbon nanotubes leading the way forward in new generation 3D tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv.2014;32(5):1000-1014.[10]Atif R, Inam F.Reasons and remedies for the agglomeration of multilayered graphene and carbon nanotubes in polymers. Beilstein J Nanotechnol.2016;7:1174-1196.[11]Sun H,Lü S,Jiang XX,et al.Carbon nanotubes enhance intercalated disc assembly in cardiac myocytes via the beta1-integrin-mediated signaling pathway.Biomaterials.2015;55:84-95.[12]Ahadian S,Yamada S,Ramón-Azcón J,et al.Hybrid hydrogel-aligned carbon nanotube scaffolds to enhance cardiac differentiation of embryoid bodies.Acta Biomater.2016;31:134-143.[13]Kharaziha M,Shin SR,Nikkhah M,et al.Tough and flexible CNT-polymeric hybrid scaffolds for engineering cardiac constructs. Biomaterials.2014;35(26):7346-7354.[14]Crowder SW,Liang Y,Rath R,et al. Poly(epsilon-caprolactone)- carbon nanotube composite scaffolds for enhanced cardiac differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanomedicine. 2013;8(11):1763-1776.[15]Shin SR,Jung SM,Zalabany M,et al.Carbon-nanotube-embedded hydrogel sheets for engineering cardiac constructs and bioactuators. Acs Nano.2013;7(3):2369-2380.[16]Li X,Zhou J,Liu Z,et al.A PNIPAAm-based thermosensitive hydrogel containing SWCNTs for stem cell transplantation in myocardial repair.Biomaterials.2014;35(22):5679-5688.[17]Zeng YZ,Lu JQ.Optothermally Responsive Nanocomposite Generating Mechanical Forces for Cells Enabled by Few-Walled Carbon Nanotubes.Acs Nano.2014;8(11):11695-11706.[18]Mananghaya M.Modeling of single-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with carboxylic and amide groups towards its solubilization in water.J Mol Liq.2015;212:592-596.[19]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon Nanotubes Instruct Physiological Growth and Functionally Mature Syncytia: Nongenetic Engineering of Cardiac Myocytes.Acs Nano. 2013; 7(7):5746-5756.[20]Bayazit MK,Coleman KS.Ester-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes via addition of haloformates.J Mater Sci. 2014;49(14):5190-5198.[21]Basiuk EV,Ramírez-Calera TJ,Meza-Laguna V,et al.Solvent-free functionalization of carbon nanotube buckypaper with amines. Appl Surf Sci.2015;357:1355-1368.[22]Wu, B,Li Y,Wang C,et al.High aqueous solubility of carboxylated-carbon nanotubes as support for PtRu nanoparticles: Enhanced dispersion and electrocatalytic performance.Int J Hydrogen Energy.2014;39(14):7318-7325.[23]Liang S,Li G,Tian R.Multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with a ultrahigh fraction of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups by ultrasound-assisted oxidation.JMater Sci.2015;51(7):3513-3524.[24]Mooney E,Mackle JN,Blond DJ,et al.The electrical stimulation of carbon nanotubes to provide a cardiomimetic cue to MSCs. Biomaterials.2012;33(26):6132-6139.[25]Kalinina I,Al-Hadeethi YF,Bekyarova E,et al.Solution-phase synthesis of chromium-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.Mater Lett.2015;142:312-316.[26]Gu SY,Gao XF,Zhang YH.Synthesis and characterization of solvent-free ionic molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) nanofluids. Mater Chem Phys.2015;149-150:587-593.[27]Parra-Vasquez AN,Behabtu N,Green MJ,et al.Spontaneous Dissolution of Ultralong Single- and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Acs Nano.2010;4(7):3969-3978.[28]Davis VA,Parra-Vasquez AN,Green MJ,et al.True solutions of single-walled carbon nanotubes for assembly into macroscopic materials.Nat Nanotechnol.2009;4(12):830-834.[29]Wese?ucha-Birczyńska A,Stodolak-Zych E,Turrell S,et al. Vibrational spectroscopic analysis of a metal/carbon nanotube coating interface and the effect of its interaction with albumin.Vib Spectrosc.2016;85:185-195.[30]Ramesh S,Ericson L,Davis VA,et al.Dissolution of pristine single walled carbon nanotubes in superacids by direct protonation.J Phys Chem B.2004;108(26):8794-8798.[31]Dyke CA,Tour JM.Covalent functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes for materials applications.J Phys Chem A. 2004;108(51):11151-11159.[32]Zhu WH,MinamiN,KazaouiS,et al.π-Chromophore-functionalized SWNTs by covalent bonding: substantial change in the optical spectra proving strong electronic interaction.J Mater Chem. 2004; 14(13):1924-1926.[33]Omastová M,Mi?ušík M,Fedorko P,et al.The synergy of ultrasonic treatment and organic modifiers for tuning the surface chemistry and conductivity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes.Surf Interface Anal.2014;46(10-11):940-944.[34]Namgung S,Baik KY,Park J,et al.Controlling the growth and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by the arrangement of individual carbon nanotubes.Acs Nano. 2011; 5(9):7383-7390.[35]Chen Z,Zhang J,Guo Y,et al.Effects of various factors on the modification of carbon nanotubes with polyvinyl alcohol in supercritical CO2 and their application in electrospun fibers.Chem Res Chin U.2014;30(4):690-697.[36]Umemura K.Hybrids of Nucleic Acids and Carbon Nanotubes for Nanobiotechnology. Nanomaterials.2015; 5(1):321-350.[37]Huang CW,Mohamed MG,Zhu CY,et al.Functional Supramolecular Polypeptides Involving pi-pi Stacking and Strong Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions: A Conformation Study toward Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Dispersion. Macromolecules. 2016; 49(15):5374-5385.[38]Nepal D,Geckeler KE.Proteins and carbon nanotubes: close encounter in water.Small.2007;3(7):1259-1265.[39]Shin SR,Bae H,Cha JM,et al.Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Hybrid Microgels as Scaffold Materials for Cell Encapsulation.Acs Nano. 2012;6(1):362-372.[40]Eguílaz M,Gutiérrez A,Rivas G.Non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with cytochrome c: Enhanced direct electron transfer and analytical applications.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2016;225:74-80.[41]Wei D,Kvarnström C,Lindfors T,et al.Electrochemical functionalization of single walled carbon nanotubes with polyaniline in ionic liquids. Electrochem commun.2007;9(2):206-210.[42]Roohi H,Khyrkhah S.Green chemical functionalization of single-wall carbon nanotube with methylimidazolium dicyanamid ionic liquid: A first principle computational exploration.J Mol Liq. 2015. 211(1):498-505.[43]Raiah K,Djalab A,Hadj-Ziane-Zafour A,et al.Influence of the hydrocarbon chain length of imidazolium-based ionic liquid on the dispersion and stabilization of double-walled carbon nanotubes in water.Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2015;469(6): 107-116. [1]Lozano R,Naghavi M,Foreman K,et al.Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (vol 380, pg 2095, 2012). Lancet.2013;381(9867): 628-628.[2]Amezcua R,Shirolkar A,Fraze C,et al.Nanomaterials for Cardiac Myocyte Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials.2016;6(7):133.[3]Chan V,Raman R,Cvetkovic C,et al.Enabling Microscale and Nanoscale Approaches for Bioengineered Cardiac Tissue.Acs Nano.2013;7(3):1830-1837.[4]Liu Y,Lu J,Xu G,et al.Tuning the conductivity and inner structure of electrospun fibers to promote cardiomyocyte elongation and synchronous beating.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69: 865-874.[5]Zhou J,Chen J,Sun H,et al.Engineering the heart: evaluation of conductive nanomaterials for improving implant integration and cardiac function.Sci Rep.2014;4:3733.[6]Chen YS,Tsou PC,Lo JM,et al.Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels with interpenetrating multiwalled carbon nanotubes for cell sheet engineering.Biomaterials.2013;34(30):7328-7334.[7]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon nanotubes promote growth and spontaneous electrical activity in cultured cardiac myocytes.Nano Lett.2012;12(4):1831-1838.[8]Pok S,Vitale F,Eichmann SL,et al.Biocompatible Carbon Nanotube-Chitosan Scaffold Matching the Electrical Conductivity of the Heart.Acs Nano.2014;8(10):9822-9832.[9]Hopley EL,Salmasi S,Kalaskar DM,et al.Carbon nanotubes leading the way forward in new generation 3D tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv.2014;32(5):1000-1014.[10]Atif R, Inam F.Reasons and remedies for the agglomeration of multilayered graphene and carbon nanotubes in polymers. Beilstein J Nanotechnol.2016;7:1174-1196.[11]Sun H,Lü S,Jiang XX,et al.Carbon nanotubes enhance intercalated disc assembly in cardiac myocytes via the beta1-integrin-mediated signaling pathway.Biomaterials.2015;55:84-95.[12]Ahadian S,Yamada S,Ramón-Azcón J,et al.Hybrid hydrogel-aligned carbon nanotube scaffolds to enhance cardiac differentiation of embryoid bodies.Acta Biomater.2016;31:134-143.[13]Kharaziha M,Shin SR,Nikkhah M,et al.Tough and flexible CNT-polymeric hybrid scaffolds for engineering cardiac constructs. Biomaterials.2014;35(26):7346-7354.[14]Crowder SW,Liang Y,Rath R,et al. Poly(epsilon-caprolactone)- carbon nanotube composite scaffolds for enhanced cardiac differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Nanomedicine. 2013;8(11):1763-1776.[15]Shin SR,Jung SM,Zalabany M,et al.Carbon-nanotube-embedded hydrogel sheets for engineering cardiac constructs and bioactuators. Acs Nano.2013;7(3):2369-2380.[16]Li X,Zhou J,Liu Z,et al.A PNIPAAm-based thermosensitive hydrogel containing SWCNTs for stem cell transplantation in myocardial repair.Biomaterials.2014;35(22):5679-5688.[17]Zeng YZ,Lu JQ.Optothermally Responsive Nanocomposite Generating Mechanical Forces for Cells Enabled by Few-Walled Carbon Nanotubes.Acs Nano.2014;8(11):11695-11706.[18]Mananghaya M.Modeling of single-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with carboxylic and amide groups towards its solubilization in water.J Mol Liq.2015;212:592-596.[19]Martinelli V,Cellot G,Toma FM,et al.Carbon Nanotubes Instruct Physiological Growth and Functionally Mature Syncytia: Nongenetic Engineering of Cardiac Myocytes.Acs Nano. 2013; 7(7):5746-5756.[20]Bayazit MK,Coleman KS.Ester-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes via addition of haloformates.J Mater Sci. 2014;49(14):5190-5198.[21]Basiuk EV,Ramírez-Calera TJ,Meza-Laguna V,et al.Solvent-free functionalization of carbon nanotube buckypaper with amines. Appl Surf Sci.2015;357:1355-1368.[22]Wu, B,Li Y,Wang C,et al.High aqueous solubility of carboxylated-carbon nanotubes as support for PtRu nanoparticles: Enhanced dispersion and electrocatalytic performance.Int J Hydrogen Energy.2014;39(14):7318-7325.[23]Liang S,Li G,Tian R.Multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with a ultrahigh fraction of carboxyl and hydroxyl groups by ultrasound-assisted oxidation.JMater Sci.2015;51(7):3513-3524.[24]Mooney E,Mackle JN,Blond DJ,et al.The electrical stimulation of carbon nanotubes to provide a cardiomimetic cue to MSCs. Biomaterials.2012;33(26):6132-6139.[25]Kalinina I,Al-Hadeethi YF,Bekyarova E,et al.Solution-phase synthesis of chromium-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.Mater Lett.2015;142:312-316.[26]Gu SY,Gao XF,Zhang YH.Synthesis and characterization of solvent-free ionic molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) nanofluids. Mater Chem Phys.2015;149-150:587-593.[27]Parra-Vasquez AN,Behabtu N,Green MJ,et al.Spontaneous Dissolution of Ultralong Single- and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Acs Nano.2010;4(7):3969-3978.[28]Davis VA,Parra-Vasquez AN,Green MJ,et al.True solutions of single-walled carbon nanotubes for assembly into macroscopic materials.Nat Nanotechnol.2009;4(12):830-834.[29]Wese?ucha-Birczyńska A,Stodolak-Zych E,Turrell S,et al. Vibrational spectroscopic analysis of a metal/carbon nanotube coating interface and the effect of its interaction with albumin.Vib Spectrosc.2016;85:185-195.[30]Ramesh S,Ericson L,Davis VA,et al.Dissolution of pristine single walled carbon nanotubes in superacids by direct protonation.J Phys Chem B.2004;108(26):8794-8798.[31]Dyke CA,Tour JM.Covalent functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes for materials applications.J Phys Chem A. 2004;108(51):11151-11159.[32]Zhu WH,MinamiN,KazaouiS,et al.π-Chromophore-functionalized SWNTs by covalent bonding: substantial change in the optical spectra proving strong electronic interaction.J Mater Chem. 2004; 14(13):1924-1926.[33]Omastová M,Mi?ušík M,Fedorko P,et al.The synergy of ultrasonic treatment and organic modifiers for tuning the surface chemistry and conductivity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes.Surf Interface Anal.2014;46(10-11):940-944.[34]Namgung S,Baik KY,Park J,et al.Controlling the growth and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by the arrangement of individual carbon nanotubes.Acs Nano. 2011; 5(9):7383-7390.[35]Chen Z,Zhang J,Guo Y,et al.Effects of various factors on the modification of carbon nanotubes with polyvinyl alcohol in supercritical CO2 and their application in electrospun fibers.Chem Res Chin U.2014;30(4):690-697.[36]Umemura K.Hybrids of Nucleic Acids and Carbon Nanotubes for Nanobiotechnology. Nanomaterials.2015; 5(1):321-350.[37]Huang CW,Mohamed MG,Zhu CY,et al.Functional Supramolecular Polypeptides Involving pi-pi Stacking and Strong Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions: A Conformation Study toward Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) Dispersion. Macromolecules. 2016; 49(15):5374-5385.[38]Nepal D,Geckeler KE.Proteins and carbon nanotubes: close encounter in water.Small.2007;3(7):1259-1265.[39]Shin SR,Bae H,Cha JM,et al.Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Hybrid Microgels as Scaffold Materials for Cell Encapsulation.Acs Nano. 2012;6(1):362-372.[40]Eguílaz M,Gutiérrez A,Rivas G.Non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with cytochrome c: Enhanced direct electron transfer and analytical applications.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2016;225:74-80.[41]Wei D,Kvarnström C,Lindfors T,et al.Electrochemical functionalization of single walled carbon nanotubes with polyaniline in ionic liquids. Electrochem commun.2007;9(2):206-210.[42]Roohi H,Khyrkhah S.Green chemical functionalization of single-wall carbon nanotube with methylimidazolium dicyanamid ionic liquid: A first principle computational exploration.J Mol Liq. 2015. 211(1):498-505.[43]Raiah K,Djalab A,Hadj-Ziane-Zafour A,et al.Influence of the hydrocarbon chain length of imidazolium-based ionic liquid on the dispersion and stabilization of double-walled carbon nanotubes in water.Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2015;469(6): 107-116. |
.jpg)
 2.2 构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的基本步骤 在心肌组织工程中,构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的基本步骤如图1所示,包括在水溶液中稳定分散碳纳米管、混合聚合物支架材料、构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架等3个步骤。
2.2 构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的基本步骤 在心肌组织工程中,构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架的基本步骤如图1所示,包括在水溶液中稳定分散碳纳米管、混合聚合物支架材料、构建碳纳米管/聚合物复合支架等3个步骤。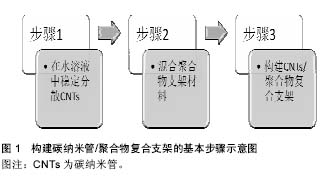
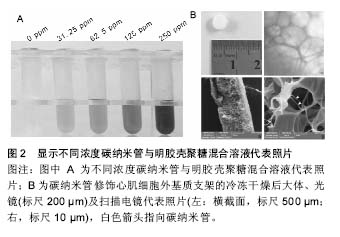
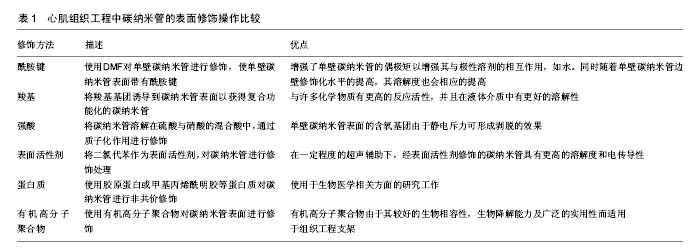
.jpg)