| [1] Ehrlich HP, Desmouliere A, Diegelmann RF, et al. Morphological and immunochemical differences between keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Pathol. 1994;145:105-113. [2] Fujita AK, Rodrigues PG, Requena MB, et al. Fluorescence evaluations for porphyrin formation during topical PDT using ALA and methyl-ALA mixtures in pig skin models. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2016;15:236-244. [3] Chun Q, Zhiyong W, Fei S, et al. Dynamic biological changes in fibroblasts during hypertrophic scar formation and regression. Int Wound J. 2016;13:257-262. [4] Zhang Z, Chen Y, Ding J, et al. Biocompatible 5-Aminolevulinic Acid/Au Nanoparticle-Loaded Ethosomal Vesicles for In Vitro Transdermal Synergistic Photodynamic/ Photothermal Therapy of Hypertrophic Scars. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017;12:622. [5] Wang XQ, Liu YK, Qing C, et al. A review of the effectiveness of antimitotic drug injections for hypertrophic scars and keloids. Ann Plast Surg. 2009;63:688-692. [6] Gauglitz GG, Korting HC, Pavicic T, et al. Hypertrophic scarring and keloids: pathomechanisms and current and emerging treatment strategies. Mol Med 2011;17:113-125. [7] Stylli SS, Howes M, MacGregor L, et al. Photodynamic therapy of brain tumours: evaluation of porphyrin uptake versus clinical outcome. J Clin Neurosci. 2004;11:584-596[8] O'Connell KA, Okhovat JP, Zeitouni NC. Photodynamic Therapy for Bowen's Disease (Squamous Cell Carcinoma in situ) Current Review and Update. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2018. DOI:10. 1016/j.pdpdt.2018.09.009.[9] van der Veer WM, Niessen FB, Ferreira JA, et al. Time course of the angiogenic response during normotrophic and hypertrophic scar formation in humans. Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19:292-301.[10] Chen B, Pogue BW, Luna JM, et al. Tumor vascular permeabilization by vascular-targeting photosensitization: effects, mechanism, and therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:917-923. [11] Peng Q, Berg K, Moan J, et al. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy: principles and experimental research. Photochem Photobiol. 1997;65:235-251.[12] Cohen DK and Lee PK. Photodynamic Therapy for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers. Cancers (Basel). 2016. DOI:10. 1016/j. pdpdt.2018.09.009.[13] Wennberg AM, Stenquist B, Stockfleth E, et al. Photodynamic therapy with methyl aminolevulinate for prevention of new skin lesions in transplant recipients: a randomized study. Transplantation. 2008;86:423-429. [14] Jarvi MT, Niedre MJ, Patterson MS, et al. Singlet oxygen luminescence dosimetry (SOLD) for photodynamic therapy: current status, challenges and future prospects. Photochem Photobiol. 2006; 82:1198-1210. [15] Chang M, Ma X, Ouyang T, et al. Potential molecular mechanisms involved in 5-aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy against human hypertrophic scars. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136:715-727.[16] Kwak DH, Bae TH, Kim WS, et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (bevacizumab) therapy reduces hypertrophic scar formation in a rabbit ear wounding model. Arch Plast Surg. 2016;43:491-497. [17] Ge X, Zhao L, He L, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2, Flk-1/KDR) protects HEK293 cells against CoCl(2) -induced hypoxic toxicity. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012;30:151-157. [18] Tschen EH, Wong DS, Pariser DM, et al. Photodynamic therapy using aminolaevulinic acid for patients with nonhyperkeratotic actinic keratoses of the face and scalp: phase IV multicentre clinical trial with 12-month follow up. Br J Dermatol. 2006;155:1262-1269. [19] Lian N, Li T. Growth factor pathways in hypertrophic scars: Molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:42-50. [20] Armour A, Scott PG and Tredget EE. Cellular and molecular pathology of HTS: basis for treatment. Wound Repair Regen. 2007;15 Suppl 1:S6-S17. [21] Hembry RM and Ehrlich HP. Immunolocalization of collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP) in hypertrophic scar tissue. Br J Dermatol. 1986;115:409-420. [22] Cao PF, Xu YB, Tang JM, et al. HOXA9 regulates angiogenesis in human hypertrophic scars: induction of VEGF secretion by epidermal stem cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7:2998-3007. [23] Bruscino N, Rossi R, Dindelli M, et al. Therapeutic Hotline: Facial skin rejuvenation in a patient treated with photodynamic therapy for actinic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2010;23:86-89. [24] Bruscino N, Lotti T and Rossi R. Photodynamic therapy for a hypertrophic scarring: a promising choice. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2011;27:334-335. [25] Landes R, Illanes A, Goeppner D, et al. A study of concentration changes of Protoporphyrin IX and Coproporphyrin III in mixed samples mimicking conditions inside cancer cells for Photodynamic Therapy. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0202349. [26] Coupienne I, Fettweis G, Rubio N, et al. 5-ALA-PDT induces RIP3-dependent necrosis in glioblastoma. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2011;10:1868-1878. [27] Yang X, Palasuberniam P, Kraus D, et al. Aminolevulinic acid-based tumor detection and therapy: molecular mechanisms and strategies for enhancement. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:25865-25880. [28] Zhang Z, Chen Y, Xu H, et al. 5-Aminolevulinic acid loaded ethosomal vesicles with high entrapment efficiency for in vitro topical transdermal delivery and photodynamic therapy of hypertrophic scars. Nanoscale 2016;8:19270-19279. [29] Fujino M, Nishio Y, Ito H, et al. 5-Aminolevulinic acid regulates the inflammatory response and alloimmune reaction. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;37:71-78. [30] da Luz Dias R, Basso B, Donadio MVF, et al. Leucine reduces the proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells through DNA damage and cell senescence. Toxicol In Vitro. 2018;48:1-10. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
光动力疗法:是用光敏药物和激光活化治疗肿瘤疾病的一种新方法。用特定波长照射肿瘤部位,能使选择性聚集在肿瘤组织的光敏药物活化,引发光化学反应破坏肿瘤。
光动力疗法的临床应用:新一代光动力疗法中的光敏药物会将能量传递给周围的氧,生成活性很强的单态氧。单态氧能与附近的生物大分子发生氧化反应,产生细胞毒性进而杀伤肿瘤细胞。与传统肿瘤疗法相比,光动力疗法的优势在于能够精确进行有效的治疗,不良反应也很小。
文题释义:
光动力疗法:是用光敏药物和激光活化治疗肿瘤疾病的一种新方法。用特定波长照射肿瘤部位,能使选择性聚集在肿瘤组织的光敏药物活化,引发光化学反应破坏肿瘤。
光动力疗法的临床应用:新一代光动力疗法中的光敏药物会将能量传递给周围的氧,生成活性很强的单态氧。单态氧能与附近的生物大分子发生氧化反应,产生细胞毒性进而杀伤肿瘤细胞。与传统肿瘤疗法相比,光动力疗法的优势在于能够精确进行有效的治疗,不良反应也很小。.jpg) 文题释义:
光动力疗法:是用光敏药物和激光活化治疗肿瘤疾病的一种新方法。用特定波长照射肿瘤部位,能使选择性聚集在肿瘤组织的光敏药物活化,引发光化学反应破坏肿瘤。
光动力疗法的临床应用:新一代光动力疗法中的光敏药物会将能量传递给周围的氧,生成活性很强的单态氧。单态氧能与附近的生物大分子发生氧化反应,产生细胞毒性进而杀伤肿瘤细胞。与传统肿瘤疗法相比,光动力疗法的优势在于能够精确进行有效的治疗,不良反应也很小。
文题释义:
光动力疗法:是用光敏药物和激光活化治疗肿瘤疾病的一种新方法。用特定波长照射肿瘤部位,能使选择性聚集在肿瘤组织的光敏药物活化,引发光化学反应破坏肿瘤。
光动力疗法的临床应用:新一代光动力疗法中的光敏药物会将能量传递给周围的氧,生成活性很强的单态氧。单态氧能与附近的生物大分子发生氧化反应,产生细胞毒性进而杀伤肿瘤细胞。与传统肿瘤疗法相比,光动力疗法的优势在于能够精确进行有效的治疗,不良反应也很小。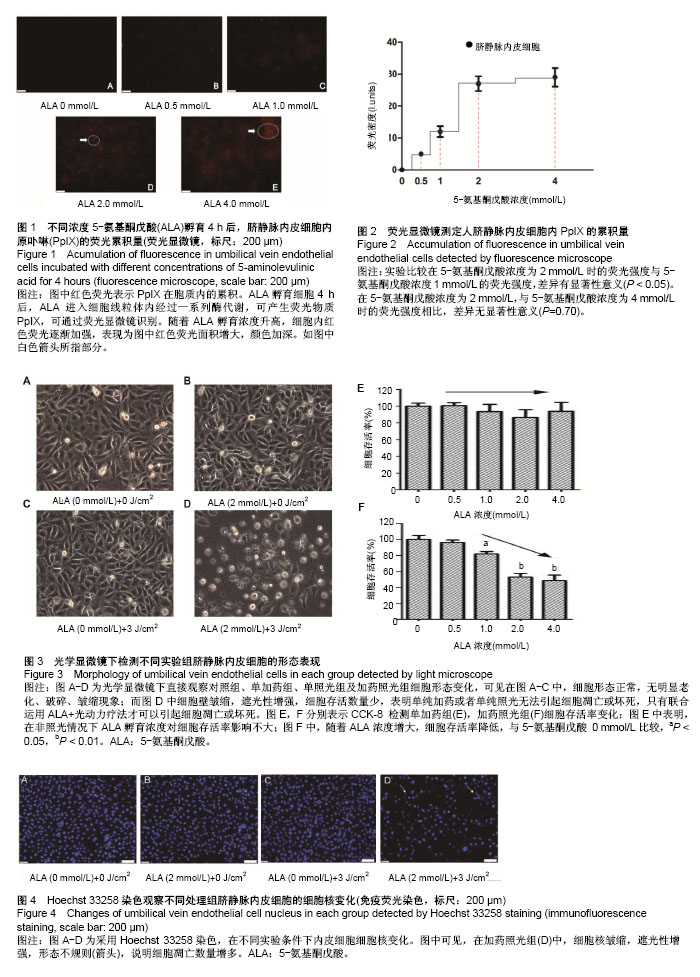
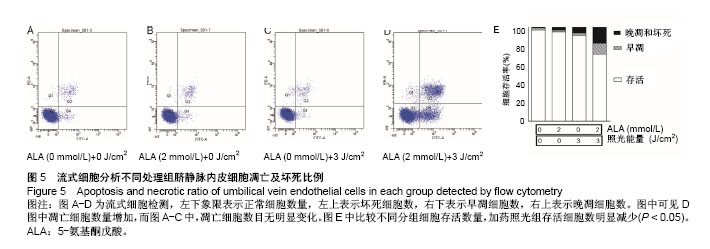
.jpg) 文题释义:
光动力疗法:是用光敏药物和激光活化治疗肿瘤疾病的一种新方法。用特定波长照射肿瘤部位,能使选择性聚集在肿瘤组织的光敏药物活化,引发光化学反应破坏肿瘤。
光动力疗法的临床应用:新一代光动力疗法中的光敏药物会将能量传递给周围的氧,生成活性很强的单态氧。单态氧能与附近的生物大分子发生氧化反应,产生细胞毒性进而杀伤肿瘤细胞。与传统肿瘤疗法相比,光动力疗法的优势在于能够精确进行有效的治疗,不良反应也很小。
文题释义:
光动力疗法:是用光敏药物和激光活化治疗肿瘤疾病的一种新方法。用特定波长照射肿瘤部位,能使选择性聚集在肿瘤组织的光敏药物活化,引发光化学反应破坏肿瘤。
光动力疗法的临床应用:新一代光动力疗法中的光敏药物会将能量传递给周围的氧,生成活性很强的单态氧。单态氧能与附近的生物大分子发生氧化反应,产生细胞毒性进而杀伤肿瘤细胞。与传统肿瘤疗法相比,光动力疗法的优势在于能够精确进行有效的治疗,不良反应也很小。