| [1] Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D,et al.Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology.2016;64(1):73-84.[2] Anstee QM, McPherson S, Day CP.How big a problem is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?BMJ. 2011;343:d3897.[3] 范晓棠,哈丽达•夏尔甫哈孜,陈新春,等.臭氧治疗非酒精性脂肪肝:细胞因子水平的变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(7): 1047-1051.[4] Watanabe S, Hashimoto E, Ikejima K,et al.Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/ nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(4): 364-377.[5] 郑刚.非酒精性脂肪性肝病与肝癌关系研究进展[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2012,21(3):216-220.[6] Popov VB, Lim JK.Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of Medical, Surgical, and Endoscopic Weight Loss.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2015;3(3):230-238.[7] 吕雪幼,叶国良.多烯磷脂酰胆碱治疗老年中重度脂肪肝的临床研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2016,32(15):1370-1373.[8] 刘锐,伍娟娟,甘国兴,等.多烯磷脂酰胆碱对非酒精性脂肪性肝病模型大鼠肝脏SREBP-1c与ABCA1蛋白表达的影响[J].广东医学,2011,32(18):2376-2378. [9] 朱梓铭,郑景辉,黄金龙,等.养心通脉有效部位方干预AMI大鼠BMSCs miRNA组学分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(16):114-120.[10] 范建高,曾民德.脂肪性肝病[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社, 2000:153[11] 马富超,张泉洋,王帅,等.非酒精性脂肪性肝病动物模型研究进展[J].国际药学研究杂志,2017,44(5):409-414.[12] 王俊杰,方会龙,李纯伟,等.非酒精性脂肪肝模型小鼠的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(24):4395-4399.[13] Wang HW, Cao LL, Fan MQ, et al. Effect of polyene phosphatidylcholine combined with fenofibrate capsules in treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2014;22(3):429-433.[14] 陈彬,林海雪.多烯磷脂酰胆碱对非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠的干预及其对肝锌指蛋白A20表达的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2018, 34(11):1353-1356.[15] 陈艳,郑意楠.茵栀黄及双歧杆菌三联活菌辅助光照治疗新生儿黄疸疗效分析[J].中国全科医学, 2012,15(21):2480-2481,2483.[16] 孙欣,高莹,杨云锋.环境微生物的宏基因组学研究新进展[J].生物多样性,2013,21(4):393-401.[17] 上官辉,谭淑燕,张积仁.肝癌易感性相关基因的文献计量学与生物信息学分析[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2015,22(4):305-311.[18] 成军,刘妍,陆荫英,等. 生物信息学技术与新基因的研究[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2003,11(4):474-477.[19] Brockhausen J, Tay SS, Grzelak CA,et al.miR-181a mediates TGF-β-induced hepatocyte EMT and is dysregulated in cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer.Liver Int. 2015;35(1): 240-253.[20] Lu CH, Hou QR, Deng LF,et al.MicroRNA-370 Attenuates Hepatic Fibrogenesis by Targeting Smoothened.Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60(7):2038-2048.[21] Li L, Li G, Yu C,et al.A role of microRNA-370 in hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury by targeting transforming growth factor-β receptor II.Liver Int. 2015;35(4):1124-1132. [22] Xu WP, Yi M, Li QQ,et al.Perturbation of MicroRNA-370/ Lin-28 homolog A/nuclear factor kappa B regulatory circuit contributes to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2013;58(6):1977-1991.[23] Zheng J, Yu L, Chen W,et al.Circulating exosomal microRNAs reveal the mechanism of Fructus Meliae Toosendan-induced liver injury in mice.ci Rep. 2018;8(1):2832.[24] Wen M, Cui J, Xu J,et al.Effects of dietary sea cucumber saponin on the gene expression rhythm involved in circadian clock and lipid metabolism in mice during nighttime-feeding.J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70(3):801-808.[25] Li Y, Yao L, Liu F,et al.Characterization of microRNA expression in serous ovarian carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2014; 34(2):491-498. [26] Benoit B, Plaisancié P, Awada M,et al.High-fat diet action on adiposity, inflammation, and insulin sensitivity depends on the control low-fat diet.Nutr Res. 2013;33(11):952-960.[27] Castrop H.Mediators of tubuloglomerular feedback regulation of glomerular filtration: ATP and adenosine.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2007;189(1):3-14.[28] Seo MS, Hong SW, Yeon SH,et al.Magnolia officinalis attenuates free fatty acid-induced lipogenesis via AMPK phosphorylation in hepatocytes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;157: 140-148.[29] 高燕翔,张勇,刘裕,等.SREBP-1c在白藜芦醇预防大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝发生中的作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(17): 1704-1708.[30] Xu G, Zhang Y, Wei J,et al.MicroRNA-21 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell proliferation through repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase 3.BMC Cancer. 2013;13:469.[31] Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H,et al.Circulating microRNA- 21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2012;56(1):167-175.[32] Gougelet A, Colnot S. Hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: Circulating microRNAs emerge as robust biomarkers.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016;40(4):367-369.[33] Zhang JJ, Zhang YZ, Peng JJ,et al.Atorvastatin exerts inhibitory effect on endothelial senescence in hyperlipidemic rats through a mechanism involving down-regulation of miR-21-5p/203a-3p.Mech Ageing Dev. 2018;169:10-18.[34] 魏益国,陈捷,石明巧,等.PNPLA3基因多态性与非酒精性脂肪性肝病肝损伤间相关性的系统评价[J].检验医学与临床, 2018, 15(2):157-160.[35] Tai CM, Huang CK, Tu HP,et al.Interactions of a PPARGC1A Variant and a PNPLA3 Variant Affect Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Severely Obese Taiwanese Patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(12):e3120.[36] Zain SM, Mohamed R, Mahadeva S,et al.A multi-ethnic study of a PNPLA3 gene variant and its association with disease severity in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Hum Genet. 2012; 131(7):1145-1152.[37] Petta S, Vanni E, Bugianesi E,et al.PNPLA3 rs738409 I748M is associated with steatohepatitis in 434 non-obese subjects with hepatitis C.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41(10): 939-948.[38] Stättermayer AF, Traussnigg S, Aigner E, et al. Low hepatic copper content and PNPLA3 polymorphism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients without metabolic syndrome.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2017;39:100-107. [39] 耿宁,辛永宁,姜曼,等.PNPLA3基因I148M多态性与肝脏疾病炎症发展相关性研究[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(20):3345-3347.[40] Sookoian S, Pirola CJ.Meta-analysis of the influence of I148M variant of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) on the susceptibility and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatology. 2011;53(6): 1883-1894. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因芯片分析:为了通过生物信息学方法从这些芯片数据中发现可能对生物效应起作用的关键基因,从中寻找特定模式并对每个基因给予注释,从而挖掘出隐含的生物学过程并抽提出生物学的或功能层面上的意义。
基因本体论:基因本体联合会所建立的数据库,皆在建立一套适用于各种物种的,对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述的,并能随着研究不断深入而更新的语义词汇标准。
文题释义:
基因芯片分析:为了通过生物信息学方法从这些芯片数据中发现可能对生物效应起作用的关键基因,从中寻找特定模式并对每个基因给予注释,从而挖掘出隐含的生物学过程并抽提出生物学的或功能层面上的意义。
基因本体论:基因本体联合会所建立的数据库,皆在建立一套适用于各种物种的,对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述的,并能随着研究不断深入而更新的语义词汇标准。.jpg) 文题释义:
基因芯片分析:为了通过生物信息学方法从这些芯片数据中发现可能对生物效应起作用的关键基因,从中寻找特定模式并对每个基因给予注释,从而挖掘出隐含的生物学过程并抽提出生物学的或功能层面上的意义。
基因本体论:基因本体联合会所建立的数据库,皆在建立一套适用于各种物种的,对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述的,并能随着研究不断深入而更新的语义词汇标准。
文题释义:
基因芯片分析:为了通过生物信息学方法从这些芯片数据中发现可能对生物效应起作用的关键基因,从中寻找特定模式并对每个基因给予注释,从而挖掘出隐含的生物学过程并抽提出生物学的或功能层面上的意义。
基因本体论:基因本体联合会所建立的数据库,皆在建立一套适用于各种物种的,对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述的,并能随着研究不断深入而更新的语义词汇标准。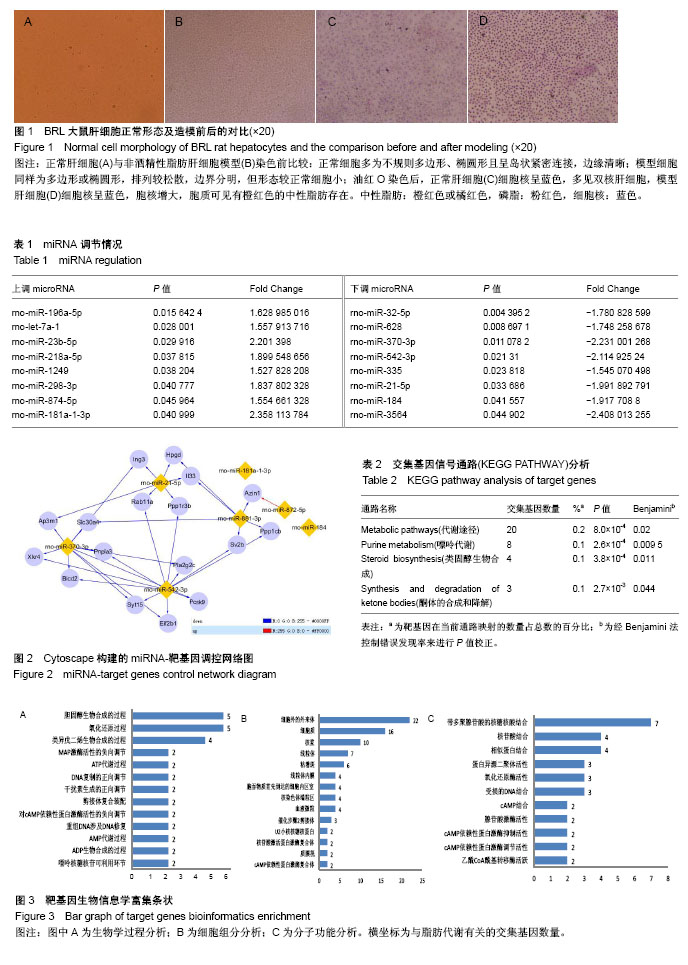

.jpg) 文题释义:
基因芯片分析:为了通过生物信息学方法从这些芯片数据中发现可能对生物效应起作用的关键基因,从中寻找特定模式并对每个基因给予注释,从而挖掘出隐含的生物学过程并抽提出生物学的或功能层面上的意义。
基因本体论:基因本体联合会所建立的数据库,皆在建立一套适用于各种物种的,对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述的,并能随着研究不断深入而更新的语义词汇标准。
文题释义:
基因芯片分析:为了通过生物信息学方法从这些芯片数据中发现可能对生物效应起作用的关键基因,从中寻找特定模式并对每个基因给予注释,从而挖掘出隐含的生物学过程并抽提出生物学的或功能层面上的意义。
基因本体论:基因本体联合会所建立的数据库,皆在建立一套适用于各种物种的,对基因和蛋白质功能进行限定和描述的,并能随着研究不断深入而更新的语义词汇标准。