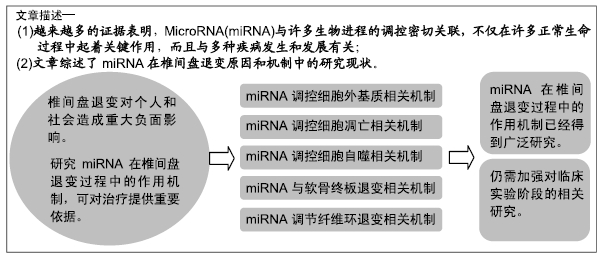
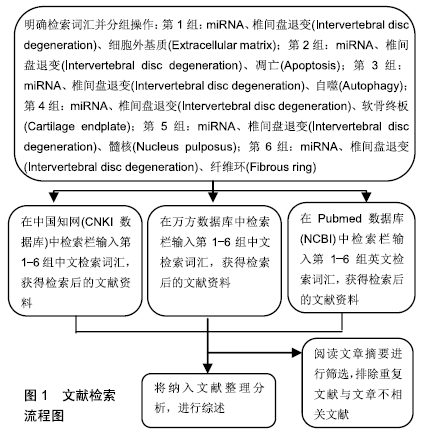
[1] BOOS N, WEISSBACH S, ROHRBACH H, et al.Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(23): 2631-2644.
[2] 邵楠,王大民,陈茁,等.腰椎融合术后生理前凸与腰痛关联性的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2012,6(24):8142-8146.
[3] ANDERSSON GBJ. Epidemiological features of chronic low-back pain. Lancet. 1999; 354(9178): 581-585.
[4] TAYLOR VM, DEYO RA, CHERKIN DC, et al. Low back pain hospitalization. Recent United States trends and regional variation. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19(11): 1207-1212; discussion 13.
[5] LUO X, PIETROBON R, SUN SX, et al. Estimates and patterns of direct health care expenditures among individuals with back pain in the United States. Spineb(Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(1): 79-86.
[6] BATTIE MC, VIDEMAN T, GIBBONS LE, et al. 1995 Volvo Award in clinical sciences. Determinants of lumbar disc degeneration. A study relating lifetime exposures and magnetic resonance imaging findings in identical twins.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20(24): 2601-2612.
[7] LEE RC, FEINBAUM RL, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell.1993; 75(5):843.
[8] STERN-GINOSSAR N, ELEFANT N, ZIMMERMANN A, et al. Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA.Science. 2007; 317(5836):376-381.
[9] BOSSÉ GD, SIMARD MJ. A new twist in the microRNA pathway: Not Dicer but Argonaute is required for a microRNA production. Cell Res.2010; 20(7): 735.
[10] JANECZKO Ł, JANECZKO M, CHRZANOWSKI R, et al. The role of polymorphisms of genes encoding collagen IX and XI in lumbar disc disease.Neurol Neurochir Pol.2014; 48(1): 60-62.
[11] LE MAITRE CL, POCKERT A, BUTTLE DJ, et al. Matrix synthesis and degradation in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Soc Trans.2007;35(Pt 4):652-655.
[12] YANG S, LI L, ZHU L, et al. Bu-Shen-Huo-Xue-Fang (BSHXF) modulates nucleus pulposus cell proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling in intervertebral disc degeneration through miR-483 regulation of Wnt pathway.J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(12):19318-19329.
[13] YANG S, LI L, ZHU L, et al. Aucubin inhibits IL-1β-or TNF-α- induced extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cell through blocking the miR-140-5p/CREB1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(8):13639-13648.
[14] LIU W, ZHANG Y, XIA P, et al. MicroRNA-7 regulates IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix degeneration by targeting GDF5 in human nucleus pulposus cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016; 83: 1414-1421.
[15] LIU W, XIA P, FENG J, et al. MicroRNA-132 upregulation promotes matrix degradation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Cell Res.2017; 359(1): 39-49.
[16] ZHANG WL, CHEN YF, MENG HZ, et al. Role of miR-155 in the regulation of MMP‐16 expression in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2017; 35(6): 1323-1334.
[17] YE D, DAI L, YAO Y, et al. miR-155 inhibits nucleus pulposus cells’ degeneration through targeting ERK 1/2. Dis Markers. 2016; 2016(1): 1-7.
[18] KANG L, YANG C, YIN H, et al. MicroRNA-15b silencing inhibits IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix degradation by targeting SMAD3 in human nucleus pulposus cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2017; 39(4): 623-632.
[19] WANG J, LIU X, SUN B, et al. Upregulated miR‐154 promotes ECM degradation in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(7): 11900-11907.
[20] 王磊,李天旺,刘建强,等. MicroRNA-491-5p 调控基质金属蛋白酶 9 参与退变性腰椎侧凸的发病机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(2): 248.
[21] SUN Y,SHI X,PENG X,et al.MicroRNA-181a exerts anti-inflammatory effects via inhibition of the ERK pathway in mice with intervertebral disc degeneration.J Cell Physiol.2019; 235(3): 2676-2686.
[22] FARROKHI MR, KARIMI MH, GHAFFARPASAND F, et al. MicroRNA-199a Upregulation Mediates Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and is Associated with Clinical Grades of Degeneration.Turk Neurosurg.2019;8:1-8.
[23] ZHOU Y, LIU S, PENG H, et al. In vivo anti-apoptosis activity of novel berberine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles effectively ameliorates osteoarthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015; 28(1): 34-43.
[24] CHENG S, HOU J, ZHANG C, et al. Minocycline reduces neuroinflammation but does not ameliorate neuron loss in a mouse model of neurodegeneration. Sci Rep.2015; 5:10535.
[25] HUANG G, ZOU J, SHI J, et al. Electroacupuncture stimulates remodeling of extracellular matrix by inhibiting apoptosis in a rabbit model of disc degeneration. J Evidence-Based Complementary Altern Med. 2015; 2015:386012.
[26] YANG SD, YANG DL, SUN YP, et al. 17β-estradiol protects against apoptosis induced by interleukin-1β in rat nucleus pulposus cells by down-regulating MMP-3 and MMP-13. Apoptosis. 2015; 20(3): 348-357.
[27] WANG T, YANG SD, LIU S, et al. 17β-estradiol inhibites tumor necrosis factor-α induced apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Med Sci Monit.2016; 22: 4312.
[28] YANG SD, MA L, YANG DL, et al. Combined effect of 17β-estradiol and resveratrol against apoptosis induced by interleukin-1β in rat nucleus pulposus cells via PI3K/Akt/caspase-3 pathway.Peer J.2016; 4:e1640.
[29] AKYUREKLI C, LE Y, RICHARDSON RB, et al. A systematic review of preclinical studies on the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived microvesicles. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015; 11(1):150-160.
[30] CHENG X, ZHANG G, ZHANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR‐21 via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and reduce intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med.2018; 22(1): 261-276.
[31] WANG W, GUO Z, YANG S, et al. Upregulation of miR-199 attenuates TNF-α-induced Human nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by downregulating MAP3K5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 505(3): 917-924.
[32] LÜ J, LI S, WAN T, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-30d attenuates the apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of degenerative human nucleus pulposus cells by up-regulating SOX9. Chem -Biol Interact.2018; 296: 89-97.
[33] LIU P, CHANG F, ZHANG T, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-125a is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration by targeting pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 antagonist killer 1. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017; 20(11): 1260.
[34] LIU J, YU J, JIANG W, et al. Targeting of CDKN 1B by miR‐222-3p may contribute to the development of intervertebral disc degeneration. FEBS Open Bio.2019; 9(4): 728-735.
[35] BISHOP E, BRADSHAW TD. Autophagy modulation: a prudent approach in cancer treatment? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018;82(6):913-922.
[36] MUKHOPADHYAY S, PANDA PK, SINHA N, et al. Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet? Apoptosis.2014; 19(4): 555-566.
[37] CHEN B, HUANG SG, JU L, et al. Effect of microRNA-21 on the proliferation of human degenerated nucleus pulposus by targeting programmed cell death 4. Braz J Med Biol Res.2016; 49(6). pii: S0100-879X2016000600602. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20155020.
[38] LIU H, HUANG X, LIU X, et al. miR-21 promotes human nucleus pulposus cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 15(3): 4007-4018.
[39] WANG WJ, YANG W, OUYANG ZH, et al. MiR-21 promotes ECM degradation through inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/akt/mTOR signaling pathway in human degenerated NP cells. Biomed Pharmacother.2018; 99: 725-734.
[40] WANG XB, WANG H, LONG HQ, et al. LINC00641 regulates autophagy and intervertebral disc degeneration by acting as a competitive endogenous RNA of miR‐153‐3p under nutrition deprivation stress. J Cell Physiol 2019; 234(5): 7115-7127.
[41] ZHANG DY, WANG ZJ,YU YB, et al. Role of microRNA‑210 in human intervertebral disc degeneration.Exp Ther Med. 2016; 11(6): 2349-2354.
[42] WANG C, ZHANG ZZ, YANG W, et al. MiR-210 facilitates ECM degradation by suppressing autophagy via silencing of ATG7 in human degenerated NP cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017; 93: 470-479.
[43] LOLLI A, NARCISI R, LAMBERTINI E, et al. Silencing of antichondrogenic microRNA‐221 in human mesenchymal stem cells promotes cartilage repair in vivo.Stem Cells.2016;34(7): 1801-1811.
[44] LOLLI A, LAMBERTINI E, PENOLAZZI L, et al. Pro-chondrogenic effect of miR-221 and slug depletion in human MSCs. Stem Cell Rev Rep.2014; 10(6):841-855.
[45] SHENG B, YUAN Y, LIU X, et al. Protective effect of estrogen against intervertebral disc degeneration is attenuated by miR-221 through targeting estrogen receptor α. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2018; 50(4):345-354.
[46] LIU MH, SUN C, YAO Y, et al. Matrix stiffness promotes cartilage endplate chondrocyte calcification in disc degeneration via miR-20a targeting ANKH expression. Sci Rep.2016; 6: 25401.
[47] CHEN H, WANG J, HU B, et al. MiR-34a promotes Fas-mediated cartilage endplate chondrocyte apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015; 406(1-2): 21-30.
[48] ZHENG Q, LI X, XIAO L, et al. MicroRNA-365 functions as a mechanosensitive microRNA to inhibit end plate chondrocyte degeneration by targeting histone deacetylase 4. Bone. 2019; 128: 115052.
[49] HAI B, MA Y, PAN X, et al. Melatonin benefits to the growth of human annulus fibrosus cells through inhibiting mir-106a-5p/ATg7 signaling pathway. Clin Interv Aging.2019;14:621.
[50] YEH CH, JIN L, SHEN F, et al. miR-221 attenuates the osteogenic differentiation of human annulus fibrosus cells. Spine J. 2016; 16(7): 896-904.
[51] CHENG X, ZHANG G, ZHANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR‐21 via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and reduce intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med.2018; 22(1):261-276.
[52] KOBAYASHI S, BABA H,TAKENO K, et al. Fine structure of cartilage canal and vascular buds in the rabbit vertebral endplate. J Neurosurg.2008;9(1): 96-103.
[53] LIU S, ZHAO B, SHI H, et al. Ligustrazine Inhibits Cartilage Endplate Hypertrophy via Suppression of TGF-β1.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2016;2016(4):1042489.
[54] VADALA G, DE STROBEL F, BERNARDINI M, et al. The transpedicular approach for the study of intervertebral disc regeneration strategies: in vivo characterization.Eur Spine J. 2013; 22(6): 972-978.
[55] LEE JM, SONG JY, BAEK MJ, et al. Interleukin‐1β induces angiogenesis and innervation in human intervertebral disc degeneration.J Orthop Res.2011; 29(2):265-269.
[56] HOU G, LU H, CHEN M, et al. Oxidative stress participates in age-related changes in rat lumbar intervertebral discs. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014; 59(3): 665-669.
[57] PARK JS, PARK JB, PARK IJ, et al. Accelerated premature stress-induced senescence of young annulus fibrosus cells of rats by high glucose-induced oxidative stress. Int Orthop. 2014; 38(6): 1311-1320.
[58] GRUBER HE, HOELSCHER GL, INGRAM JA, et al. Autophagy in the Degenerating Human Intervertebral Disc: In Vivo Molecular and Morphological Evidence, and Induction of Autophagy in Cultured Annulus Cells Exposed to Proinflammatory Cytokines- Implications for Disc Degeneration.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2015; 40(11): 773-782.
|