• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
脂肪肝模型大鼠自体原位肝移植后的脂质代谢变化
丁 晨1,江 艺2,潘 凡2,蔡秋程2
- (1福建医科大学附属第三医院,福建医科大学附属协和医院肝胆外科,福建省福州市 350001; 2解放军南京军区福州总医院肝胆外科,福建省福州市 350025)
Lipid metabolism after autologous orthotopic liver transplantation in rat models of fatty liver
Ding Chen1, Jiang Yi2, Pan Fan2, Cai Qiucheng2
- (1Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University & Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, Fujian Province, China; 2Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Fuzhou General Hospital of Nanjing Military Command, Fuzhou 350025, Fujian Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
自体肝移植:是指应用肝移植技术,使肝脏处于全离体或半离体情况下,在低温保存及低温持续灌注条件下,完成病灶的切除和余肝的修整,最后将修整好的余肝重新移植回体内的一种外科技术。临床上自体肝移植不但为不能常规手术切除的肝脏占位性病灶患者提供了手术治愈的可能,同时也为缓解供肝短缺开辟了新的途径,在基础研究方面可运用自体肝移植研究缺血再灌注相关研究。
脂质代谢:是指机体摄入的脂肪经胆汁乳化成小颗粒,胰腺和小肠内分泌的脂肪酶将脂肪里的脂肪酸水解成游离脂肪酸和甘油单酯,甘油、短链等小分子可被小肠吸收进入血液,大分子被吸收后先在小肠细胞中重新合成三酰甘油,并和磷脂、胆固醇和蛋白质形成乳糜微粒,由淋巴系统进入血液循环。经历移植过程,缺血再灌注损伤对肝脏脂质调节形成不同程度影响,甚至关系到移植的成败。
文题释义:
自体肝移植:是指应用肝移植技术,使肝脏处于全离体或半离体情况下,在低温保存及低温持续灌注条件下,完成病灶的切除和余肝的修整,最后将修整好的余肝重新移植回体内的一种外科技术。临床上自体肝移植不但为不能常规手术切除的肝脏占位性病灶患者提供了手术治愈的可能,同时也为缓解供肝短缺开辟了新的途径,在基础研究方面可运用自体肝移植研究缺血再灌注相关研究。
脂质代谢:是指机体摄入的脂肪经胆汁乳化成小颗粒,胰腺和小肠内分泌的脂肪酶将脂肪里的脂肪酸水解成游离脂肪酸和甘油单酯,甘油、短链等小分子可被小肠吸收进入血液,大分子被吸收后先在小肠细胞中重新合成三酰甘油,并和磷脂、胆固醇和蛋白质形成乳糜微粒,由淋巴系统进入血液循环。经历移植过程,缺血再灌注损伤对肝脏脂质调节形成不同程度影响,甚至关系到移植的成败。
.jpg) 文题释义:
自体肝移植:是指应用肝移植技术,使肝脏处于全离体或半离体情况下,在低温保存及低温持续灌注条件下,完成病灶的切除和余肝的修整,最后将修整好的余肝重新移植回体内的一种外科技术。临床上自体肝移植不但为不能常规手术切除的肝脏占位性病灶患者提供了手术治愈的可能,同时也为缓解供肝短缺开辟了新的途径,在基础研究方面可运用自体肝移植研究缺血再灌注相关研究。
脂质代谢:是指机体摄入的脂肪经胆汁乳化成小颗粒,胰腺和小肠内分泌的脂肪酶将脂肪里的脂肪酸水解成游离脂肪酸和甘油单酯,甘油、短链等小分子可被小肠吸收进入血液,大分子被吸收后先在小肠细胞中重新合成三酰甘油,并和磷脂、胆固醇和蛋白质形成乳糜微粒,由淋巴系统进入血液循环。经历移植过程,缺血再灌注损伤对肝脏脂质调节形成不同程度影响,甚至关系到移植的成败。
文题释义:
自体肝移植:是指应用肝移植技术,使肝脏处于全离体或半离体情况下,在低温保存及低温持续灌注条件下,完成病灶的切除和余肝的修整,最后将修整好的余肝重新移植回体内的一种外科技术。临床上自体肝移植不但为不能常规手术切除的肝脏占位性病灶患者提供了手术治愈的可能,同时也为缓解供肝短缺开辟了新的途径,在基础研究方面可运用自体肝移植研究缺血再灌注相关研究。
脂质代谢:是指机体摄入的脂肪经胆汁乳化成小颗粒,胰腺和小肠内分泌的脂肪酶将脂肪里的脂肪酸水解成游离脂肪酸和甘油单酯,甘油、短链等小分子可被小肠吸收进入血液,大分子被吸收后先在小肠细胞中重新合成三酰甘油,并和磷脂、胆固醇和蛋白质形成乳糜微粒,由淋巴系统进入血液循环。经历移植过程,缺血再灌注损伤对肝脏脂质调节形成不同程度影响,甚至关系到移植的成败。摘要
背景:研究显示,重度脂肪肝移植后移植物原发性无功能和早期移植物功能不良发生率明显升高,因此何种程度脂肪变性能最大程度提高移植物和受体的存活率,有待进行更深入的研究。
目的:探讨不同程度脂肪肝大鼠行自体原位肝移植对脂质代谢的影响。
方法:取160只SD大鼠(福建医科大学实验动物中心提供),通过高脂饮食分别建立中、重度脂肪肝模型,每种模型80只大鼠;将中度脂肪肝大鼠随机分2组,模型组(A组)进行自体原位肝移植手术,对照组(C组)不做手术;将重度脂肪肝大鼠随机分2组,模型组(B组)进行自体原位肝移植手术,对照组(D组)不做手术。术前、术后1 d、术后1周、术后3周、术后5周分别进行肝功能、脂质代谢及肝脏组织病理学检查。
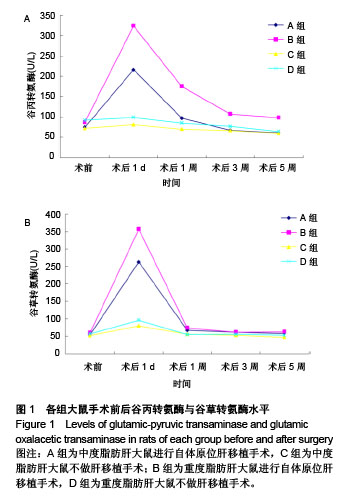
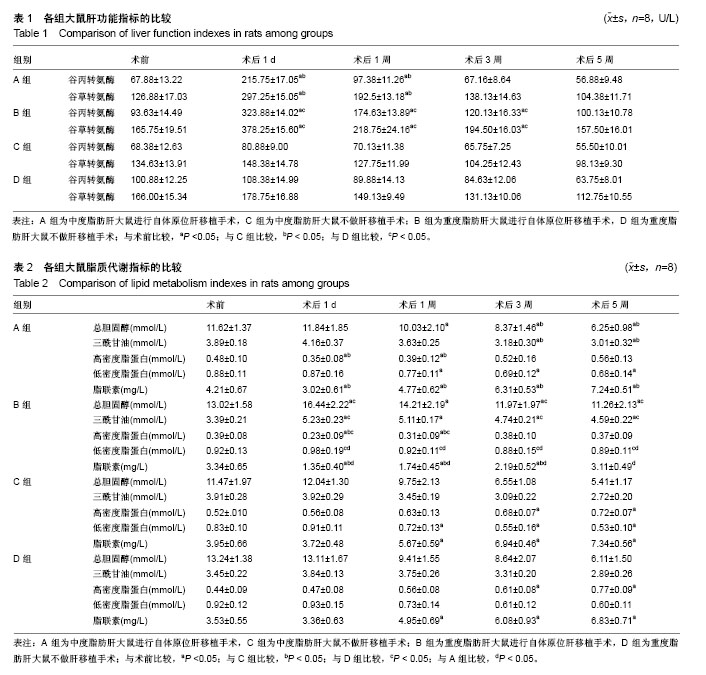
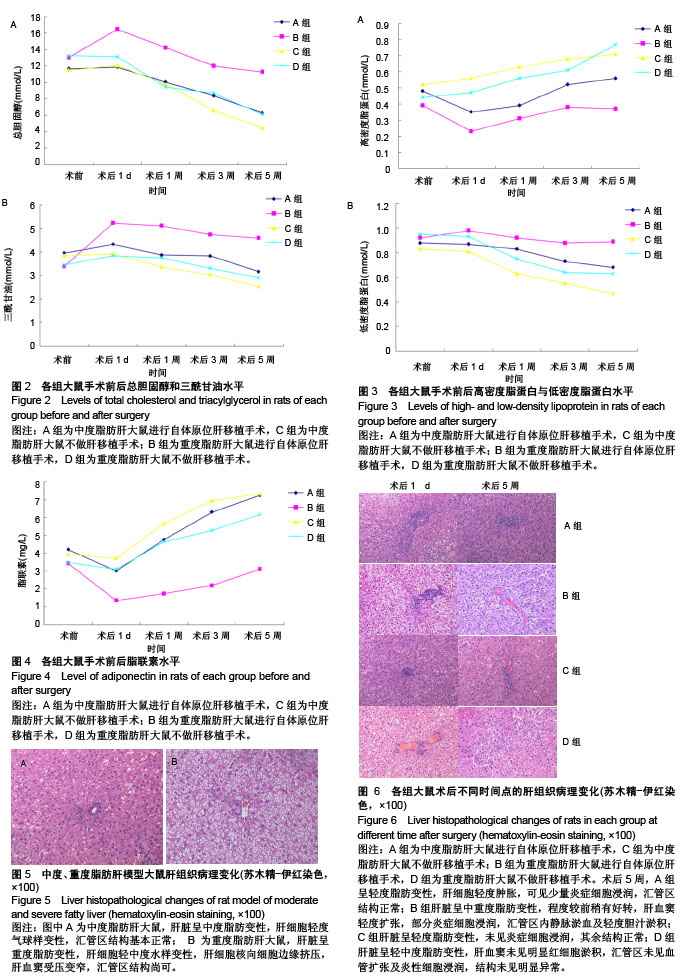
结果与结论:①肝功能:A组谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶水平均于术后1 d达峰值,随后逐渐下降,B组术后5周的谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶水平高于A组;②脂质代谢:4组大鼠术后总胆固醇、三酰甘油和低密度脂蛋白水平总体呈下降趋势,高密度脂蛋白、脂联素水平总体呈升高趋势;术后第5周,A组总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白水平低于B组(P < 0.05),高密度脂蛋白、脂联素水平高于B组(P < 0.05);③肝脏组织病理学:A组术后1 d肝脏呈中度脂肪变性,术后5周脂肪变性程度逆转;B组术后1 d肝脏呈重度脂肪变性,术后5周呈中、重度脂肪变性,未见明显好转,可见炎症细胞浸润,汇管区内静脉淤血及轻度胆汁淤积;④结果表明:中、重度脂肪肝大鼠行自体原位肝移植后,均有不同程度加重脂质代谢紊乱,重度脂肪肝较中度脂肪肝可产生更严重的脂质代谢紊乱且恢复更加缓慢。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-9368-5525(丁晨)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
自体肝移植:是指应用肝移植技术,使肝脏处于全离体或半离体情况下,在低温保存及低温持续灌注条件下,完成病灶的切除和余肝的修整,最后将修整好的余肝重新移植回体内的一种外科技术。临床上自体肝移植不但为不能常规手术切除的肝脏占位性病灶患者提供了手术治愈的可能,同时也为缓解供肝短缺开辟了新的途径,在基础研究方面可运用自体肝移植研究缺血再灌注相关研究。
脂质代谢:是指机体摄入的脂肪经胆汁乳化成小颗粒,胰腺和小肠内分泌的脂肪酶将脂肪里的脂肪酸水解成游离脂肪酸和甘油单酯,甘油、短链等小分子可被小肠吸收进入血液,大分子被吸收后先在小肠细胞中重新合成三酰甘油,并和磷脂、胆固醇和蛋白质形成乳糜微粒,由淋巴系统进入血液循环。经历移植过程,缺血再灌注损伤对肝脏脂质调节形成不同程度影响,甚至关系到移植的成败。
文题释义:
自体肝移植:是指应用肝移植技术,使肝脏处于全离体或半离体情况下,在低温保存及低温持续灌注条件下,完成病灶的切除和余肝的修整,最后将修整好的余肝重新移植回体内的一种外科技术。临床上自体肝移植不但为不能常规手术切除的肝脏占位性病灶患者提供了手术治愈的可能,同时也为缓解供肝短缺开辟了新的途径,在基础研究方面可运用自体肝移植研究缺血再灌注相关研究。
脂质代谢:是指机体摄入的脂肪经胆汁乳化成小颗粒,胰腺和小肠内分泌的脂肪酶将脂肪里的脂肪酸水解成游离脂肪酸和甘油单酯,甘油、短链等小分子可被小肠吸收进入血液,大分子被吸收后先在小肠细胞中重新合成三酰甘油,并和磷脂、胆固醇和蛋白质形成乳糜微粒,由淋巴系统进入血液循环。经历移植过程,缺血再灌注损伤对肝脏脂质调节形成不同程度影响,甚至关系到移植的成败。