| [1] Davie CA. A review of Parkinson's disease. Br Med Bull. 2008; 86:109-127.[2] Philippens IH, 't Hart BA, Torres G. The MPTP marmoset model of parkinsonism: a multi-purpose non-human primate model for neurodegenerative diseases. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15(23-24):985-990.[3] Chakrabarti S, Khemka VK, Banerjee A, et al. Metabolic Risk Factors of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease: Implications in the Pathology, Pathogenesis and Treatment. Aging Dis. 2015;6(4): 282-299.[4] B?aszczyk JW. Nigrostriatal interaction in the aging brain: new therapeutic target for Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2017;77(1):106-112.[5] Wongprayoon P, Govitrapong P. Melatonin as a mitochondrial protector in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(21):3999-4014.[6] Manoharan S, Guillemin GJ, Abiramasundari RS, et al. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and Huntington's Disease: A Mini Review. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016: 8590578.[7] Nandipati S, Litvan I. Environmental Exposures and Parkinson's Disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016; 13(9): E881.[8] Moreira EL, Rial D, Aguiar AS Jr, et al. Proanthocyanidin-rich fraction from Croton celtidifolius Baill confers neuroprotection in the intranasal 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine rat model of Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2010;117(12):1337-1351.[9] Collart-Dutilleul PY, Chaubron F, De Vos J, et al. Allogenic banking of dental pulp stem cells for innovative therapeutics. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(7):1010-1021.[10] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.[11] Kunisada T, Tezulka K, Aoki H, et al. The stemness of neural crest cells and their derivatives. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014;102(3):251-262.[12] Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W, et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002;81(8): 531-535.[13] Jimi E, Hirata S, Osawa K, et al. The current and future therapies of bone regeneration to repair bone defects. Int J Dent. 2012;2012:148261.[14] Sakai K, Yamamoto A, Matsubara K, et al. Human dental pulp-derived stem cells promote locomotor recovery after complete transection of the rat spinal cord by multiple neuro-regenerative mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(1): 80-90.[15] Király M, Kádár K, Horváthy DB, et al. Integration of neuronally predifferentiated human dental pulp stem cells into rat brain in vivo. Neurochem Int. 2011;59(3):371-381.[16] Király M, Porcsalmy B, Pataki A, et al. Simultaneous PKC and cAMP activation induces differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into functionally active neurons. Neurochem Int. 2009;55(5):323-332.[17] Ellis KM, O'Carroll DC, Lewis MD, et al. Neurogenic potential of dental pulp stem cells isolated from murine incisors. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):30.[18] Arthur A, Rychkov G, Shi S, et al. Adult human dental pulp stem cells differentiate toward functionally active neurons under appropriate environmental cues. Stem Cells. 2008; 26(7):1787-1795.[19] Inoue T, Sugiyama M, Hattori H, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth-derived conditioned medium enhance recovery of focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(1-2):24-29.[20] De Almeida FM, Marques SA, Ramalho Bdos S, et al. Human dental pulp cells: a new source of cell therapy in a mouse model of compressive spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2011; 28(9):1939-1949.[21] Hao ZC, Lu J, Wang SZ, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: A promising strategy for fracture healing. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(5): e12359.[22] Mortada I, Mortada R, Al Bazzal M. Dental pulp stem cells and the management of neurological diseases: An update. J Neurosci Res. 2018;96(2):265-272.[23] Ke C, Biao H, Qianqian L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases: promise and challenge. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10(6):499-508.[24] Morizane A, Takahashi J. A challenge towards the clinical application of induced pluripotent stem cell technology for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Brain Nerve. 2012;64(1): 29-37.[25] Caplan AI.Why are MSCs therapeutic. New data: new insight.J Pathol. 2009;217(2):318-324.[26] Tatullo M, Marrelli M, Shakesheff KM, et al. Dental pulp stem cells: function, isolation and applications in regenerative medicine. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(11):1205-1216.[27] Apel C, Forlenza OV, de Paula VJ, et al. The neuroprotective effect of dental pulp cells in models of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009;116(1): 71-78.[28] Anilkumar U, Prehn JH. Anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins in acute neural injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:281.[29] Antonsson B. Mitochondria and the Bcl-2 family proteins in apoptosis signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004; 256-257(1-2):141-155.[30] Drobný M, Kurca E. Possible extrapyramidal system degradation in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res Bull. 2000; 53(4):425-430. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
牙髓干细胞:具有获取容易、自我更新、增殖能力强等特点,日益受到广泛关注。已有相关报道,牙髓干细胞在体外对中脑神经元起到支持作用,并能分化为神经元,且将牙髓干细胞与中脑神经元联合培养后移植到帕金森病模型内,牙髓干细胞通过分泌神经营养因子,对1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子导致的神经损伤起到保护作用。
1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子(1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridinium,MPP+):由一种神经毒剂1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶在黑质细胞内脱氢生成,能够选择性的损害黑质多巴胺能神经元,能够抑制线粒体复合酶,使细胞死亡,并导致出现类似于帕金森病的症状。目前MPP+被广泛用于帕金森病的各种细胞和动物模型研究。
文题释义:
牙髓干细胞:具有获取容易、自我更新、增殖能力强等特点,日益受到广泛关注。已有相关报道,牙髓干细胞在体外对中脑神经元起到支持作用,并能分化为神经元,且将牙髓干细胞与中脑神经元联合培养后移植到帕金森病模型内,牙髓干细胞通过分泌神经营养因子,对1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子导致的神经损伤起到保护作用。
1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子(1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridinium,MPP+):由一种神经毒剂1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶在黑质细胞内脱氢生成,能够选择性的损害黑质多巴胺能神经元,能够抑制线粒体复合酶,使细胞死亡,并导致出现类似于帕金森病的症状。目前MPP+被广泛用于帕金森病的各种细胞和动物模型研究。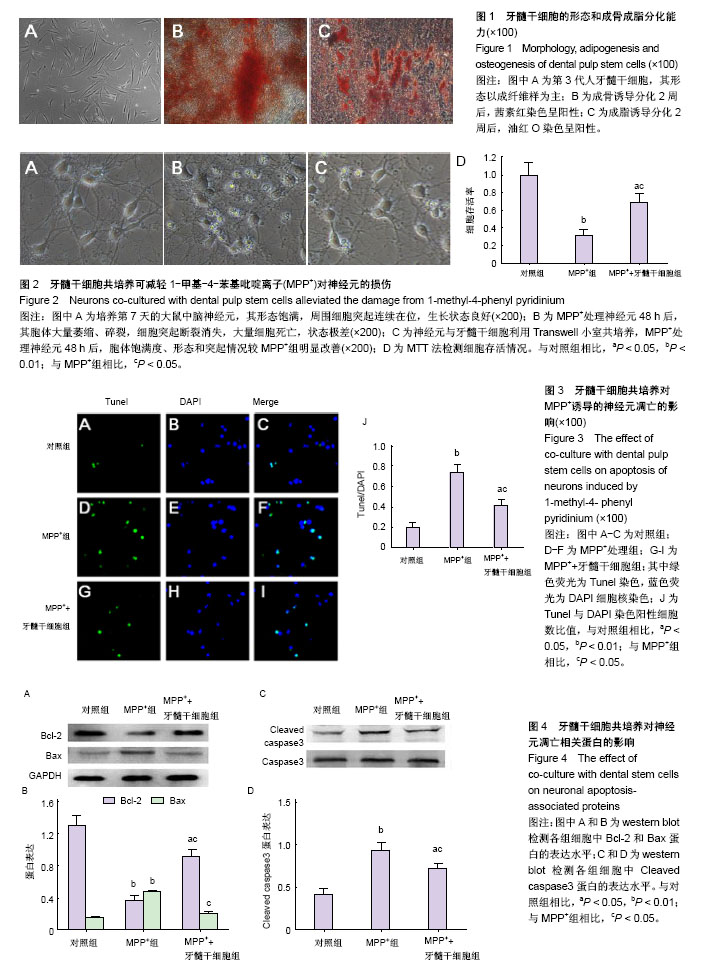
.jpg) 文题释义:
牙髓干细胞:具有获取容易、自我更新、增殖能力强等特点,日益受到广泛关注。已有相关报道,牙髓干细胞在体外对中脑神经元起到支持作用,并能分化为神经元,且将牙髓干细胞与中脑神经元联合培养后移植到帕金森病模型内,牙髓干细胞通过分泌神经营养因子,对1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子导致的神经损伤起到保护作用。
1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子(1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridinium,MPP+):由一种神经毒剂1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶在黑质细胞内脱氢生成,能够选择性的损害黑质多巴胺能神经元,能够抑制线粒体复合酶,使细胞死亡,并导致出现类似于帕金森病的症状。目前MPP+被广泛用于帕金森病的各种细胞和动物模型研究。
文题释义:
牙髓干细胞:具有获取容易、自我更新、增殖能力强等特点,日益受到广泛关注。已有相关报道,牙髓干细胞在体外对中脑神经元起到支持作用,并能分化为神经元,且将牙髓干细胞与中脑神经元联合培养后移植到帕金森病模型内,牙髓干细胞通过分泌神经营养因子,对1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子导致的神经损伤起到保护作用。
1-甲基-4-苯基吡啶离子(1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridinium,MPP+):由一种神经毒剂1-甲基-4-苯基-1,2,3,6-四氢吡啶在黑质细胞内脱氢生成,能够选择性的损害黑质多巴胺能神经元,能够抑制线粒体复合酶,使细胞死亡,并导致出现类似于帕金森病的症状。目前MPP+被广泛用于帕金森病的各种细胞和动物模型研究。