| [1] Schlickewei CW, Laaff G, Andresen A, ET AL. Bone augmentation using a new injectable bone graft substitute by combining calcium phosphate and bisphosphonate as composite-an animal model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10: 116.[2] Dimitriou R, Mataliotakis GI, Angoules AG, et al. Complications following autologous bone graft harvesting from the iliac crest and using the RIA: a systematic review. Injury.2011;42(5):S3-15.[3] Sims L, Kulyk P, Woo A. Intraoperative culture positive allograft bone and subsequent postoperative infections: a retrospective review. Can J Surg. 2017;60(2):94-100.[4] Hinsenkamp M, Muylle L, Eastlund T, et al. Adverse reactions and events related to musculoskeletal allografts: reviewed by the World Health Organisation Project NOTIFY. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(3):633-641.[5] Mroz TE, Joyce MJ, Lieberman IH, et al. The use of allograft bone in spine surgery: is it safe? Spine. 2009; 9(4): 303-308.[6] Samorezov JE, Alsberg E. Spatial regulation of controlled bioactive factor delivery for bone tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015; 48:45-67[7] Mini AR, Laurencin CT, Nukavarapu SP. Bone tissue engineering: recent advances and challenges. Crit Rev Biomed Eng.2012;40( 5):363-408.[8] Bose S, Roy M, Bandyopadhyay A. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol.2012; 30(10): 546-554. [9] Lebouvier A, Poignard A, Cavet M, et al. Development of a simple procedure for the treatment of femoral head osteonecrosis with intra-osseous injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells: study of their biodistribution in the early time points after injection. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015; 6(1): 68. [10] May AN, Radhakrishnan V, Dalia A, et al. Human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue and skin exhibit differences in molecular phenotype and differentiation potential. Stem Cell Rev. 2013; 9(1):32.[11] Sekiya I, Larson BL, Vuoristo JT, et al. Adipogenic differentiation of human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma (MSCs). J Bone Miner Res. 2004; 19(2): 256-264.[12] Escors D, Breckpot K, Lentiviral vectors in gene therapy: their current status and future potential. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz).2010;58(2):107-119.[13] Suwanmanee T, Hu G, Gui T, et al. Integration-deficient lentiviral vectors expressing codon-optimized R338L human FIXrestore normal hemostasis in Hemophilia B mice. Mol Ther. 2014;22(3):567-574.[14] 李强,孙正义,严冬雪,等.脱钙骨基质材料的生物学表现:降解性能、孔隙率及其黏附性能特征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(31):6112-6124.[15] 陈佳滨,李强,茹嘉,等.腺病毒介导BMP-2 和EGFP基因转染兔骨髓基质干细胞及种植脱钙骨的体外观察[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(8):869-874.[16] 李诗鹏,李强,石正松,等.基因重组腺病毒载体与慢病毒载体转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 12(9): 1340-1345.[17] Baltzer AW, Lattermann C, Whalen J D, et al. A gene therapy approach to accelerating bone healing. Evaluation of gene expression in a New Zealand white rabbit model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1999; 7(3):197-202.[18] Lane JM, Sandhu HS. Current approaches to experimental bone grafting. Orthop Clin North Am.1987; 18(2):123-225.[19] 陈佳滨,武成聪,李强,等.转基因技术及骨髓间充质干细胞在骨缺损修复中的应用与展望[J].临床医学工程,2013, 20(11): 1457-1459.[20] Vo TN, Shah SR, Lu S, et al. Injectable dual-gelling cell-laden composite hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2016; 83:1-11.[21] Cui N, Qian J, Wang J, et al. Preparation, physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of PBLG/PLGA/bioglass composite scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Biomim Supramol Syst. 2017;71:118-124.[22] Pot M W, De L K, Van PDK, et al. Unidirectional BMP2-loaded collagen scaffolds induce chondrogenic differentiation. Biomed Mater.2017; 13(1):015007.[23] Peng K T, Hsieh M Y, Lin C T, et al. Treatment of critically sized femoral defects with recombinant BMP-2 delivered by a modified mPEG-PLGA biodegradable thermosensitive hydroge. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016; 17(1):286.[24] Sharma S, Sapkota D, Xue Y, et al. Adenoviral mediated expression of BMP2 by bone marrow stromal cells cultured in 3D copolymer scaffolds enhances bone formation. Plos One. 2016;11(1):e0147507.[25] Krishnan L, Priddy LB, Esancy C, et al. Delivery vehicle effects on bone regeneration and heterotopic ossification induced by high dose BMP-2. Acta Biomater. 2017;49: 101-112.[26] Tatara AM, Mikos AG. Tissue engineering in orthopaedics. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016; 98(13):1132-1139.[27] Mauffrey C, Barlow BT, Smith W. Management of segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):143-153.[28] 陈思圆,王簕,江汕,等.植入含感觉神经束和血管束组织工程骨修复股骨大段骨缺损:降钙素基因相关肽Ⅰ型受体的中长期表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,12(6):488-853.[29] Kang JW, Suh DH, Park JH, et al. Repair of large segmental bone defect using vascularized small corticocancellous bone in rabbit femur. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2017; 33(9):649-659.[30] Baltzer AW, Lattermann C, Whalen JD, et al. Genetic enhancement of fracture repair: healing of an experimental segmental defect by adenoviral transfer of the BMP-2 gene. Gene Ther. 2000;7(9):734-739. |
.jpg)
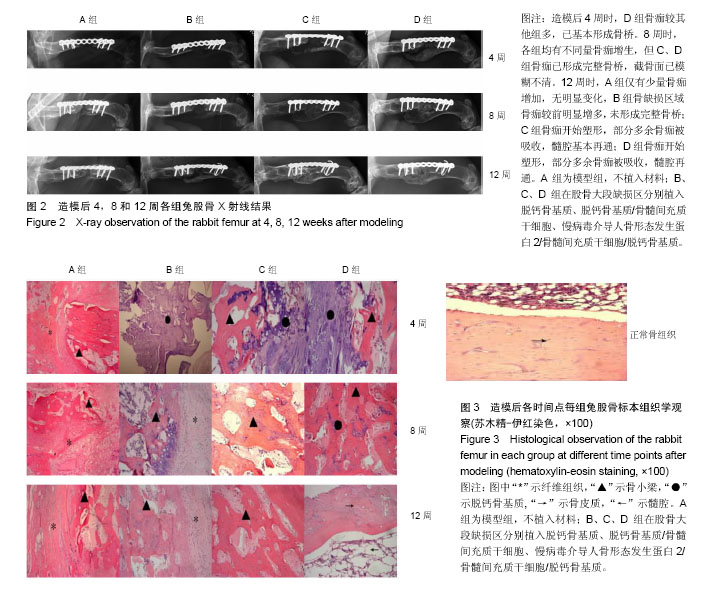
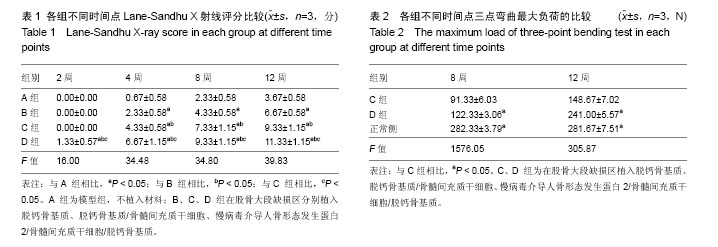
.jpg)
.jpg)