| [1] Burchfield JS, Paul AL, Lanka V, et al. Pharmacological priming of adipose-derived stem cells promotes myocardial repair. J Investig Med. 2016;64(1):50-62.[2] Schenke-Layland K, Strem BM, Jordan MC, et al. Adipose tissue-derived cells improve cardiac function following myocardial infarction. J Surg Res. 2009;153(2):217-223.[3] Wang L, Deng J, Tian W, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells are an effective cell candidate for treatment of heart failure: an MR imaging study of rat hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009; 297(3):H1020-1031.[4] Mazo M, Planat-Bénard V, Abizanda G, et al. Transplantation of adipose derived stromal cells is associated with functional improvement in a rat model of chronic myocardial infarction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008;10(5):454-462.[5] Sanz-Rosa D, García-Prieto J, Ibanez B. The future: therapy of myocardial protection. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2012;1254:90-98.[6] Miyahara Y, Nagaya N, Kataoka M, et al. Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium after myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):459-465.[7] Madonna R, Geng YJ, De Caterina R. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells: characterization and potential for cardiovascular repair. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(11):1723-1729.[8] Alfaro MP, Vincent A, Saraswati S, et al. sFRP2 suppression of bone morphogenic protein (BMP) and Wnt signaling mediates mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) self-renewal promoting engraftment and myocardial repair. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(46):35645-35653.[9] Bourin P, Bunnell BA, Casteilla L, et al. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: a joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy. 2013;15(6):641-648.[10] Cai A, Zheng D, Dong Y, et al. Efficacy of Atorvastatin combined with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on cardiac function in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(11):857-866.[11] Bai X, Yan Y, Song YH, et al. Both cultured and freshly isolated adipose tissue-derived stem cells enhance cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(4):489-501.[12] Chen L, Qin F, Ge M, et al. Application of adipose-derived stem cells in heart disease. Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2014;7(7):651-663.[13] Hong SJ, Kihlken J, Choi SC, et al. Intramyocardial transplantation of human adipose-derived stromal cell and endothelial progenitor cell mixture was not superior to individual cell type transplantation in improving left ventricular function in rats with myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2013;164(2):205-211.[14] Hsiao ST, Lokmic Z, Peshavariya H, et al. Hypoxic conditioning enhances the angiogenic paracrine activity of human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(10):1614-1623.[15] Song SY, Chung HM, Sung JH. The pivotal role of VEGF in adipose-derived-stem-cell-mediated regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(11):1529-1537.[16] Yang D, Wang W, Li L, et al. The relative contribution of paracine effect versus direct differentiation on adipose-derived stem cell transplantation mediated cardiac repair. PLoS One. 2013;8(3): e59020.[17] 姜亦瑶,刘晓程,裴宇,等.不同氧分压时人脂肪干细胞细胞因子的分泌[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(45):7861-7868.[18] 龚启梅.低氧对成体干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2011,38(6):696-699.[19] 李丹,郭杏,谭美云.低氧环境对脂肪源性间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].泸州医学院学报,2017,40(2):202-205.[20] Harris WM, Zhang P, Plastini M, et al. Evaluation of function and recovery of adipose-derived stem cells after exposure to paclitaxel. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(2):211-221.[21] 廖建泉,毛晓波,曾秋棠.心肌细胞微环境对脂肪基质干细胞的作用[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2009, 25(5): 381-385.[22] Houtgraaf JH, den Dekker WK, van Dalen BM, et al. First experience in humans using adipose tissue-derived regenerative cells in the treatment of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(5):539-540.[23] Henry TD, Pepine CJ, Lambert CR, et al. The Athena trials: Autologous adipose-derived regenerative cells for refractory chronic myocardial ischemia with left ventricular dysfunction. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2017;89(2):169-177.[24] Planat-Bénard V, Menard C, André M, et al. Spontaneous cardiomyocyte differentiation from adipose tissue stroma cells. Circ Res. 2004;94(2):223-229.[25] Chang JC, Lee PC, Lin YC, et al. Primary adipose-derived stem cells enriched by growth factor treatment improves cell adaptability toward cardiovascular differentiation in a rodent model of acute myocardial infarction. J Stem Cells. 2011;6(1):21-37.[26] Meliga E, Strem BM, Duckers HJ, et al. Adipose-derived cells. Cell Transplant. 2007;16(9):963-970.[27] Gnecchi M, Zhang Z, Ni A, et al. Paracrine mechanisms in adult stem cell signaling and therapy. Circ Res. 2008;103(11):1204-1219.[28] Rehman J, Traktuev D, Li J, et al. Secretion of angiogenic and antiapoptotic factors by human adipose stromal cells. Circulation. 2004;109(10):1292-1298.[29] Lee EY, Xia Y, Kim WS, et al. Hypoxia-enhanced wound-healing function of adipose-derived stem cells: increase in stem cell proliferation and up-regulation of VEGF and bFGF. Wound Repair Regen. 2009;17(4):540-547.[30] Yang J, Zhang H, Zhao L, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived stem cells protect impaired cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/ reoxygenation injury through hypoxia-induced paracrine mechanism. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012;30(6):505-514. |
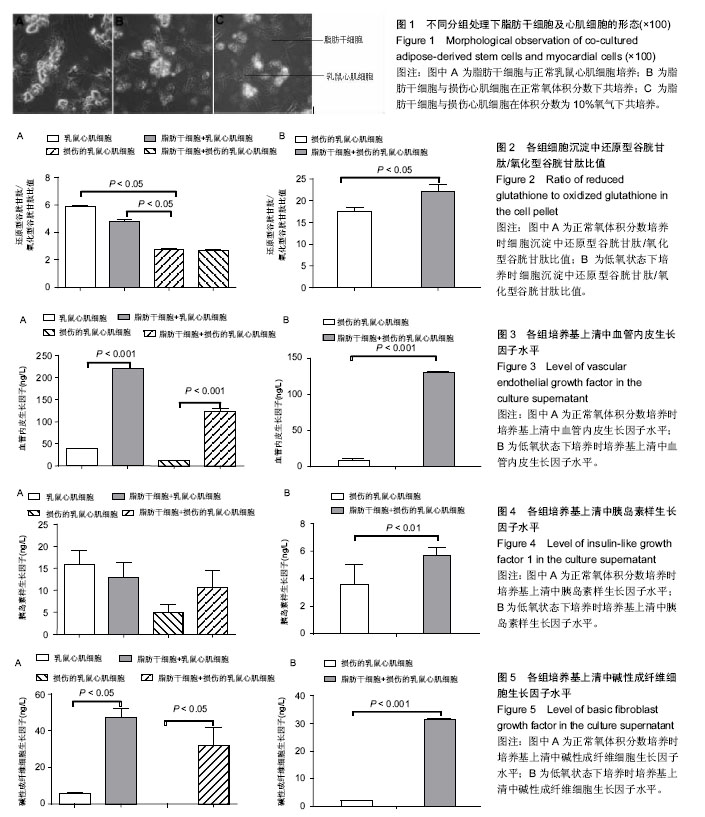
.jpg)
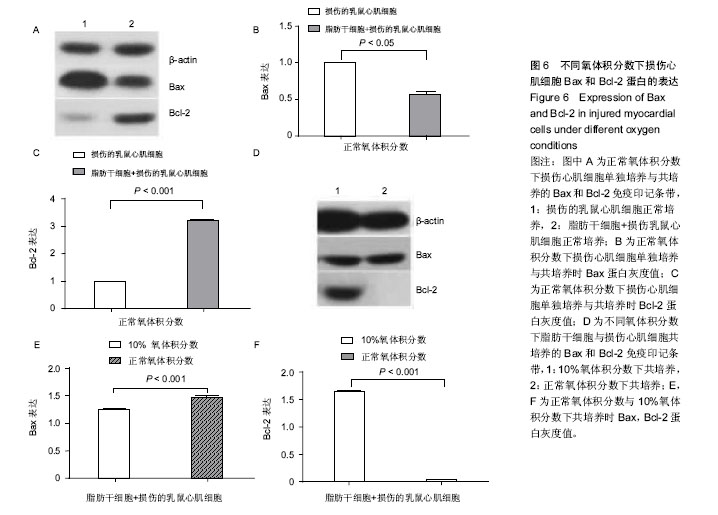
.jpg)