| [1] Rier HN, Jager A, Meinardi MC, et al.Severe sarcopenia might be associated with a decline of physical independence in older patients undergoing chemotherapeutic treatment.Support Care Cancer. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s00520-017-4018-8.[2] Fielding RA, Vellas B, Evans WJ, et al. Sarcopenia: an undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc.2011;12(4):249-256.[3] Scherbakov N, Doehner W. Searching for a relevant definition of sarcopenia: results from the cross-sectional EPIDOS study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.2016;7(1): 100-101.[4] Cheng Q, Zhu X, Zhang X, et al. A cross-sectional study of loss of muscle mass corresponding to sarcopenia in healthy Chinese men and women: reference values, prevalence, and association with bone mass. J Bone Miner Metab.2014;32(1): 78-88.[5] Peterson SJ, Braunschweig CA. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Associated Outcomes in the Clinical Setting.Nutr Clin Pract.2016; 31(1):40-48.[6] Morley JE, Anker SD, von Haehling S. Prevalence, incidence, and clinical impact of sarcopenia: facts, numbers, and epidemiology- update 2014.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2014; 5(4):253-259.[7] Naseeb MA, Volpe SL. Protein and exercise in the prevention of sarcopenia and aging. Nutr Res.2017;40:1-20.[8] Makanae Y, Fujita S. Role of exercise and nutrition in the prevention of sarcopenia. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).2015;61 Suppl:S125-127.[9] Binkley N, Krueger D, Buehring B. What's in a name revisited: should osteoporosis and sarcopenia be considered components of "dysmobility syndrome?". Osteoporos Int.2013;24(12):2955-2959.[10] DiGirolamo DJ, Clemens TL, Kousteni S. The skeleton as an endocrine organ. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(11):674-683.[11] Frost HM. Muscle, bone, and the Utah paradigm: a 1999 overview. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2000; 32(5):911-917.[12] Bogl LH, Latvala A, Kaprio J, et al. An investigation into the relationship between soft tissue body composition and bone mineral density in a young adult twin sample.J Bone Miner Res.2011;26(1): 79-87.[13] Frost HM. The Utah paradigm of skeletal physiology: an overview of its insights for bone, cartilage and collagenous tissue organs.J Bone Miner Metab.2000;18(6): 305-316.[14] Tagliaferri C, Wittrant Y, Davicco MJ, et al. Muscle and bone, two interconnected tissues. Ageing Res Rev.2015;21: 55-70.[15] Laurent MR, Dubois V, Claessens F, et al. Muscle-bone interactions: From experimental models to the clinic? A critical update. Mol Cell Endocrinol.2016;432: 14-36.[16] Qin W, Sun L, Cao J, et al. The central nervous system (CNS)- independent anti-bone-resorptive activity of muscle contraction and the underlying molecular and cellular signatures. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288(19):13511-13521.[17] Edwards WB, Schnitzer TJ, Troy KL. Bone mineral loss at the proximal femur in acute spinal cord injury. Osteoporos Int.2013;24(9): 2461-2469.[18] Gomez C, David V, Peet NM, et al. Absence of mechanical loading in utero influences bone mass and architecture but not innervation in Myod-Myf5-deficient mice. J Anat. 2007;210(3):259-271.[19] Kawao N, Kaji H. Interactions between muscle tissues and bone metabolism. J Cell Biochem.2015;116(5):687-695.[20] Colaianni G, Cuscito C, Mongelli T, et al. The myokine irisin increases cortical bone mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(39): 12157-12162.[21] Karsenty G, Olson EN. Bone and Muscle Endocrine Functions: Unexpected Paradigms of Inter-organ Communication. Cell.2016; 164(6):1248-1256.[22] Schiaffino S, Mammucari C. Regulation of skeletal muscle growth by the IGF1-Akt/PKB pathway: insights from genetic models. Skelet Muscle. 2011; 1(1): 4.[23] Govoni KE, Wergedal JE, Florin L, et al. Conditional deletion of insulin-like growth factor-I in collagen type 1alpha2-expressing cells results in postnatal lethality and a dramatic reduction in bone accretion. Endocrinology. 2007;148(12):5706-5715.[24] Bren-Mattison Y, Hausburg M, Olwin BB. Growth of limb muscle is dependent on skeletal-derived Indian hedgehog. Dev Biol. 2011; 356(2):486-495.[25] Quarles LD. Role of FGF23 in vitamin D and phosphate metabolism: implications in chronic kidney disease. Exp Cell Res.2012;318(9):1040-1048.[26] Borsheim E, Herndon DN, Hawkins HK, et al. Pamidronate attenuates muscle loss after pediatric burn injury. J Bone Miner Res.2014;29(6): 1369-1372.[27] Stewart JW, Alekel DL, Ritland LM, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is related to indicators of overall physical fitness in healthy postmenopausal women. Menopause. 2009;16(6):1093-1101.[28] Mastaglia SR, Seijo M, Muzio D, et al. Effect of vitamin D nutritional status on muscle function and strength in healthy women aged over sixty-five years. J Nutr Health Aging. 2011;15(5):349-354.[29] Kuchuk NO, Schoor NMV, Pluijm SM, et al. Vitamin D status, parathyroid function, bone turnover, and BMD in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: global perspective. J Bone Miner Res.2009; 24(4):693-701.[30] Meier C, Nguyen TV, Handelsman DJ, et al. Endogenous sex hormones and incident fracture risk in older men: the Dubbo Osteoporosis Epidemiology Study. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(1):47-54.[31] Ryan CW, Huo D, Bylow K, et al. Suppression of bone density loss and bone turnover in patients with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer and receiving zoledronic acid.BJU Int. 2007;100(1):70-75.[32] Storer TW, Miciek R, Travison TG. Muscle function, physical performance and body composition changes in men with prostate cancer undergoing androgen deprivation therapy. Asian J Androl. 2012;14(2):204-221.[33] LeBlanc ES, Wang PY, Lee CG, et al. Higher testosterone levels are associated with less loss of lean body mass in older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2011;96(12): 3855-3863.[34] Hallangerås M, Angerås U, Zamir O, et al. Effect of the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist RU 38486 on muscle protein breakdown in sepsis. Surgery.1991;109(4): 468.[35] Hall-Angerås M, Angerås U, Zamir O, et al. Interaction between corticosterone and tumor necrosis factor stimulated protein breakdown in rat skeletal muscle, similar to sepsis. Surgery. Surgery. 1990;108(2): 460.[36] Zhou H, Mak W, Zheng Y, et al. Osteoblasts directly control lineage commitment of mesenchymal progenitor cells through Wnt signaling.J Biol Chem.2008;283(4): 1936-1945.[37] Murphy DR, Smolen LJ, Klein TM, et al. The cost effectiveness of teriparatide as a first-line treatment for glucocorticoid-induced and postmenopausal osteoporosis patients in Sweden. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2012;13(1):213.[38] Kauh E, Mixson L, Malice MP, et al. Prednisone affects inflammation, glucose tolerance, and bone turnover within hours of treatment in healthy individuals. Eur J Endocrinol.2012;166(3):459-467.[39] Zhou H, Mak W, Kalak R, et al. Glucocorticoid-dependent Wnt signaling by mature osteoblasts is a key regulator of cranial skeletal development in mice. Development. 2009;136(3):427-436.[40] Bellido T. Antagonistic interplay between mechanical forces and glucocorticoids in bone: A tale of kinases. J Cell Biochem.2010;111(1):1-6.[41] Henneicke H, Herrmann M, Kalak R, et al. Corticosterone selectively targets endo-cortical surfaces by an osteoblast-dependent mechanism. Bone. 2011;49(4): 733.[42] Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Mizutani Y, et al. Prevalence of sarcopenia in Japanese women with osteopenia and osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab.2013;31(5):556-561.[43] Monaco MD, Vallero F, Monaco RD, et al. Prevalence of sarcopenia and its association with osteoporosis in 313 older women following a hip fracture. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.2011;52(1):71-74.[44] Go SW, Cha YH, Lee JA, et al. Association between Sarcopenia, Bone Density, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Men. Korean J Fam Med. 2013; 34(4): 281-288.[45] Pereira FB, Leite AF, de Paula AP. Relationship between pre-sarcopenia, sarcopenia and bone mineral density in elderly men. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2015;59(1):59-65.[46] Verschueren S, Gielen E, O'Neill TW, et al. Sarcopenia and its relationship with bone mineral density in middle-aged and elderly European men. Osteoporos Int.2013; 24(1): 87-98.[47] 帅波,沈霖,杨艳萍,等.武汉地区中老年男性肌肉减少症与骨密度的相关性[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2016,9(3):257-263.[48] Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Orav JE, Kanis JA, et al. Comparative performance of current definitions of sarcopenia against the prospective incidence of falls among community-dwelling seniors age 65 and older. Osteoporos Int.2015;26(12): 2793-2802.[49] Szulc P, Feyt C, Chapurlat R. High risk of fall, poor physical function, and low grip strength in men with fracture—the STRAMBO study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2015;7(3): 299-311[50] Tarantino U, Piccirilli E, Fantini M, et al. Sarcopenia and fragility fractures: molecular and clinical evidence of the bone-muscle interaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2015; 97(5):429-437. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌肉减少症:是新型老年综合征,主要表现为与增龄相关的进行性、全身肌量减少和/或肌强度下降或肌肉生理功能减退,其降低患者生活质量,增加老年人的住院率,给患者、家庭及社会带来沉重的负担并且其病因复杂。肌肉减少症和许多疾病具有相关性,其中,和骨质疏松的联系近期受到广泛重视。
失用性骨骼肌萎缩:是肢体在固定及失重状态下发生的一系列的生理、生化、形态学及功能的变化。表现为肌纤维由慢速型(1型)向快速型(2型)的转变、肌肉蛋白合成代谢减弱、分解代谢增强、肌蛋白丢失、肌质量的减少、肌纤维横截面积的减少、毛细血管容量下降、血液供应减少、肌收缩力下降等。
文题释义:
肌肉减少症:是新型老年综合征,主要表现为与增龄相关的进行性、全身肌量减少和/或肌强度下降或肌肉生理功能减退,其降低患者生活质量,增加老年人的住院率,给患者、家庭及社会带来沉重的负担并且其病因复杂。肌肉减少症和许多疾病具有相关性,其中,和骨质疏松的联系近期受到广泛重视。
失用性骨骼肌萎缩:是肢体在固定及失重状态下发生的一系列的生理、生化、形态学及功能的变化。表现为肌纤维由慢速型(1型)向快速型(2型)的转变、肌肉蛋白合成代谢减弱、分解代谢增强、肌蛋白丢失、肌质量的减少、肌纤维横截面积的减少、毛细血管容量下降、血液供应减少、肌收缩力下降等。.jpg) 文题释义:
肌肉减少症:是新型老年综合征,主要表现为与增龄相关的进行性、全身肌量减少和/或肌强度下降或肌肉生理功能减退,其降低患者生活质量,增加老年人的住院率,给患者、家庭及社会带来沉重的负担并且其病因复杂。肌肉减少症和许多疾病具有相关性,其中,和骨质疏松的联系近期受到广泛重视。
失用性骨骼肌萎缩:是肢体在固定及失重状态下发生的一系列的生理、生化、形态学及功能的变化。表现为肌纤维由慢速型(1型)向快速型(2型)的转变、肌肉蛋白合成代谢减弱、分解代谢增强、肌蛋白丢失、肌质量的减少、肌纤维横截面积的减少、毛细血管容量下降、血液供应减少、肌收缩力下降等。
文题释义:
肌肉减少症:是新型老年综合征,主要表现为与增龄相关的进行性、全身肌量减少和/或肌强度下降或肌肉生理功能减退,其降低患者生活质量,增加老年人的住院率,给患者、家庭及社会带来沉重的负担并且其病因复杂。肌肉减少症和许多疾病具有相关性,其中,和骨质疏松的联系近期受到广泛重视。
失用性骨骼肌萎缩:是肢体在固定及失重状态下发生的一系列的生理、生化、形态学及功能的变化。表现为肌纤维由慢速型(1型)向快速型(2型)的转变、肌肉蛋白合成代谢减弱、分解代谢增强、肌蛋白丢失、肌质量的减少、肌纤维横截面积的减少、毛细血管容量下降、血液供应减少、肌收缩力下降等。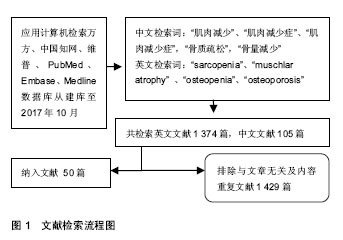

.jpg) 文题释义:
肌肉减少症:是新型老年综合征,主要表现为与增龄相关的进行性、全身肌量减少和/或肌强度下降或肌肉生理功能减退,其降低患者生活质量,增加老年人的住院率,给患者、家庭及社会带来沉重的负担并且其病因复杂。肌肉减少症和许多疾病具有相关性,其中,和骨质疏松的联系近期受到广泛重视。
失用性骨骼肌萎缩:是肢体在固定及失重状态下发生的一系列的生理、生化、形态学及功能的变化。表现为肌纤维由慢速型(1型)向快速型(2型)的转变、肌肉蛋白合成代谢减弱、分解代谢增强、肌蛋白丢失、肌质量的减少、肌纤维横截面积的减少、毛细血管容量下降、血液供应减少、肌收缩力下降等。
文题释义:
肌肉减少症:是新型老年综合征,主要表现为与增龄相关的进行性、全身肌量减少和/或肌强度下降或肌肉生理功能减退,其降低患者生活质量,增加老年人的住院率,给患者、家庭及社会带来沉重的负担并且其病因复杂。肌肉减少症和许多疾病具有相关性,其中,和骨质疏松的联系近期受到广泛重视。
失用性骨骼肌萎缩:是肢体在固定及失重状态下发生的一系列的生理、生化、形态学及功能的变化。表现为肌纤维由慢速型(1型)向快速型(2型)的转变、肌肉蛋白合成代谢减弱、分解代谢增强、肌蛋白丢失、肌质量的减少、肌纤维横截面积的减少、毛细血管容量下降、血液供应减少、肌收缩力下降等。