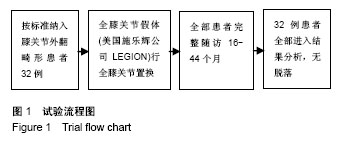
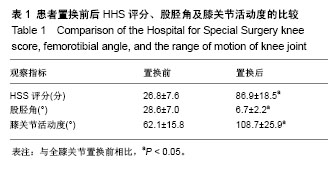
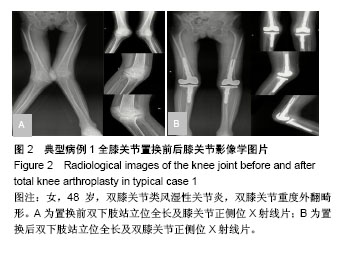
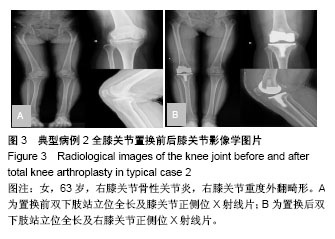
| [1] Williot A,Rosset P,Favard L,et al. Total knee arthroplasty in valgusknee. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010;96(4 Suppl): S37-S42.[2] Krackow KA, Jones MM, Teeny SM, et al. Primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with fxed valgus deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1991;273:9-18.[3] Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, et al. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg (Am).2005;87 Suppl 1(Pt 2):271-284.[4] Elkus M, Ranawat CS, Rasquinha VJ, et a1.Total knee arthmplasty for severe valgus deformity.Five to fourteen year follow up. J Bone Joint Surg.2004;86(12):2671-2676.[5] Favorito PJ, Mihalko WM, Krackow KA. Total knee arthroplasty in the valgus knee. Am Acad Orthop Surg.2002;10(1):16-24.[6] Krackow KA, Mihalko WM. Flexion-extension joint gap changes after lateral structure release for valgus deformity correction in total knee arthroplasty: a cadaveric study. J Arthroplasty.1999;14(8):994-1004.[7] Miyasaka KC, Ranawat CS, Mullaji A. 10- to 20-year followupof total knee arthroplasty for valgus deformities. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; 345:29-37.[8] Insall JN, Easley ME. Surgical techniques and instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2001;3:1717-1738.[9] Whiteside LA. Correction of ligament and bone defects in total arthroplasty of the severely valgus knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;288:234-245.[10] 王宏伟,周殿阁.髂胫束松解在外翻膝全膝关节置换术中的作用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015,30(8):812-814.[11] 马军,牛东生,孙玺淳,等.个体化的软组织平衡技术在膝外翻全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志,2012,06(5):27-30.[12] Nikolopoulos D, Michos I, Safos G, et al. Current surgical strategies for total arthroplasty in valgus knee. World J Orthop.2015;6(6):469-482.[13] Ke X, Lyons ST. Soft tissue releases in total knee arthroplasty for valgus deformities. J Arthroplasty.2017; 32(6):1814-1818.[14] Keblish PA. The lateral approach to the valgus knee. Surgical technique and analysis of 53 cases with over two-year follow-up evaluation. CIin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(271):52-62.[15] Gore DR, Murray MP, Sepic SB, et al. Correlations between objective measures of function and a clinical knee rating scale following total knee replacement.Orthopedics. 1986;9(10):1363-1367.[16] Gwynne-Jones DP, Martin G, Crane C. Enhanced recovery after surgery for hip and knee replacements. Orthop Nurs. 2017;36(3): 203-210.[17] Christelis N, Wallace S, Sage CE, et al.An enhanced recovery after surgery program for hip and knee arthroplasty. Med J Aust. 2015;202 (7):363-368.[18] 周宗科,翁习生,向兵,等.中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复-围术期贫血诊治专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2016,9(1):10-14.[19] Aglietti P, Lup D, Cuomo P, et al. Total knee arthroplasty using a piecrusting technique for valgus deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464: 73-77.[20] 郭江,张忠杰,夏波,等.后稳定型固定平台假体修复膝关节外翻畸形:中期随访.[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(31):4927-4932.[21] 加亨,刘振峰,李雷疆,等.软组织平衡技术在维吾尔族膝外翻人工关节置换中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(26):4144-4148.[22] Boettner F, Renner L, Narbarte DA, et al. Total knee arthroplasty for valgus osteoarthritis: the results of a standardized soft-tissue release technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(8):1-7.[23] Elkus M, Ranawat CS, Rasquinha VJ, et al. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. Five to fourteen-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2005;1(2):271-284.[24] Rahm S, Camenzind RS, Hingsammer A, et al.Postoperative alignment of TKA in patients with severe preoperative varus or valgus deformity: is there a difference between surgical techniques?BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2017;18(272):1-8.[25] Stern SH, Moeckel BH, Insall JN. Total knee arthroplasty in valgusknees. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1991;273: 5-8.[26] Boyer P, Boublil D, Magrino B, et al. Total knee replacement in the fixed valgus deformity using alateral approach:role of the all tomatic iliotibial band release for a successful balancing. Int Orthop.2009; 33(6):1577-1583.[27] Engh GA. The difficult knee: severe varus and valgus. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;416 : 58-63.[28] Insall J, Scott WN, Ranawat CS. The total condylar knee prosthesis. A report of two hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1979; 61(2): 173?180.[29] Whiteside LA. Selective ligament release in total knee arthroplasty of the knee in valgus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;367(367):130-140.[30] Aglietti P, Buzzi R, Giron F, et al. The Insall-Burstein posterior stabilized total knee replacement in the valgus knee. Am J Knee Surg. 1996;9(1):8-12. |
.jpg)
.jpg)