| [1] Abdel-Salam A, Eyres KS. Effects of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty. A prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(2):250-253.[2] Yavarikia A, Amjad GG, Davoudpour K. The influence of tourniquet use and timing of its release on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Pak J Biol Sci. 2010;13(5):249-252.[3] Tetro AM, Rudan JF. The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 2001;44(1):33.[4] Vandenbussche E, Duranthon LD, Couturier M, et al. The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2002;26(5):306-309 .[5] Håkan L, Per A, Lars G. Tourniquet use in total knee replacement does not improve fixation, but appears to reduce final range of motion. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(5):499.[6] Mori N, Kimura S, Onodera T, et al. Use of a pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty increases the risk of distal deep vein thrombosis: a prospective, randomized study. Knee. 2016;23(5):887.[7] Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, et al. Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(371): 169.[8] Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, et al. Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(24):2209-2215.[9] Zhang FJ, Xiao Y, Liu YB, et al. Clinical effects of applying a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty on blood loss. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(21): 3030-3033.[10] Li B, Wen Y, Wu H, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1263-1268.[11] 王刚,曹晓瑞,陈晓勇,等.膝关节置换中止血带的使用对术后加速康复的影响[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2017,10(1):27-32.[12] 张阳,钱齐荣,吴海山,等.止血带对全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(10):910-914.[13] Zhang Q, Dong J, Gong K, et al. Effects of tourniquet use on perioperative outcome in total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;30(4):421.[14] Kumar N, Yadav C, Singh S, et al. Evaluation of pain in bilateral total knee replacement with and without tourniquet: a prospective randomized control trial. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6(2):85.[15] Ejaz A, Laursen AC, Kappel A, et al. Faster recovery without the use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2014;85(4):422-426 .[16] 沈忠伟,童培建,邵营钢,等.止血带对全膝关节置换术后肿胀及功能影响的临床研究[J].浙江临床医学,2010,12(3):261-262.[17] 鲍航行,王金法,蔡运火,等.全膝关节置换术后止血带性缺血再灌注损伤的临床研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(3):242-246 .[18] 杨健齐,魏鲁青,张健平,等.全膝关节置换中止血带应用对假体骨水泥厚度影响的对照研究[J].重庆医学,2017,46(6):782-785 .[19] 潘凡武,毕树雄.气压止血带在四肢骨科手术中应用研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(1):33-36 .[20] Huda R, Solanki D R, Mathru M. Inflammatory and redox responses to ischaemia/reperfusion in human skeletal muscle. Clin Sci. 2004;107(5): 497-503.[21] Smith TO, Hing CB. Is a tourniquet beneficial in total knee replacement surgery? A meta-analysis and systematic review. Knee. 2009;17(2): 141-147. [22] Thorey F, Stukenborgcolsman C, Windhagen H, et al. The effect of tourniquet release timing on perioperative blood loss in simultaneous bilateral TKA. 2010.[23] Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty?Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee.2005;7(3):151-155.[24] Chen S, Li J P, Peng H, et al. The influence of a half-course tourniquet strategy on peri-operative blood loss and early functional recovery in primary total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):355-359 .[25] Johnson DP. Infection after knee arthroplasty. Clinical studies of skin hypoxia and wound healing. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 2009;252(1):1-48 .[26] 周媛.人工全膝关节置换术后感染相关危险因素分析[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2014.[27] Shimizu M, Kubota R, Nasu M, et al. The influence of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty on perioperative blood loss and postoperative complications. Masui. 2016;65(2):131-135 .[28] Katsumata S, Nagashima M, Kato K, et al. Changes in coagulation-fibrinolysis marker and neutrophil elastase following the use of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty and the influence of neutrophil elastase on thromboembolism. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49(4): 510-516.[29] Kato N, Nakanishi K, Yoshino S, et al. Abnormal echogenic findings detected by transesophageal echocardiography and cardiorespiratory impairment during total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Anesthesiology. 2002;97(97):1123-1128. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: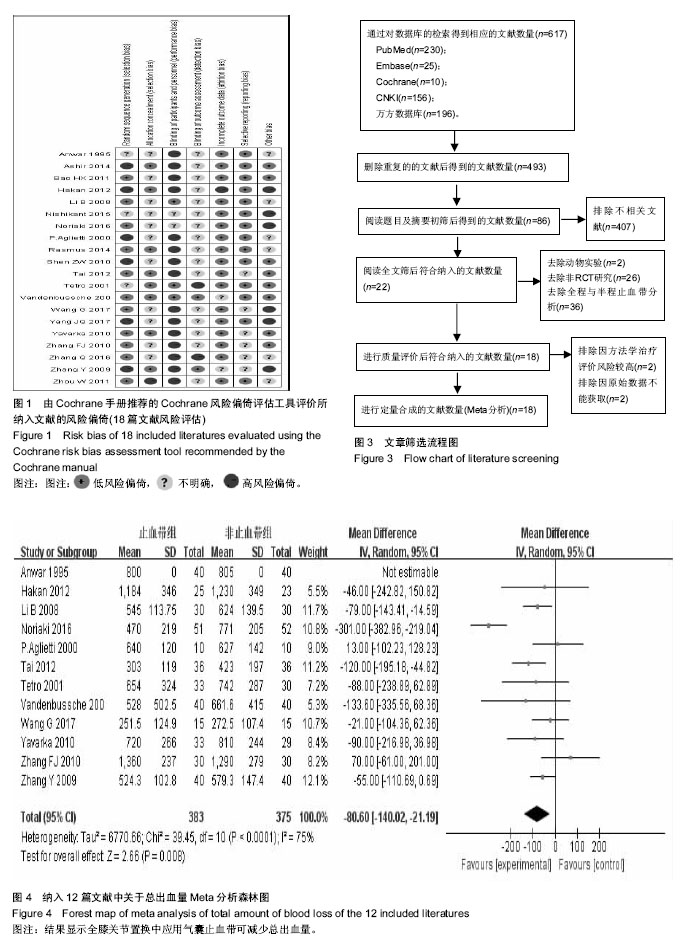
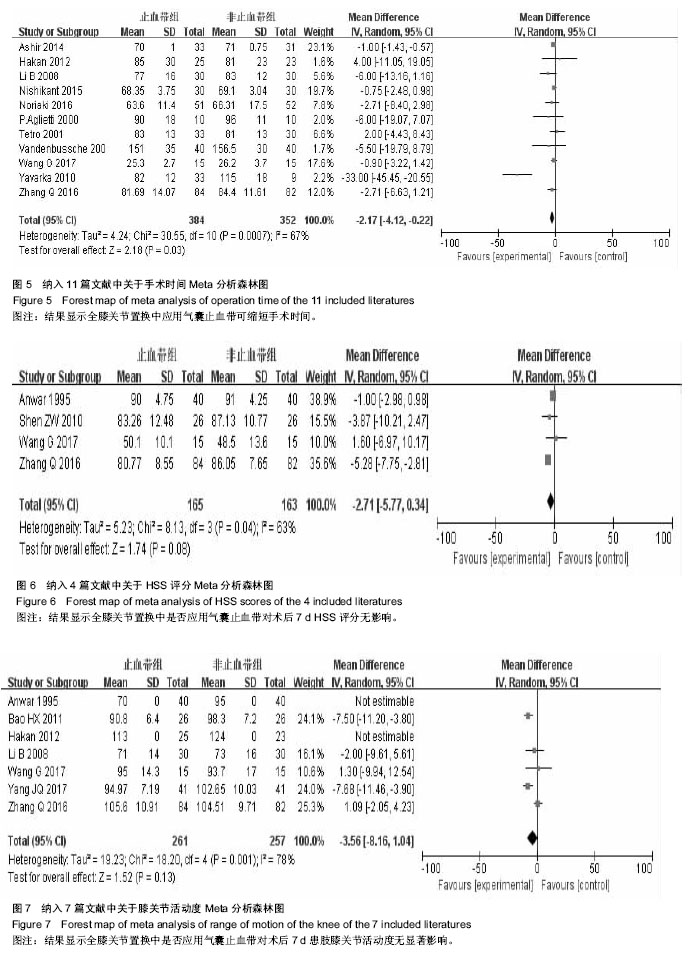
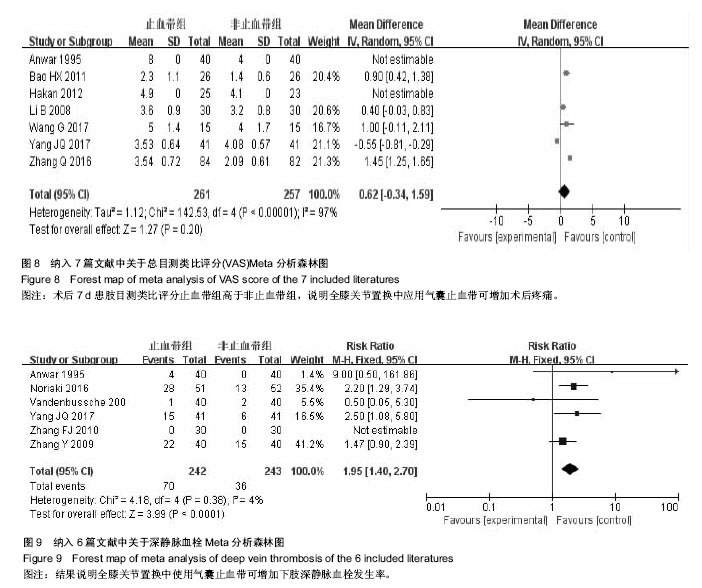
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: