中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (15): 2437-2445.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0251
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
中国老年髋部骨折患者术后发生谵妄相关因素的Meta分析
吕 阳1,刘启宇2,刘 军1,陈海云1,潘建科1,李希文1
- 1广州中医药大学第二附属医院/广东省中医院骨科,广东省广州市 510120;2广东省中医院大学城分院骨科创伤组,广东省广州市 510000
A meta-analysis of risk factors of postoperative delirium of elderly hip fracture patients in China
Lü Yang1, Liu Qi-yu2, Liu Jun1, Chen Hai-yun1, Pan Jian-ke1, Li Xi-wen1
- 1The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine/Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2Orthopedics Trauma Group in the University City branch of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
髋部骨折:主要指股骨颈骨折和股骨转子间骨折。髋部骨折后患者髋部明显疼痛、肿胀,髋部皮下可见淤血斑,大转子处压痛及叩击痛,下肢短缩、外旋、内收等畸形,股骨纵向叩击痛。常规髋部X 射线片检查可清晰显示骨折情况,包括部位、类型及移位等。CT 及MRI 检查能在横断面上了解骨折程度及移位情况,特别是三维成像技术能显示骨折的立体形态,具有非常大的指导意义。
术后谵妄:是指患者在经历外科手术后出现的以认知功能障碍等相关症状为表现的急性精神病理性综合征,表现为机体意识、注意力、感知力、记忆、思维、情绪和睡眠周期紊乱,出现异常精神运动行为,持续时间可长可短,严重程度可轻可重。其发生具有明显的时间特点,通常始于恢复室,在术后5 d明显出现,但因识别率相对较低,绝大多数患者没有得到足够的重视与相应的处理或治疗。因此,在老年住院患者中发病率及死亡率均很高。
摘要
背景:目前国内老年髋部骨折术后谵妄的危险因素尚未达成共识,并未出现能有效评估老年髋部骨折术后发生谵妄的风险预测系统。
目的:探讨中国老年髋部骨折术后发生谵妄的危险因素。
方法:计算机检索国内有关老年髋部骨折术后发生谵妄的相关研究,通过进行文献质量评价,应用RevMan 5.3分析软件进行敏感性和异质性分析,并采用固定效应或随机效应模型计算合并后的综合效应。
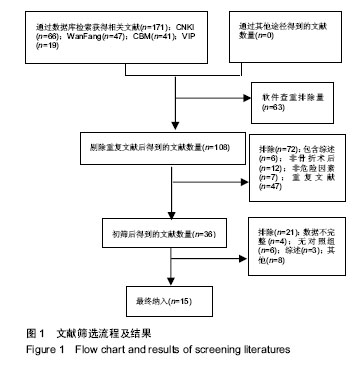
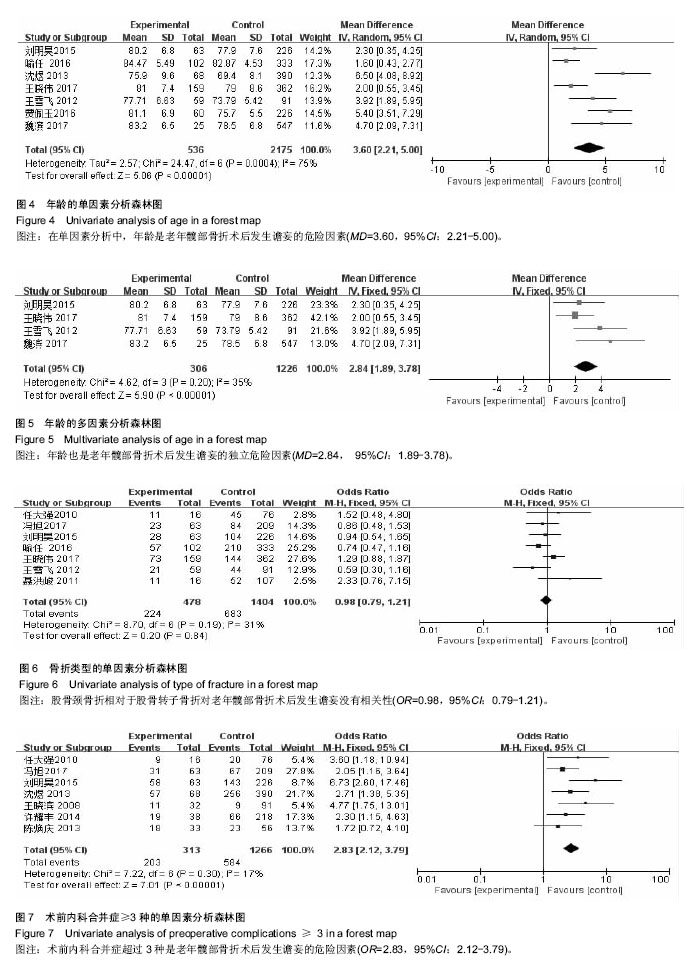
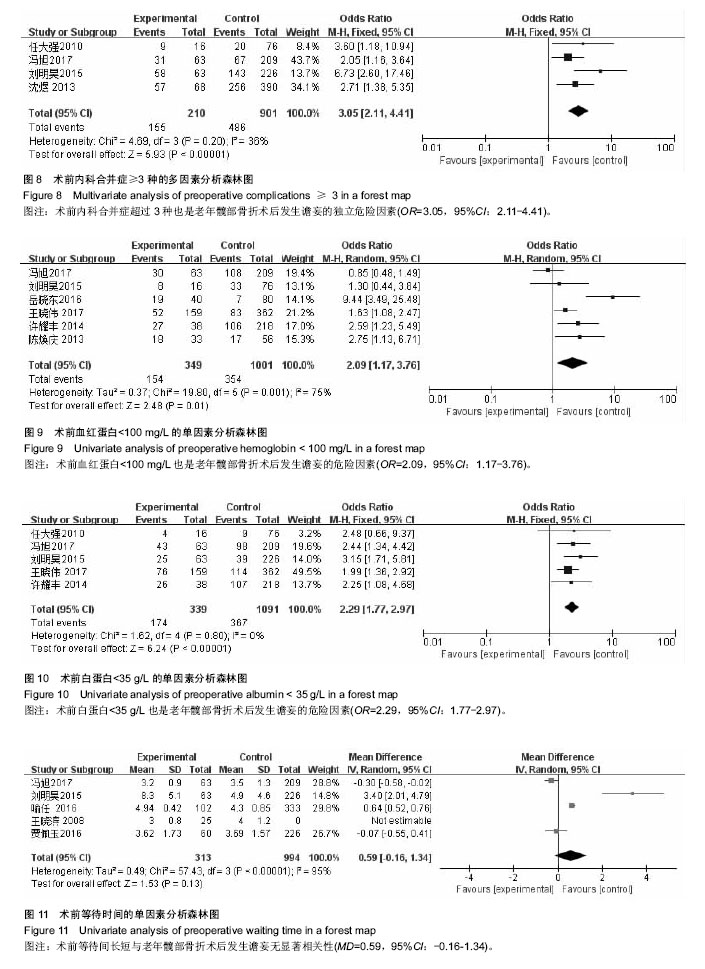
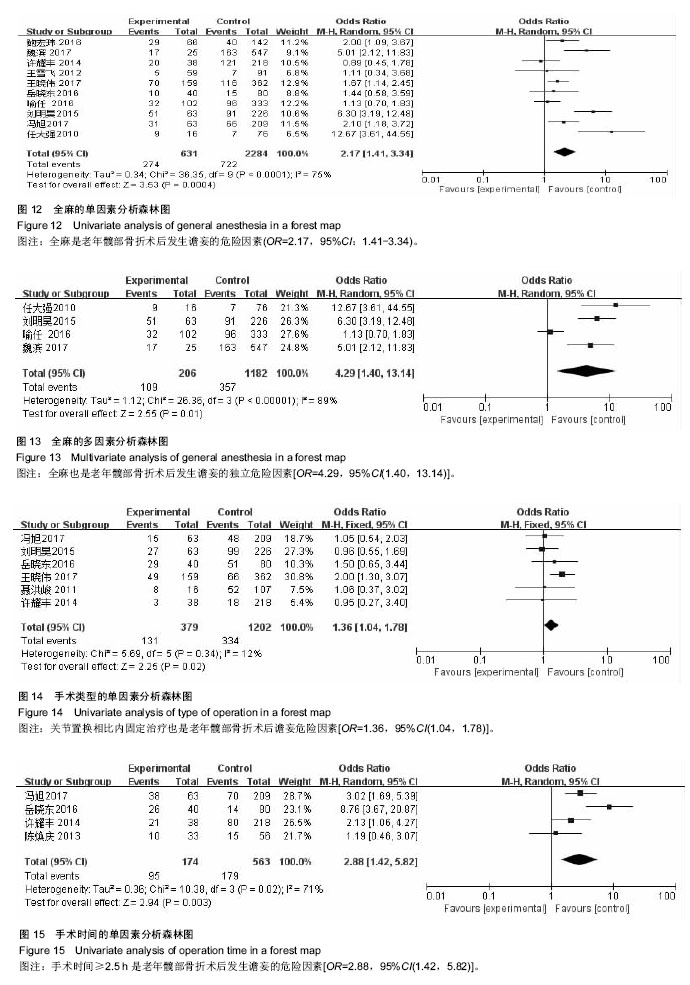
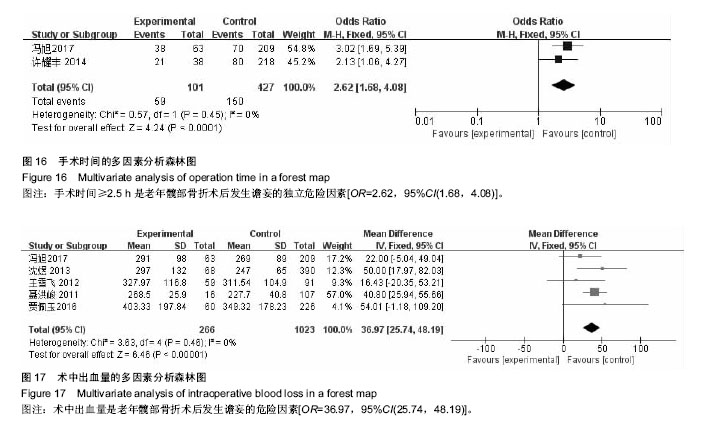
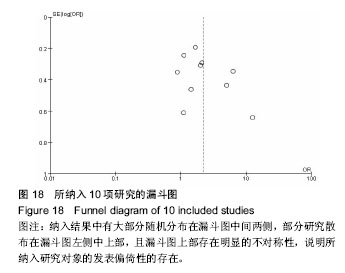
结果与结论:①共纳入15个研究,其中谵妄组872例,非谵妄组3 221例;②Meta分析单因素分析结果:术前认知障碍[合并OR值为4.99,95%CI(2.66,9.37),P=0.000]、年龄[合并MD值为3.60,95%CI(2.21,5.00),P=0.000]、术前内科合并症≥3[合并OR值为2.83,95%CI(2.12,3.79),P=0.000]、术前血红蛋白<100 mg/L[合并OR值为2.09,95%CI(1.17,3.76),P=0.01]、术前白蛋白<35 g/L[合并OR值为=2.29,95%CI(1.77,2.97),P=0.01]、全麻[合并OR值为2.17,95%CI(1.41,3.34),P=0.000 4]、手术方式[合并OR值=1.36,95%CI(1.04,1.78),P=0.02]、手术时间[合并OR值为2.88,95%CI(1.42,5.82),P=0.003]、术中出血量[合并MD值为36.97,95%CI(25.74,48.19),P=0.000]是老年髋部骨折术后发生谵妄的危险因素;③Meta分析多因素分析显示:术前认知障碍[合并OR值为4.94,95%CI(2.23,10.95),P=0.000]、年龄[合并MD值为2.84,95%CI(1.89,3.78),P=0.000]、术前内科合并症≥3 [合并OR值为3.05,95%CI(2.11,4.41),P=0.000]、全麻[合并OR值为4.29,95%CI(1.40,13.14),P=0.01]、手术时间≥ 2.5 h[合并OR值为=2.62,95%CI(1.68,4.08),P=0.000]是老年髋部骨折术后发生谵妄的独立危险因素;④综上,术前认知障碍、年龄、术前内科合并症≥3、全麻、手术时间是中国老年髋部骨折术后发生谵妄的独立危险因素,骨折类型、术前等待时间、手术类型与术后谵妄并无显著相关性;受纳入研究数量和质量影响,需开展更多高质量研究证实上述结论。
中图分类号:
.jpg)