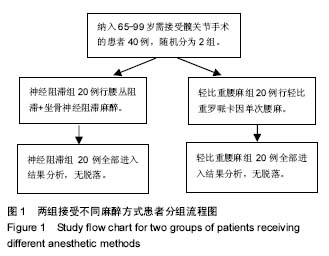
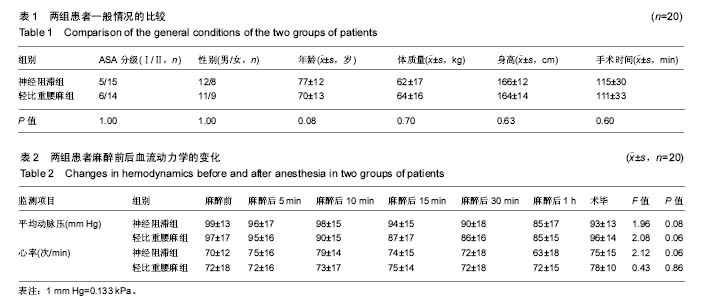
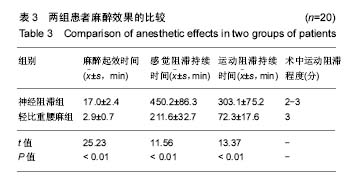
| [1] Kesmezacar H, Ayhan E, Unlu MC, et al. Predictors of mortality in elderly patients with an intertrochanteric or a femoral neck fracture. J Trauma. 2010; 68(1):153-158.[2] Kanis JA, Oden A, McCloskey EV. A systematic review of hipfracture incidence and probability of fracture worldwide. OsteoporosInt. 2012; 23(9) :2239-2256.[3] Bergstrom U, Johnson H, Gustafson Y, et al. The hip fracture incidence curve is shifting to the right. ActaOrthop. 2009;80(5):520-524.[4] 米勒,邓小明,曾因明. 米勒麻醉学[M]. 北京:北京大学医学出版社, 2011.[5] Cantürk M, K?lc? O, Ornek D, et al. Ropivacaine for unilateral spinal anesthesia; hyperbaric or hypobaric? Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2012; 62(3):298-311.[6] Cooper C, Campion G, Melton L. Hip fractures in the elderly: a worldwide projection. Osteoporos Int. 1992;2(6):285-289. [7] Schurch MA, Rizzoli R, Mermillod B, et al. A prospective study on socioeconomic aspects of fracture of the proximal femur. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11(12):1935-1942.[8] 毛烨,赵晶,高玉凤,等.右美托咪啶和丙泊酚对老年髋部骨折术后重症患者镇静效果的比较[J].中华医学杂志,2015,95(19):1493-1495.[9] 季英楠,阿良,赵忠海,等.骨折分型及外侧壁厚度对动力髋螺钉治疗外侧壁完整的股骨粗隆间骨折的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2015,44(9) : 818-821.[10] 刘粤,郝玮,张岩,等. 多学科协作综合治疗老年髋部骨折的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(19) :5481-5484.[11] 王伯尧,王云华,高志强,等.多学科综合治疗对老年髋部骨折预后的影响[J].实用老年医学,2017, 31(12):1121-1131.[12] 杨格,赵猛,徐圣康,建立老年髋部骨折绿色通道的早期疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志年,2017,32(12):1281-1282.[13] 张长青,张伟.我国老年髋部骨折绿色通道建设的现实意义[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,30(3):196-198.[14] Johnell O, Kanis JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence, mortality and disability associated with hip fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(11):897-902. [15] Keene GS, Parker MJ, Pryor GA. Mortality and morbidity after hip fractures. BMJ. 1993;307(6914):1248-1250. [16] Vestergaard P, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L. Increased mortality in patients with a hip fracture-effect of pre-morbid conditions and post-fracture complications. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18(12):1583-1593. [17] Valizadeh M, Mazloomzadeh S, Golmohammadi S, et al. Mortality after low trauma hip fracture: a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:143. [18] Leibson CL, Tosteson AN, Gabriel SE, et al. Mortality, disability, and nursing home use for persons with and without hip fracture: a population-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50(10):1644-1650.[19] Gijsen R, Hoeymans N, Schellevis FG, et al. Causes and consequencesof comorbidity: a review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54 (7) : 661-674.[20] 胡强,汤守营,郑立生,等.老年髋部骨折患者围术期并发症影响因素分析[J].临床合理用药,2018,11(1):167-168.[21] 塔拉提百克•买买提居马,刘恒. 老年髋部骨折患者住院期间死亡和严重并发症危险因素分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(10):937-941.[22] Dorotka R, Schoechtner H, Buchinger W. The influence of immediatesurgical treatment of proximal femoral fractures on mortality and qualityof life. Operation within sex hours of the fracture versus lateral thansix hours. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85: 1107-1113.[23] 邓遵生,叶作明,雷廷文,等.骨科老年髋部骨折围手术期内科处理体会[J].中国社区医疗医学专业,2018 ,11(1):167-168.[24] Hoenig H,Rubenstein LV,Sloane R,et al. What is the role of timmingin the surgical and rehabilitative case of community dwelling olderpatients with acture hip fracture. Arch Int Med.1997;157:513-520.[25] Raats JW, van Eijsden WA, Crolla RM, et al. Risk factors and outcomes for postoperative delirium after major surgery in elderly patients. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136071.[26] Ruggiero C, Bonamassa L, Pelini L, et al. Early post-surgical cognitive dysfunction is a risk factor for mortality among hip fracture hospitalized older persons. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(2):667-675.[27] Mazzola P, Bellelli G, Brogginni V, et al. Postoperative delirium and pre-fracture disability predict 6-month mortality among the oldest old hip fracture patients. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2015;27(1):53-60.[28] Shih YJ, Hsieh CH, Kang TW, et al. General versus spinal anesthesia:which is a risk factor for octogenarian hip fracture repair patients. Int J Gerontol. 2010;4(1):37-42.[29] Parker MJ, Handoll HH, Griffiths R. Anaesthesia for hip fracture surgeryin adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(4):CD000521.[30] Brandt C, Hott U, Sohr D, et al. Operating room ventilation with laminarairflow shows no protective effect on the surgical site infectionratein orthopedic and abdominal surgery. Ann Surg.2008;248( 5):695-700.[31] Wei B, Zhang H, Xu M, et al. Effect of different anesthetic methods on postoperative outcomes in elderly patients undergoinghip fracture surgery. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017;49(6):1008-1013.[32] Guay J, Parker MJ, Gajendragadkar PR, et al. Anaesthesia for hip fracture surgery in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD000521.[33] Murthy S, Hepner DL, Cooper Z, et al. Controversies in anaesthesia for noncardiac surgery in older adults. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115(Suppl 2): ii15-25.[34] Roberts KC, Brox WT. AAOS clinical practice guideline: management of hip fractures in the elderly. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23:138-140.[35] Wang XT, MA WH, Li RS. Dose-effect relationship of hypobaric ropivacaine in spinal anesthesia in the elderly undergoing hip replacement. J Clin Anesthesiol. 2008.[36] Zhou J, Jia R. Application of spinal anesthesia with ropivacaineor bupivacaine in the elderly. J Clin Anesthesiol. 2006;22(8):580-581.[37] Demirel I, Ozer AB, Duzgol O, et al. Comparison of unilateral spinal anesthesia and L1paravertebral block combined with psoas compartment and sciatic nerve block in patients to undergo partial hip prosthesis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014; 18(7):1067-1072.[38] Gamli M, Sacan O, Baskan S, et al. Combined lumbar plexus and sciatic nerve block for hip fracture surgery in a patient with severe aortic stenosis. J Anesthesia. 2011; 25(5):784-785. |
.jpg)
.jpg)