| [1] 郑东,杨述华.微创全髋关节置换术研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2005,26(1):7-9.[2] 陈长留,舒勇.微创小切口与传统切口应用于全髋关节置换的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(35):6503-6507.[3] Chow J, Penenberg B, Murphy S. Modified micro-superior percutaneously-assisted total hip: early experiences & case reports. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2011; 4(3):146-150.[4] Kennon R, Keggi J, Zatorski LE, et al. Anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty: beyond the minimally invasive technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86(suppl 2):91.[5] Li J, Xiao J, Zhang Z, et al. A novel fast mobile-window small incision technique for hip arthroplasty in the elderly and comparison with conventional incision. Med Sci Monit. 2017;3: 3303-3310.[6] Rasuli KJ, Gofton W. Percutaneously assisted total hip (PATH) and Supercapsular percutaneously assisted total hip (SuperPATH) arthroplasty: learning curves and early outcomes. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(13):179.[7] Xie J, Zhang HX, Wang L, et al. Comparison of supercapsular percutaneously assisted approach total hip versus conventional posterior approach for total hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12:138.[8] Wei W, Wei B. Comparison of topical and intravenous tranexamic acid on blood loss and transfusion rates in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(11): 2113-2116.[9] Gillette BP, Desimone LJ, Trousdale RT, et al. Low risk of thromboembolic complications with tranexamic acid after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471(1):150-154.[10] Gombotz H, Gries M, Sipurzynski S, et al. Preoperative treatment with recombinant human erythropoietin or predeposit of autologous blood in women undergoing primary hip replacement. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.2000; 44(6):737-742.[11] Kagoma Y, Crowther MJ, Bhandari M, et al. Use of antifibrinolytic therapy to reduce transfusion in patients undergoing orthopedic surgery: a systematic review of randomized trials. Thromb Res. 2009;123(5):687.[12] Alsaleh K, Alotaibi GS, Almodaimegh HS, et al. The use of preoperative erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) in patients who underwent knee or hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(9):1463-1472.[13] Vaishya R, Agarwal AK, Gupta N, et al. Sartorius muscle pedicle iliac bone graft for the treatment of avascular necrosis of femur head. J Hip Preserv Surg. 2016; 3(3): 215-222.[14] Liu C, Liu MT, Li P, et al. Efficacy evaluation for the treatment of subcapital femoral neck fracture in young adults by capsulotomy reduction and closed reduction. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015; 128(4): 483-488.[15] Sugano N, Atsumi T, Ohzono K, et al. The 2001 revised criteria for diagnosis, classification, and staging of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Sci. 2002;7(5):601-605.[16] Domb BG, MD, Sgroi TA, PT, VanDevender JC. Physical therapy protocol after hip arthroscopy. Sports Health. 2016; 8(4): 347-354.[17] Suarez-Ahedo C, Gui CC, Rabe SM, et al. Relationship between age at onset of symptoms and intraoperative findings in hip arthroscopic surgery. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017; 5(11): 2325967117737480.[18] Karkouti K, Wijeysundera DN, Beattie WS. Risk associated with preoperative anemia in cardiac surgery: a multicenter cohort study. Anesthesiology. 2008;117(4):478-484.[19] Musallam KM, Tamim HM, Richards T, et al. Preoperative anaemia and postoperative outcomes in non-cardiac surgery: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2011; 378(9800):1396-1407.[20] Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty? Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000; 7(3):151-155.[21] Pang WW, Schrier SL. Anemia in the elderly. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2012; 19(3):133-140.[22] Listed N. Practice guidelines for perioperative blood management: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Blood Management. Anesthesiology. 2015; 122(2):241-275.[23] Clevenger B, Mallett SV, Klein AA, et al. Patient blood management to reduce surgical risk. Br J Surg. 2015;102(11): 1325-1337.[24] Sambandam B, Batra S, Gupta R, et al. Blood conservation strategies in orthopedic surgeries: a review. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2013;4(4):164-170.[25] Marek M, Ma?gorzata K, Ma?gorzata K. Effect of pre-surgical stress on recovery of patients undergoing hip replacement procedures. Przegl Lek. 2016;73(1):25-28.[26] Brown CA, Boling J, Manson M, et al. Relation between prefracture characteristics and perioperative complications in the elderly adult patient with hip fracture. South Med J. 2012; 105(6):306-310.[27] Joshi GP, Cushner FD, Barrington JW, et al. Techniques for periarticular infiltration with liposomal bupivacaine for the management of pain after hip and knee arthroplasty: a consensus recommendation. J Surg Orthop Adv. 2015; 24(1):27-35.[28] Zhao Y, Jiang C, Peng H, et al. The effectiveness and safety of preoperative use of erythropoietin in patients scheduled for total hip or knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine. 2016;95(27):e4122.[29] Wu YG, Zeng Y, Shen B, et al. Combination of erythropoietin and tranexamic acid in bilateral simultaneous total hip arthroplasty: a randomised, controlled trial. Hip Int. 2016; 26(4):331-337.[30] Na HS, Shin SY, Hwang JY, et al. Effects of intravenous iron combined with low-dose recombinant human erythropoietin on transfusion requirements in iron-deficient patients undergoing bilateral total knee replacement arthroplasty (CME). Transfusion. 2011; 51(1):118-124.[31] Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty. Correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86(4):561-565.[32] Rosencher N, Poisson D, Albi A, et al. Two injections of erythropoietin correct moderate anemia in most patients awaiting orthopedic surgery. Can J Anaesth. 2005; 52(2):160-165.[33] Bose WJ. The potential use of human recombinant erythropoietin in orthopedic surgery. Orthopedics. 1996;19(4): 325-328. |
.jpg)
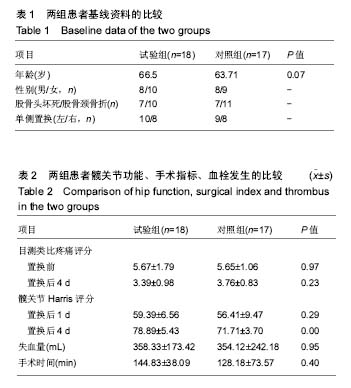
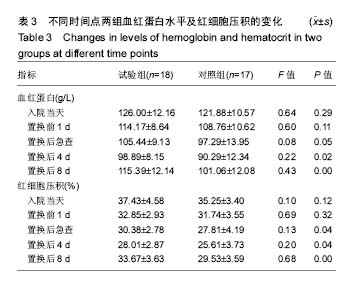
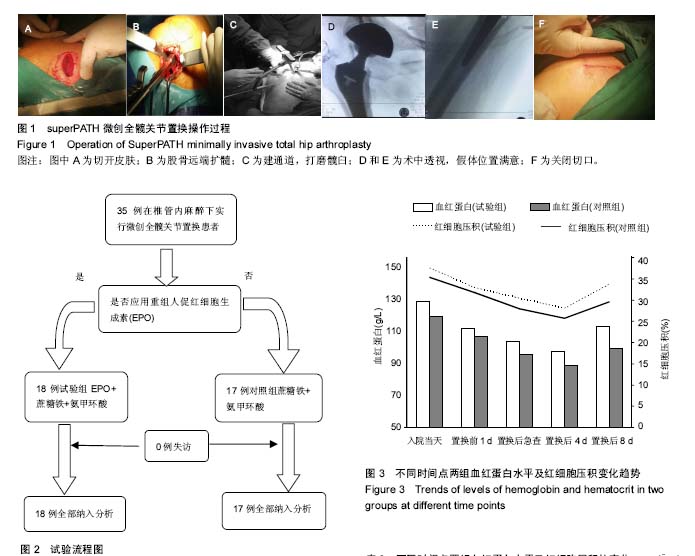
.jpg)